* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Health, Disease, and Treatment, a Systems Perspective
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
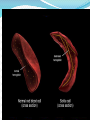
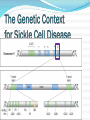
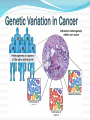
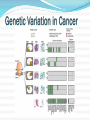
Mattie Robinson, MS, MA INCOSE – Orlando Chapter Feb 18 2016 • Overview of Medical Doctrines • Genetics Terms • A Systems View of Sickle Cell Disease • A Systems View of Cancer Microflora (gut, skin) Environment Nutrients Lifestyle Western (United States) Traditional Medicine Folk Medic Holistic (Europe) Ayurveda (India) Western Medicine (United States) •Comparatively new system of medical education and practice •Used throughout North America, Europe, and a growing number of developing countries Ayurveda (Traditional Indian Medicine) •Individualized treatment based on the balance of body fluids and other factors within each patient. •Interventions are primarily herbal, dietary, and lifestyle interventions. Eastern Medicine (Traditional Chinese Medicine) •Ancient systems of integrated medical practice •Used throughout Asia, Chinese medicine is most well known Folk Medicine •Community-based models, rely on spiritual as well as herbal and lifestyle treatments* •Practiced in a variety of socioeconomic settings, from remote tribes to enclaves within large cities (New Orleans) Minimized the preceding models to pinpoint individual symptoms and syndromes for treatment •Practitioners see hundreds to thousands of patients with whom they have little to no personal relationship •In US, primarily focused on pharmaceutical intervention • Diagnostics and treatments are highly standardized •Only individual differences with an immediate impact are considered when prescribing treatment (ie: allergies, drug intolerances) •Metrics are used to quantitatively track therapeutic progress •Even patient responses are gauged in a quantitative fashion “The greatest mistake in the treatment of diseases is that there are physicians for the body and physicians for the soul, although the two cannot be separated.” Plato • The rise of molecular genetics brought a new understanding of the human system. • The current trend shifts the focus to molecular medicine • Genetic testing is relied on to: • • Characterize a patient Predict successful therapies Different sequences, same meaning 11 Molecules Hemoglobin T 11 BCL11A HS1L & MYB TOX SAR1A FCPL •A single base can be crucial to the function of a gene •Each person with SCD is genetically unique •The HbS allele only tells part of the story •Variation at other locations in the genome can alter the severity of a disease mutation •Many cancers have genetic alterations that ramp up growth signaling pathways •Because of the rapid, uncontrolled growth of cancer cells, tumors accumulate replication errors over time Many cancers have genetic alterations that ramp up growth signaling pathways Because of the rapid, uncontrolled growth of cancer cells, tumors accumulate replication errors over time Previously the only therapies available for cancer patients were •Chemotherapy •Radiation therapy •Surgery • A growing knowledge of the molecular basis of cancer paved the way toward targeted therapies. • Functions that are crucial to cancer cells are shut down, thereby sparing the patient’s healthy cells. • • Populations of cancer cells continue to evolve as they replicate. With time, cancer cells may even “outsmart” a previously effective therapy • Cancer is a collection of genetically unique diseases • Cancer starts with one mutated cell, but continues to evolve over time • Cell signaling is often altered in cancer cells; new cancer drugs are being developed to target these alterations Johns Hopkins Hospital National Institutes of Health





























![Gasparini - Tumori Rari 190913 [modalità compatibilità]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007830911_1-9897586e1674194d943bfb4b631f7097-150x150.png)









