* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download carbon compound
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
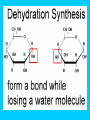
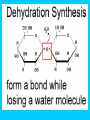
Carbon Compounds Chapter 2, Section 3 pp. 44 - 48 Carbon Compounds • What does it mean to be organic? • Organic compounds - compounds containing CARBON • Carbon atoms contain 4 valence electrons – Valence – electrons in the outer energy level of the atom – Carbon can form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms • Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons Large Carbon Compounds with Analogy (in this analogy assume that the ATOMS are similar to LETTERS) • Monomers are simple carbon molecules “mono” = one (Ex. one word) • Polymers are molecules made of many monomers (monomer + monomer = polymer) “poly” = many (Ex. a sentence) • Macromolecules are made of many polymers (polymer + polymer = macromolecule) “macro” = large (Ex. a paragraph) How do Monomers link to form Polymers??? • Dehydration Synthesis Reactions (also called condensation reactions) – Dehydration = to lose water – Synthesis = to put together – chemical reaction in which two monomers are linked together and a molecule of water is lost • one monomer donates a hydroxyl (OH-) and the other monomer donates a hydrogen (H+) forming water (H2O) How do polymers break down into monomers??? • Hydrolysis reactions – Hydro – water – Lysis – to break apart – The bond between two monomers is broken & a molecule of water breaks down • One monomer receives an (OH) and the other receives an (H) – This is the reverse of a dehydration synthesis reaction. Hydrolysis Organic Compounds There are 4 main classes of organic compounds which are essential to the life processes of all living things. Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids 1. Proteins Elements: C, H, O, N Used to build body structures – muscles, hair, skin, etc. Most enzymes are proteins as well Monomer = Amino Acids (20 kinds) Amino Acid Structure Each amino acid includes 1 central carbon with 4 things attached: 1. 1 carboxyl group (-COOH) 2. An amino group (-NH2) 3. An “R” group –functional group that determines the difference between Amino Acids. 4. A Hydrogen atom Proteins Proteins are made of chains of amino acids linked together Dipeptides – 2 Amino Acids Polypeptides- many Amino Acids Enzymes = polypeptides II. Lipids (Fats) Elements: C, H (in high ratio) & O NOT water soluble (do NOT dissolve in water) Monomer = 1 glycerol + fatty acids Used to store excess energy Important part in cell membranes and waterproof coverings Ex. Fats, oils, waxes – Fatty acids – Complex Lipids Complex Lipids 1 fatty acid + a glycerol molecule = a wax 2 fatty acids + a glycerol molecule =phospholipid (which makes up the cell membrane) 3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol molecule = a triglyceride III. Carbohydrates Elements: C, H, O in 1:2:1 ratio (double hydrogen) Main fuel provider and energy source of living things, used for structures in cells Exists in 2 forms: (ring formation common) Monosaccharides –monomer of carbs like sugars Polysaccharides- polymer of carbs Polysaccharides Polymer made of 3 or more monosaccharides Ex. 1. Glycogen (animal starch) Glycogen is broken down & excess sugar is released from liver when your blood sugar runs low 2. Cellulose (in plants) Tough, flexible (found in cell wall) gives plants rigidity & strength. IV. Nucleic Acids Elements : C, H, O, N, P Monomer = Nucleotide made of 3 components 1. phosphate group 2. 5-carbon sugar 3. Nitrogen base Store important information for the cell Ex. DNA cellular information RNA stores/transfers information to make proteins