* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Size
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
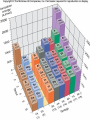
Atomic Size The atomic radius increases from top to bottom in a group in the periodic table. As you move down a group in the periodic table, atomic size generally increases. • WHY? The atomic radius decreases from left to right across a period in the periodic table. • WHY? • The apparent discontinuities in this diagram reflect the difficulty of comparing the radii of atoms of metallic and nonmetallic bonding types. Radii of the noble gas elements are estimates from those of nearby elements. • Lithium has the largest atomic radius in the second period. • As the number of electrons added to the same energy level increases, atomic size generally decreases. • List the symbols for sodium, sulfur, and cesium in order of increasing atomic radii _____________________ • Sulfur, Sodium, Cesium • The largest atom in Group 1A is _____ • Fr • The smallest atom in Group 7A is _____ • F Ions and Ionization • Ions form when electrons enter or leave atoms. • The charge of a cation is positive. Cations are smaller than the original atom. • An anion has a negative charge. Anions are larger than the original atom. • Removing one electron from an atom results in the formation of an ion with a 1+ charge. • Adding one electron to an atom results in the formation of an ion with a 1charge. • Ionization energy - energy required to move an electron out of an atom • Ionization energy decreases from top to bottom and increases from left to right on the periodic table. Among Na, K, and Cs, which element has the lowest ionization energy? • Cesium (Cs) Which is larger, K or K+? • K Which is smaller, Li, Li+, F, or F? • Li+