* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download continental-drift-and-the-theory-of-plate-tectonics-fran-et-al
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
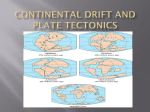
Continental Drift and the theory of Plate Tectonics What is Continental Drift? Definition: The gradual movement of the continents across the earth's surface through geological time. How is it caused? Plate tectonics suggests that Earth's entire crust is composed of a number of large plates that are constantly moving in relation to each other What is initial evidence of continental drift? Well, there’s four main areas, that support the theory of continental fit, we are going to look at: • Continental fit • Climatological • Biological • Geological Continental fit: If we look at a world map, it appears the continents fit together like puzzle pieces Continents that match include: • South America and Africa • Australia and Antarctica • North America and Europe We can see this puzzle like fit in these diagrams: Climatological: Wegener collected ancient climate information to confirm his glacial data. • The data from the sedimentary rocks showed a change in climate – which can only be explained by continental drift • The data of fossils of tropical plants were found in coal in Antarctica – which means Antarctica must have previously been close to the equator • Glacial Deposits were found in South Africa – meaning South Africa must've been further away from the equator for water to have formed Biological: Biological evidence of continental drift includes: • Dinosaur fossils were found in Australia's Dinosaur Cave of dinosaurs adapted to colder climates – so Australia must’ve been closer to the poles to create these colder climates • Rocks in mild climates show scarring of much colder climates • Plant remains from humid swamps have been found in both Antarctica and India • Fossil formations have been found on either side of the Atlantic Geological: Geological evidence of continental drift includes: • The ‘same’ rocks have been found in south-east Brazil and South Africa. • The trends of the mountains in the eastern USA and northwest Europe are similar • Similar glacial deposits are found in Antarctica, South America and India, which are now thousands of km apart. Subsequent discoveries that support the theory of continental drift The two discoveries we are now going to look at are: • Sea floor spreading • Palaeomagnetism Sea floor spreading Sea Floor Spreading = the formation of fresh areas of Oceanic crust which occurs through the upwelling of magma at Mid-Ocean Ridges Harry Hammond Hess • His time as a navy officer during World War 2 meant he used sonar (also known as echo sounding) to map the ocean floor across the North Pacific • Everyone thought that the ground was completely flat under the sea like this: • However Harry Hess found that the oceans were shallower in the middle and discovered Mid-Ocean Ridges: • He outlined a theory that explained that the continents actually drift, this is now known as Sea Floor Spreading • Hess believed that ocean trenches were the places where the oceans grew from Palaeomagnetism Palaeomagnetism= the study of fossil magnetism in rocks and the investigation of the Earths magnetic field • Frederick Vine and Drummond Matthews studied the patterns of magnetic stripes on the ocean floor • The magma rises from the mantle and cools to make new crust which preserves a record of the polarity of the Earths magnetic field • They noticed that the stripes were symmetrical on each side of the Mid-Ocean Ridge and this is the same with the ages of the rocks where the youngest is closest to the ridge and the oldest is furthest away Sea floor spreading diagram Why were scientists sceptical of his ideas? • Many people embraced the idea that the two continents (South America and Africa) were a result of a land bridge between the two continents • Wegner actually specialised in meteorology and astronomy, not geology – so his theories were not taken seriously • His ideas were not concrete – scientists said centrifugal force and tidal pull were not strong enough to cause continental drift Is Wegener theory of continental drift now accepted? Yes o Continental drift is now widely accepted in the scientific community o Palaeomagnetism suggests continents do move o Sea floor spreading shows how new oceanic crust is formed However is the theory of continental drift as robust as it may seem? After all we’ve said there are actually some cracks in Wegener's theory. So we are going to look at another theory (we’ll call it expanding earth theory) that may prove Wegener wrong: The theory is… The size of the earth was much smaller than it is today and so all continents were together as a single huge land mass (called Pangea) then and as earth continued grow in size all these continents looked like as if they are moving apart whereas they actually have just reached their current positions! However how robust is the argument of the ‘expanding earth’ • The continents do crash and bump into each other "willy-nilly“ according to GPS measurements so there definitely is continental movement • The young seafloor is evidence for spreading and subduction • There is much more evidence of continental drift that does not rely on theory So, to conclude • When Wegener first proposed the idea of continental drift, it was widely not accepted • However new discoveries (e.g. palaeomagnetism and sea floor spreading) have since meant it is now widely accepted • There are some other theories; however these are a lot less robust than the theory of continental drift Thankyou for listening! Photo Courtesy of Chloe