* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiration and Respiratory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
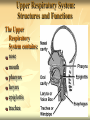
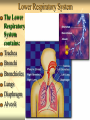
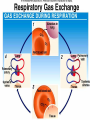
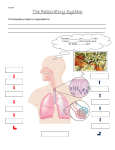
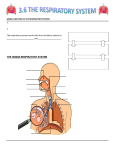
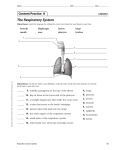
Respiration & Human Respiratory System Objectives Explain the process of respiration Explain the role of breathing in the respiratory system Identify the structures of the respiratory system and explain their functions. Describe the process of gas exchange Explain how smoking affects the respiratory system Respiration Body cells need oxygen in order to release energy from nutrients. Respiration is the process by which the body uses oxygen to release energy from nutrients. C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2 + Energy The respiratory system is the system that provides the body with the oxygen it needs for respiration. Upper Respiratory System: Structures and Functions The Upper Respiratory System contains: nose mouth pharynx larynx epiglottis trachea Upper respiratory system structures and functions Structure Nose Function Filters and warms inhaled air Pharynx Larynx Connects nose and mouth Opening of trachea, contains vocal chords Epiglottis Flap of cartilage; covers entrance of trachea when swallowing Trachea Windpipe that branches into two; leads inhaled air into lungs Lower Respiratory System The Lower Respiratory System contains: Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs Diaphragm Alveoli Lower Respiratory System Structures & Functions Structure Bronchi Function Bronchioles Two branches of the trachea; lead into each lung Smaller branches of the bronchi; continue to branch and get smaller until they end in the alveoli (air sacs) Lungs Gas exchange organs inflate with inhaled air. Diaphragm Large flat breathing muscle, expands and contracts during breathing Alveoli Tiny clusters of air sacs covered with capillaries; site of gas exchange Other Essential Structures Cilia- Small hair-like projections of the cells lining the trachea. They beat rhythmically moving mucus and foreign particles toward the pharynx. Scanning Electron Micrograph of tracheal cilia. Other Essential Structures Mucous membrane – Cells lining the nasal passages, trachea, and bronchi also secrete mucus which traps foreign particles so they can be swept up to the pharynx and out of the respiratory tract by the cilia Breathing Breathing: The movement of air into and out of the lungs A. Inhalation: Diaphragm contracts, volume of chest cavity increases, air goes in to lungs. (This is an active process) B. Exhalation: Diaphragm relaxes, volume of chest cavity decreases, air is forced out of lungs. (This is a passive process) Control of Breathing You can control when you breathe, but it is not a completely voluntary action. After a while of holding your breath, your body takes over and forces you to breathe. Breathing is so important that your nervous system will not let you have complete control over it. The medula oblongata in the brain controls breathing. It forces you to breathe even if you are willing yourself not to. Gas Exchange – Lungs and RBC’s After an inhalation, the amount of oxygen in the alveoli is greater than the amount of oxygen in the blood. Oxygen diffuses from the area of higher O2 concentration (in the alveoli) to the area of lower O2 concentration (the blood). CO2 CO2 poor Alveoli O2 rich Diffusion O2 Diffusion CO2 rich RBC O2 poor Gas Exchange – RBC’s & Body Cells In the capillaries, O2 diffuses from the blood (O2 rich) to the cells of the body (O2 poor). Also CO2 diffuses from the cells (CO2 rich) to the blood (CO2 poor). Each gas is diffusing from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Gas Exchange – RBC’s & Body Cells In the capillaries, O2 diffuses from the blood (O2 rich) to the cells of the body (O2 poor). Also CO2 diffuses from the cells (CO2 rich) to the blood (CO2 poor). Each gas is diffusing from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration CO2 O2 rich RBC CO2 poor Diffusion O2 Diffusion O2 poor BODY CELL O2 rich Oxygen Transport Most oxygen is carried from the lungs to the body tissue by the red blood cells. Hemoglobin (abbreviated Hb) is a red, iron containing protein in RBC’s that combines easily with oxygen. The amount of oxygen in the surrounding tissues will determine whether hemoglobin will bind to or release oxygen. Respiratory Diseases Asthma Bronchitis Emphysema Respiratory Diseases Pneumonia Lung Cancer Questions 1. List and describe the four stages of gas exchange. 2. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged by the blood and alveoli by which process? 3. Why is inhalation considered and active process? Questions 4. Describe the structure and function of cilia in the cells lining the nasal passages, trachea, and bronchi. 5. What is the difference between internal respiration and external respiration? Questions 6. List the structures of the upper respiratory system and briefly describe their function. 7. Explain the structure and function of the alveoli in the lungs. Questions 8. List and describe 4 diseases that affect the respiratory system.