* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
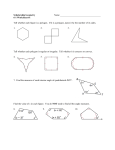
Download Polygons A polygon is a closed figure that is drawn on a plane. It
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
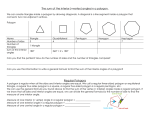
Part 5: Polygons A polygon is a closed figure that is drawn on a plane. It must have at least three sides that are segments. The segments can intersect only at their endpoints, the segments cannot intersect (cross) and adjacent segments are not collinear. PQRST is a polygon. WXYZ is not closed, therefore it is not a polygon. ABCDEF is a polygon, but it is a concave polygon. We will study only convex polygons. There is a test to determine if a polygon is concave. In figure ABCDE, choose two points in the interior of the figure. If the segment created from those two points falls anywhere outside the boundaries of the polygon, then the polygon is concave. A polygon is named by listing its vertices consecutively in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. You may choose any vertex of the polygon to start its name. Thus PQRST is also TSRQP and STPQR and QRSTP and QPTSR and several other names. There are actually 10 possible names for this polygon. Many polygons have special names which you will need to recognize. The names are based on the number of sides (or angles) of the polygon. Sides 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 n Name triangle quadrilateral pentagon hexagon septagon octagon nonagon decagon dodecagon n-gon There is a neat exploration for you to do that will help develop your understanding of the next theorem, the Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem. Activity: You will need two sheets of paper for this activity. Copy the following table onto one sheet of paper. Polygon triangle n number of sides 3 number of triangles formed 1 Sum of the interior angle measures 180 quadrilateral X 180 = pentagon X 180 = hexagon X 180 = septagon X 180 = octagon X 180 = Draw a quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, septagon and octagon on the other sheet of paper. (If you want to draw them a little larger you may put your drawings on two sheets of paper.) Choose one vertex on each polygon and draw the diagonals from that vertex to all of the other nonadjacent vertices. Count the number of triangles formed within each polygon and record it on the paper. You know that each triangle contains 180o. Calculate in the last column of the table the sum of the interior angle measures by multiplying the number of triangles created by 180. When you are done, you may go to the next page for a summary of the results. Your table should look something like the one below: number of triangles formed 1 Sum of the interior angle measures 180 Polygon triangle n number of sides 3 quadrilateral 4 2 2 X 180 = 360 pentagon 5 3 3 X 180 = 540 hexagon 6 4 4 X 180 =720 septagon 7 5 5 X 180 =900 octagon 8 6 6x 180 =1080 For each polygon with n sides, there are n-2 triangles formed within the polygon from a single vertex. Each triangle contains 180o, therefore each polygon contains (n-2)x180o total interior degrees. We sum this up with a theorem. Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem The sum of the measures of the angles of an n-gon is (n-2)180. Next, watch the video of an example problem that illustrates the Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem. Example: Solve for x. This polygon has 6 sides, so its interior angle measures sum to (6-2)(180) = 720o. x + 5x + 3x + 17 + 4x + 36 + 2x + 5x + 7 = 720 20 x + 60 = 720 20x = 660 X = 33 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Suppose that a polygon is a regular polygon. A regular polygon is a polygon that is equiangular – all of its angles have the same measure. A regular polygon also has all of its sides congruent. We use the polygon angle-sum theorem to find the measure of an interior angle of a regular polygon. For example, an equiangular triangle has 180o divided amongst its three angles, so each angle measures = 60o. A square has 360o divided amongst its four angles, so each angle of a square measures = 90o. How big is the interior angle of a regular 14-gon? (14 – 2)(180) = 2160o = 154.2o How big is the interior angle of a regular 22-gon? (22-2)(180) = 3600o o Let’s examine the exterior angles of a triangle. The exterior angle of a triangle always forms a linear pair with its corresponding interior angle. By the Triangle Angle-Sum Theorem we know a + b + c = 180o. The sum of the three exterior angles is (180-a) + (180 – b)+ (180 – c) = exterior angles sum 540 – a – b – c 540 – (a + b + c) 540 – 180 = 360o The conclusion is the sum of the exterior angles of the triangle sum to 360 o. This result applies to all convex polygons in the following theorem. Polygon Exterior Angle-Sum Theorem The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a polygon, one at each vertex, is 360 o. For the hexagon, The Polygon Exterior Angle-Sum Theorem is very helpful when trying to find the measure of the exterior angle of a regular polygon. Remember, regular polygons have all interior angles congruent. From this information, we can recognize that all exterior angles are also congruent. Often this knowledge can give us an alternate way to determine the measure of an interior angle. Example: Find the measures of the exterior and the interior angles of an octagon. Solution: Sum of the measures of the exterior angles = 360o = 45o 8 sides in an octagon 8 So each exterior angle measures 45o in a regular hexagon. Each exterior angle is a linear pair with the interior angle: 45 + interior angle measure = 180 Interior angle measure = 135o This answer can be verified by the Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem: (8 – 2)(180) = 1080 = total interior angle measures 1080 = 135o = measure of an interior angle of a regular octagon 8