* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
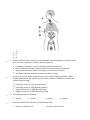
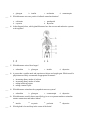
Endocrine System Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What distinguishes target cells from other cells? a. b. c. d. ____ 2. Which gland produces and releases a thyroid-stimulating hormone? a. b. c. d. ____ overproduction of human growth hormone overproduction of insulin underproduction of human growth hormone underproduction of insulin 4. Which term best describes the actions of adrenaline and noradrenaline? a. b. c. d. ____ anterior pituitary hypothalamus posterior pituitary thyroid 3. What causes giantism? a. b. c. d. ____ amount of cellulose in cell membrane amount of phospholipids in cell membrane hormone-specific cell surface receptors hormone-specific cytoplasmic receptors antagonistic complementary negative feedback positive feedback 5. Which gland in the diagram below is responsible for controlling metabolism in the heart, liver, kidney, and muscle tissues? a. b. c. d. ____ A B C D 6. What would be the best treatment for an individual with an intolerance to cold, decreased heart rate, and weight gain, despite a decreased appetite? a. b. c. d. ____ combination of insulin, exercise, and diet to control insulin levels diet to reduce the amount of dietary iodine, increasing thyroxine production increase the amount of vitamin D to increase levels of blood calcium injections of thyroid hormone to increase metabolic activity 7. A newly discovered drug is found to increase the volume of urine production. When ADH is administered, the volume of urine returns to normal. Which best describes the action of the new drug? a. b. c. d. ____ blocks the release of ADH from the kidney blocks the release of ADH from the pituitary triggers the release of ADH from the kidney triggers the release of ADH from the pituitary 8. Which gland releases melatonin? a. adrenal ____ b. pineal c. pituitary d. thymus 9. How does insulin affect blood in a normal human body? a. decreases calcium levels c. increases calcium levels b. decreases glucose levels d. increases glucose levels ____ 10. Which best describes the action of a drug that stimulates weight loss? a. b. c. d. decreases the activity of the thymus gland decreases the activity of the thyroid gland increases the activity of the thymus gland increases the activity of the thyroid gland ____ 11. Which hormone best fits the graph below? a. adrenaline b. estrogen c. melatonin d. thyroxine ____ 12. Which disorder is caused by a deficiency of thyroxine? a. dwarfism b. giantism c. hyperthyroidism d. hypothyroidism ____ 13. Which would result if the target gland were not stimulated during a negative feedback loop? a. b. c. d. The hypothalamus would be inhibited. The hypothalamus would be stimulated. The target gland would not secrete its hormone. The target gland would secrete its hormone. ____ 14. The graph below shows the blood glucose levels of a healthy person over a short period of time. Which hormone is most likely secreted by the pancreas at point A? a. glucagon b. insulin c. melatonin d. somatotropin ____ 15. Which hormone acts on a positive feedback control mechanism? a. calcitonin b. oxytocin c. parathyroid d. thyroxine ____ 16. In the diagram below, which gland illustrates how the nervous and endocrine systems work together? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 17. Which hormone raises blood sugar? a. adrenaline b. glucagon c. insulin d. thyroxine ____ 18. A person has a swollen neck and experiences fatigue and weight gain. Which would a physician most likely recommend as appropriate treatment? a. b. c. d. increasing dietary intake of calcium increasing dietary intake of iodine taking insulin injections taking vitamin D pills ____ 19. Which hormone stimulates the sympathetic nervous system? a. adrenaline b. glucagon c. somatotropin d. thyroxine ____ 20. Which hormone would a doctor most likely give to an expectant mother to stimulate uterine contractions and induce labour? a. insulin b. oxytocin c. prolactin ____ 21. Which gland is located deep in the centre of the brain? d. thyroxine a. adrenal b. pineal c. pituitary d. thymus ____ 22. Which hormone regulates sugar uptake by cells? a. insulin b. melatonin c. somatotropin d. thyroxine ____ 23. A boy entering grade one is 1.5 m tall and in grade three he is 2.0 m tall. If the other grade three children are 1.2 m tall, which hormone is overactive in this boy? a. cortisol b. glucagon c. somatotropin d. testosterone ____ 24. Which hormone is released from the pineal gland? a. ADH b. FSH c. melatonin d. oxytocin ____ 25. When going through puberty, how does testosterone put hair on a boy’s chest? a. b. c. d. creates a second messenger effects cells to change shape interacts with DNA in the nuclei of cells triggers nerve impulses in cells ____ 26. Which hormones are produced in the adrenal gland? a. ADH and FSH b. aldosterone and cortisol c. GH and GnRH d. oxytocin and thymosin ____ 27. What is the target organ for the hormone insulin? a. adrenal cortex b. heart c. kidney d. liver ____ 28. A tumour detected on the thyroid gland inhibits thyroid function. What is the effect on thyroxin and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)? a. A b. B ____ 29. Which gland secretes melatonin? c. C d. D a. lacrimal b. pineal c. pituitary d. sweat ____ 30. Which gland functions improperly when there is a lack of iodine in the diet? a. adrenal b. salivary c. tear d. thyroid ____ 31. Why do protein hormones need to trigger a second messenger to activate a target cell? a. b. c. d. They are not water soluble. They bind to multiple types of cells. They cannot cross cell membranes. They require activation by ATP. ____ 32. Which disorder is caused by an over-secretion of the human growth hormone (HGH)? a. diabetes mellitus b. dwarfism c. giantism d. hyperthyroidism ____ 33. Which is responsible for maintaining a relatively constant body temperature? a. antagonistic hormones b. negative feedback system c. pituitary hormones d. positive feedback system ____ 34. What is most likely present in high amounts in an individual who has been fasting for 24 hours? a. glucagon b. glucose c. insulin d. oxytocin ____ 35. Which gland controls calcium levels in blood? a. adrenal b. pineal c. thymus d. thyroid ____ 36. Dwarfism is caused by the under-secretion of which hormone? a. adrenaline b. HGH c. LH d. thyroxine ____ 37. The graph below shows the blood glucose levels of a healthy person over a short period of time. Which hormone is most likely secreted by the pancreas at point Y? a. glucagon b. insulin c. melatonin d. somatotropin ____ 38. Which is a result of hyperthyroidism? a. b. c. d. decreased blood vessel diameter decreased mental capacity increased bone calcium increased metabolic rate ____ 39. What is the main role of the endocrine system? a. b. c. d. coordinate movement of the body defend the body against illness and infection produce chemicals that affect other parts of the body remove waste products from the blood ____ 40. A disruption in the feedback loop of which structure below results in a slower metabolism? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 41. If an adult male lacks facial hair, has a high pitched voice and above average body fat, which hormone is most likely secreted in low amounts? a. HGH b. estrogen c. melatonin d. testosterone ____ 42. Which hormone can be used to treat diabetes mellitus? a. glucagon b. insulin c. somatotropin d. thyroxine ____ 43. If a drug completely destroys the cells in the pancreas, which conditions could be expected to develop in the body fluids? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 44. Which gland produces melatonin? a. adrenal b. anterior pituitary c. pineal d. thyroid ____ 45. Which hormone is responsible for uterine contractions during childbirth? a. adrenaline b. HGH c. oxytocin d. TSH ____ 46. Which structure below regulates the secretion of hormones from the ovaries? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 47. If a person has experienced an extended period of starvation, which describes the hormone levels of insulin and glucagon in their blood? a. A b. B ____ 48. Which endocrine gland releases thyroxin? c. C d. D a. adrenal b. hypothalamus c. pineal d. thyroid ____ 49. Which hormone triggers the cellular release of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids into the bloodstream? a. glucagon b. insulin c. melatonin d. thyroxine ____ 50. Why might a doctor prescribe exposure to sunlight for a person experiencing symptoms of depression and an overwhelming desire for sleep? a. decrease melatonin levels b. decrease somatotropin levels c. increase acetylcholine levels d. increase thyroxine levels ____ 51. Which type of hormones penetrate target cells to combine with genes to produce proteins? a. ACTH b. carbohydrates c. non-steroids d. steroids ____ 52. Which disease is caused by an excessive production of thyroxine by the thyroid gland? a. diabetes mellitus b. gigantism c. hyperthyroidism d. hypothyroidism ____ 53. Which is directly involved in the action of most non-steroid based hormones? a. permeable membrane b. prostaglandins c. second messenger d. testosterone ____ 54. Which hormones have antagonistic effects? a. b. c. d. epinephrine and ADH insulin and glucagon thyroxine and calcitonin thyroxine and parathyroid hormone ____ 55. Which gland is represented by X? a. adrenal medulla b. pancreas c. posterior pituitary d. thyroid ____ 56. Which describes the blood hormone concentration of a person who has not eaten for 24 hours? a. high insulin, high glucagon b. high insulin, low glucagon c. low insulin, high glucagon d. low insulin, low glucagon ____ 57. What causes acromegaly? a. b. c. d. overproduction of human growth hormone underproduction of human growth hormone overproduction of insulin underproduction of insulin ____ 58. Which gland produces and releases adrenocorticotropin? a. anterior pituitary b. hypothalamus c. posterior pituitary d. thyroid ____ 59. As we age the level of this hormone decreases, resulting in diminished muscle mass and wrinkles. a. thyroxine c. somatotropin b. ADH d. prolactin ____ 60. Which hormones have complementary effects? a. b. c. d. calcitonin and parathyroid hormone vitamin D and prolactin adrenaline and noradrenaline insulin and glucagon ____ 61. Which of the following substances is NOT used by the body to make hormones? a. proteins b. glucose c. cholesterol d. polypeptides ____ 62. Which of the following is normally not part of the fight-or-flight reflex? a. b. c. d. increase in blood glucose level increase in oxygen level in blood increase in thyroid hormone level in blood increase in adrenaline level in blood ____ 63. Elevated levels of this hormone can enhance the symptoms of seasonal affective disorder. a. somatotropin b. thymosin c. thyroxine d. melatonin ____ 64. Which of the following statements is true? a. b. c. d. steroid hormones are manufactured from proteins steroid hormones are hydrophobic steroid hormones use a second messenger steroid hormones are not fat soluble ____ 65. Which of the following statements is false? a. b. c. d. non-steroid hormones are composed of proteins, peptides or amino acids non-steroid hormones are fat soluble non-steroid hormones use cAMP as a second messenger non-steroid hormones bind to a receptor protein in the plasma membrane ____ 66. Which of the following hormones stimulates lactogenesis? a. cortisol b. prolactin c. oxytocin d. thyroxine ____ 67. Which of the following is not a part of the body where excess nutrients, surplus to our immediate needs, are stored? a. b. c. d. adipose tissue liver muscle tissue kidney ____ 68. When blood Ca2+ levels are too high the ________ gland secretes _________ which results in the uptake of Ca2+ in the bones. a. b. c. d. parathyroid gland; calcitonin parathyroid gland; parathyroid hormone thyroid gland; calcitonin thyroid gland; parathyroid hormone ____ 69. Which of the following glands secrete hormones that provide a sustained stress response? a. b. c. d. adrenal cortex adrenal medulla pancreas thymus gland ____ 70. During times of stress, ACTH triggers the adrenal cortex to secrete higher levels of which hormone? a. b. c. d. adrenaline aldosterone cortisol noradrenaline ____ 71. Which of the following hormones is also a neurotransmitter in the sympathetic nervous system? a. adrenaline b. aldosterone c. cortisol d. thymosin ____ 72. Which gland produces a hormone that stimulates the production and maturation of lymphocytes into T cells? a. adrenal galnd b. pineal gland c. thymus gland d. thyroid gland ____ 73. Which disorder of the endocrine system is thought to develop when the immune system attacks and destroys the beta cells of the pancreas? a. b. c. d. acromegaly Grave’s disease myxedema type 1 diabetes ____ 74. What is the most common cause of an excess production of HGH? a. b. c. d. lack of dietary iodine tumour in the pituitary gland destruction of beta cells in the pancreas lack of sunshine/daylight ____ 75. If a problem arises in the thyroid gland that results in a decrease in thyroxine production, how does this affect the level of thyroid stimulating hormone that is then produced? a. b. c. d. levels will decrease levels will stay the same levels will increase thyroxine production has no effect on thyroid stimulating hormone production ____ 76. Which of the following relationships best demonstrates the overlapping functionality of the nervous system and the endocrine system? a. b. c. d. adrenal cortex and the production of cortisol adrenal medulla and production of adrenaline pancreas and the production of insulin thymus gland and the production of thymosin ____ 77. If a pregnant woman failed to produce oxytocin, what would be the result? a. b. c. d. ____ 78. Urination would be more frequent. ADH levels in the bloodstream would drop. Uterine contractions would not begin for labour. Oxytocin levels would increase in the bloodstream. Normally, inhibition of the pituitary gland would occur if the secretion of hormone X a. b. c. d. increased, causing a decrease in the secretion of hormone Y decreased, causing a decrease in the secretion of hormone Y increased, causing an increase in the secretion of hormone Y decreased, causing an increase in the secretion of hormone Y ____ 79. The endocrine function of the pancreas was studied in Canada using dogs as experimental animals. The pancreatic cells with an endocrine function are a. islet cells b. blood cells c. Sertoli cells d. interstitial cells ____ 80. Use the following information to answer the next question. BST could probably be obtained naturally from which gland in a cow? a. Thyroid b. Adrenal c. Pituitary d. Pancreatic ____ 81. Use the following information to answer the next question. In a cow’s mammary gland, BST is most similar in its effect to a. estrogen b. oxytocin c. prolactin d. progesterone ____ 82. During an emergency situation, the adrenal gland is stimulated to release a hormone that directly causes an increase in a. insulin levels b. blood glucose levels c. parasympathetic stimulation d. conversion of glucose to glycogen ____ 83. Possible symptoms of phenochromocytoma include a. b. c. d. increased heart rate, increased blood sugar, increased metabolic rate decreased heart rate, increased blood sugar, increased metabolic rate increased heart rate, decreased blood sugar, decreased metabolic rate decreased heart rate, decreased blood sugar, decreased metabolic rate ____ 84. Hormones X and Y, respectively, are a. b. c. d. insulin and glucagon glucagon and insulin insulin and epinephrine epinephrine and insulin ____ 85. If the physiological factor influencing this negative feedback loop were the metabolic rate, then 1, 2, and 3, respectively, would be the a. b. c. d. hypothalamus, pituitary, and thyroid thyroid, hypothalamus, and pituitary pituitary, thyroid, and hypothalamus pituitary, hypothalamus, and thyroid ____ 86. The response to increased glucose levels in the blood is the conversion of glucose to glycogen. This response is the result of the secretion of a. b. c. d. insulin by the adrenal medulla glucagon by the adrenal medulla insulin by the islets of Langerhans glucagon by the islets of Langerhans ____ 87. While playing a vigorous game of basketball, a person’s overall rate of metabolism increases. Which two hormone levels rise so that blood glucose levels meet the needs of the increased metabolic rate? a. Cortisol and ADH b. Steroids and HGH c. Insulin and acetylcholine d. Epinephrine and glucagon Endocrine System Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: C A A B B D B B B D C D C B B B B B A B B A C C C B D A B D C C B A D B A D C A D PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: 2 1 1 1 2 2 3 1 1 2 2 1 3 2 2 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 2 1 2 1 1 3 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: Aug 04 #4 Aug 04 #5 Aug 04 #6 Aug 04 #7 Aug 04 #12 Aug 04 #14 Aug 04 #15 Aug 05 #13 Aug 05 #14 Aug 05 #15 Aug 06 #11 Aug 06 #12 Aug 06 #13 Aug 06 #14 Aug 06 #15 Aug 07 #11 Aug 07 #12 Aug 07 #13 Aug 07 #14 Aug 07 #15 Aug 08 #13 Aug 08 #14 Aug 08 #15 Aug 09 #11 Aug 09 #12 Aug 09 #13 Aug 09 #14 Aug 09 #15 June 04 #10 June 04 #11 June 04 #12 June 04 #13 June 04 #14 June 04 #15 June 05 #12 June 05 #13 June 05 #14 June 05 #15 June 06 #11 June 06 #12 June 06 #13 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: B A C C A C D A A D C C B B C A A C C B C D B B B D C A C A C D B C B C C A C C B A A A C D PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: 1 2 1 1 REF: REF: REF: REF: June 06 #14 June 06 #15 June 07 #12 June 07 #13 DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 2 REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: June 07 #15 June 08 #13 June 08 #14 June 08 #15 June 09 #10 June 09 #11 June 09 #12 June 09 #13 June 09 #14 June 09 #15