* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Psychology Curriculum
Cyberpsychology wikipedia , lookup
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Social computing wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Ethnoscience wikipedia , lookup
Vladimir J. Konečni wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
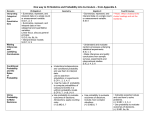
Curriculum Unit Name of Course: AP Psychology Brief Description (Course Catalog): Length of Course (Qtr, Sem or Year): Grade Level(s): 11-12 Semester Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Introduction to Psychology Brief Description: Induction to the field of psychology and the history of the current theoretical perspectives. Length of Course (Days/Weeks): 6 days Essential Questions: 1. Summarize the origins of psychology and identify major historical figures. 2. Describe & compare different theoretical approaches in explaining behavior; recognize the strengths and limitations of applying theories to explain behavior --structuralism, functionalism, & behaviorism in the early years --psychoanalytic/psychodynamic and humanism emerging later --evolutionary, biological, and cognitive as more contemporary approaches 3. List and describe professional specialties/careers in psychology Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Summarize the origins of psychology and identify major historical figures. Multiple Choice & Free Response 2. Describe & compare different theoretical approaches in explaining behavior; recognize the strengths and limitations of Exam applying theories to explain behavior --structuralism, functionalism, & behaviorism in the early years --psychoanalytic/psychodynamic and humanism emerging later --evolutionary, biological, and cognitive as more contemporary approaches 3. List and describe professional specialties/careers in psychology Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Brief Description: Methods of Psychological Research Methods of psychological research is examined, as well as how research is analyzed and interpreted. Length of Course (Days/Weeks): Essential Questions: 9 days 1. Summarize the necessity and advantages of a scientific approach in psychology 2. Differentiate each of the descriptive/correlational research methods with regard to purpose, strengths & weaknesses. 3. Describe positive & negative correlations and their significance. 4. Summarize the experimental method: explain the difference between and independent & dependent variables & identify important factors (including strengths and weaknesses) in experimentation. 5. List and describe the key concepts in descriptive and inferential statistics as applied to psychological research. 6. Describe ethical research guidelines and practices. Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Summarize the necessity and advantages of a scientific approach in psychology Multiple Choice & Free Response 2. Differentiate each of the descriptive/correlational research methods with regard to purpose, strengths & weaknesses. Exam 3. Describe positive & negative correlations and their significance. 4. Summarize the experimental method: explain the difference between and independent & dependent variables & identify important factors (including strengths and weaknesses) in experimentation. 5. List and describe the key concepts in descriptive and inferential statistics as applied to psychological research. 6. Describe ethical research guidelines and practices. Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Brief Description: Biological Psychology Length of Course (Days/Weeks): Essential Questions: The Nervous System – neuron, nerve systems, brain, as related to human behavior. Endocrine system is also examined. 10 days 1. Summarize the basics of neural functioning, including parts of the neuron, the neural impulse, and role of neurotransmitters. Describe specific neurotransmitters and their roles in the NS, including the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters. 2. Describe the workings of the Neural (Central and Peripheral) systems and Hormonal (Endocrine) system, summarize how they interact. 3. Describe several techniques for studying the brain. 4. Summarize the key structures and functions of the human brain, including the cortexes and association areas. Explain the brain’s plasticity following injury or illness. Describe split-brain research. Summarize relationships between brain organization & handedness. 5. Discuss the relationship between genetics and behavior, and explain how traits and behaviors can be selected for their adaptive value. Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Summarize the basics of neural functioning, including parts of the neuron, the neural impulse, and role of Multiple Choice & Free Response neurotransmitters. Describe specific neurotransmitters and their roles in the NS, including the influence of drugs on Exam neurotransmitters. 2. Describe the workings of the Neural (Central and Peripheral) systems and Hormonal (Endocrine) system, summarize how they interact. 3. Describe several techniques for studying the brain. 4. Summarize the key structures and functions of the human brain, including the cortexes and association areas. Explain the brain’s plasticity following injury or illness. Describe split-brain research. Summarize relationships between brain organization & handedness. 5. Discuss the relationship between genetics and behavior, and explain how traits and behaviors can be selected for their adaptive value. Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Sensation & Perception Brief Description: Human senses and pathways to the brain are examined, as well as visual perceptual abilities Length of Course (Days/Weeks): 10 days Essential Questions: 1. Summarize basic principles of sensory transduction, including absolute & difference threshold, signal detection, & sensory adaptation. 2. Describe sensory processes (hearing, vision, touch, taste, smell, vestibular, kinesthetic, pain), including the specific nature of energy transduction, relevant anatomical structures, and specialized pathways in the brain for each of the senses. 3. Explain the process of color vision. 4. Identify and define the principles of perceptual organization. 5. Summarize the following types of perception. Provide examples for each: a. Perception of depth & distance b. Perception of motion c. Perception of constancy (size, shape, brightness) d. Perceptional illusions e. Perceptual set f. Perceptual Adaptations 6.Explain and evaluate the experience of ESP. Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Summarize basic principles of sensory transduction, including absolute & difference threshold, signal detection, & Multiple Choice & Free Response sensory adaptation. Exam 2. Describe sensory processes (hearing, vision, touch, taste, smell, vestibular, kinesthetic, pain), including the specific nature of energy transduction, relevant anatomical structures, and specialized pathways in the brain for each of the senses. 3. Explain the process of color vision. 4. Identify and define the principles of perceptual organization. 5. Summarize the following types of perception. Provide examples for each: g. Perception of depth & distance h. Perception of motion i. Perception of constancy (size, shape, brightness) j. Perceptional illusions k. Perceptual set l. Perceptual Adaptations 6.Explain and evaluate the experience of ESP. Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Learning Brief Description: Length of Course (Days/Weeks): Essential Questions: Classical conditioning, Operant Conditioning, & Social Learning theory are examined 10 days 1. Describe and evaluate classical conditioning and the key elements in this form of learning. 2. Summarize important names, terms, & experiments associated with Classical Conditioning. 3. Describe and evaluate operant conditioning and the key elements in this form of learning. 4. Summarize important names, terms, & experiments associated with Operant Conditioning. 5. Describe the key elements in observational learning (terms, experiments, names). 6. Interpret graphs that exhibit the results of learning experiments. 7. Provide examples of how biological constraints create learning predispositions. Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Describe and evaluate classical conditioning and the key elements in this form of learning. Multiple Choice & Free Response 2. Summarize important names, terms, & experiments associated with Classical Conditioning. 3. Describe and evaluate operant conditioning and the key elements in this form of learning. 4. Summarize important names, terms, & experiments associated with Operant Conditioning. 5. Describe the key elements in observational learning (terms, experiments, names). 6. Interpret graphs that exhibit the results of learning experiments. 7. Provide examples of how biological constraints create learning predispositions. Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Memory Brief Description: Length of Course (Days/Weeks): Essential Questions: Encoding, Storage and Retrieval processes of memory as well as issues related to forgetting. 7 days 1. Outline the principles that underlie effective encoding, storage, and construction of memories. 2. Summarize the information processing theory of memory, and list and describe the different types of memory. 3. Describe the various ways in which we remember, and how factors can influence our memory. 4. Explain the various measures of forgetting, and factors that may influence forgetting/retrieval. 5. Summarize evidence on the physiology of memory. Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Outline the principles that underlie effective encoding, storage, and construction of Multiple Choice & Free Response memories. 2. Summarize the information processing theory of memory, and list and describe the different types of memory. 3. Describe the various ways in which we remember, and how factors can influence our memory. 4. Explain the various measures of forgetting, and factors that may influence forgetting/retrieval. 5. Summarize evidence on the physiology of memory. Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Thinking, Language Brief Description: Length of Course (Days/Weeks): Essential Questions: Human Cognitions are examined. 7 days 1. Define cognition. 2. Describe the roles of categories, hierarchies, definitions, and prototypes in concept formation 3. Compare algorithms and heuristics as problem-solving strategies, and explain how insight differs from both of them. 4. Contrast the confirmation bias and fixation, and explain how they can interfere with effective problem solving. 5. Contrast the representativeness and availability heuristics, and explain how they can cause us to underestimate or ignore important information. 6. Describe the drawbacks and advantages of overconfidence in decision making 7. Describe how others can use framing to elicit from us the answers they want 8. Discuss how our preexisting beliefs can distort our logic 9. Describe the remedy for the belief perseverance phenomenon. 10. Describe the basic structural units of a language. 11. Trace the course of language acquisition from the babbling stage through the two-word stage. 12. Discuss Skinner’s and Chomsky’s contributions to the nature-nurture debate over how children acquire language, and explain why statistical learning and critical periods are important concepts in children’s language learning. 13. Summarize Whorf’s linguistic determinism hypothesis, and comment on its standing in contemporary psychology. 14. Discuss the value of thinking in images. 15. List five cognitive skills shared by the great apes and humans. 16. Outline the arguments for and against the idea that animals and humans share the capacity for language Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Define cognition. Multiple Choice & Free Response 2. Describe the roles of categories, hierarchies, definitions, and prototypes in concept formation 3. Compare algorithms and heuristics as problem-solving strategies, and explain how insight differs from both of them. 4. Contrast the confirmation bias and fixation, and explain how they can interfere with effective problem solving. 5. Contrast the representativeness and availability heuristics, and explain how they can cause us to underestimate or ignore important information. 6. Describe the drawbacks and advantages of overconfidence in decision making 7. Describe how others can use framing to elicit from us the answers they want 8. Discuss how our preexisting beliefs can distort our logic 9. Describe the remedy for the belief perseverance phenomenon. 10. Describe the basic structural units of a language. 11. Trace the course of language acquisition from the babbling stage through the two-word stage. 12. Discuss Skinner’s and Chomsky’s contributions to the nature-nurture debate over how children acquire language, and explain why statistical learning and critical periods are important concepts in children’s language learning. 13. Summarize Whorf’s linguistic determinism hypothesis, and comment on its standing in contemporary psychology. 14. Discuss the value of thinking in images. 15. List five cognitive skills shared by the great apes and humans. 16. Outline the arguments for and against the idea that animals and humans share the capacity for language Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Intelligence Brief Description: Length of Course (Days/Weeks): Essential Questions: Human intelligence is examined 4 days 1. Define intelligence & describe different definitions/types of intelligence. 2. Describe the relationship between intelligence and the anatomy of the brain. 3. Compare measures, types, and factors of intelligence. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Outline the history of intelligence testing and explain its significance. Describe relevant labels related to intelligence testing (gifted, cognitively disabled, savant). Differentiate between standardization, test norms, reliability, & validity. Debate the appropriate testing practices, particularly in relation to culture-fair test uses. Summarize how genetic, environmental, and cultural influences affect intelligence. Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Define intelligence & describe different definitions/types of intelligence. Multiple Choice & Free Response 2. Describe the relationship between intelligence and the anatomy of the brain. 3. Compare measures, types, and factors of intelligence. 4. Outline the history of intelligence testing and explain its significance. 5. Describe relevant labels related to intelligence testing (gifted, cognitively disabled, savant). 6. Differentiate between standardization, test norms, reliability, & validity. 7. Debate the appropriate testing practices, particularly in relation to culture-fair test uses. 8. Summarize how genetic, environmental, and cultural influences affect intelligence. Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: States of Consciousness Brief Description: Sleep & dreams, influence of drugs, hypnosis, meditation – all states of consciousness are examined Length of Course (Days/Weeks): 4-5 days Essential Questions: 1. Summarize various states of consciousness & their impact on behavior 2. Explain what is known about biological clocks. 3. Describe the specifics of the sleep cycle and summarize the stages of sleep. 4. Explain the multiple theories of sleep and dreaming. 5. List and describe sleep disorders & treatments. 6. Summarize hypnosis as an alternative state of consciousness, explain uses of hypnosis, and describe hypnotic phenomena (suggestibility, dissociation). 7. Identify the major drug categories and classify specific drugs, including their psychological and physiological effects. 8. Explain drug dependence, addiction, tolerance, & withdrawal. Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Summarize various states of consciousness & their impact on behavior Multiple Choice & Free Response 2. Explain what is known about biological clocks. 3. Describe the specifics of the sleep cycle and summarize the stages of sleep. 4. Explain the multiple theories of sleep and dreaming. 5. List and describe sleep disorders & treatments. 6. Summarize hypnosis as an alternative state of consciousness, explain uses of hypnosis, and describe hypnotic phenomena (suggestibility, dissociation). 7. Identify the major drug categories and classify specific drugs, including their psychological and physiological effects. 8. Explain drug dependence, addiction, tolerance, & withdrawal. Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Brief Description: Motivation, Emotion, Stress & Health What motivates human/animal behavior, physical and psychological emotional experiences, and influence of stress on psyche and health are examined Length of Course (Days/Weeks): 8 days Essential Questions: Motivation: 1. Describe Drive-reduction, Incentive, Instinct, & Arousal theories 2. Describe Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs & criticisms 3. Summarize physiological motivators – hunger, thirst, sex 4. Summarize psychological motivators – power, affiliation, achievement 5. Summarize the role of motivation at work Emotion: 1. 2. 3. 4. Describe the 3 components of an emotion Summarize the role of the autonomic nervous system in emotions Describe the role & influence of arousal on emotions and performance Describe & differential between James-Lange, Schacter-Singer, & Cannon Bard’s theories of emotion 5. Describe the similarities & differences between cultures & facial expressions Stress & Health 1. Summarize the cause of stress and types of stressors 2. Summarize the effects of stress on the body 3. Describe & differentiate the 3 types of conflict 4. Explain the Holmes & Rahe scale of life changes and its relation to illness 5. Summarize Hans Selye’s GAS theory 6. Explain the different constructive ways to deal with stress Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) Motivation: 1. Describe Drive-reduction, Incentive, Instinct, & Arousal theories Multiple Choice & Free Response 6. Describe Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs & criticisms 7. Summarize physiological motivators – hunger, thirst, sex 8. Summarize psychological motivators – power, affiliation, achievement 9. Summarize the role of motivation at work Emotion: 1. 6. 7. 8. Describe the 3 components of an emotion Summarize the role of the autonomic nervous system in emotions Describe the role & influence of arousal on emotions and performance Describe & differential between James-Lange, Schacter-Singer, & Cannon Bard’s theories of emotion 9. Describe the similarities & differences between cultures & facial expressions Stress & Health 1. Summarize the cause of stress and types of stressors 7. Summarize the effects of stress on the body 8. Describe & differentiate the 3 types of conflict 9. Explain the Holmes & Rahe scale of life changes and its relation to illness 10. Summarize Hans Selye’s GAS theory 11. Explain the different constructive ways to deal with stress Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Human Development Brief Description: Length of Course (Days/Weeks): Essential Questions: Physical, Cognitive & Social development across the human lifespan 10-11 days 1. Compare the interaction of nature and nurture in the determination of behavior. 2. Summarize physical and motor development of the neonate and infant. 3. Summarize and evaluate Piaget’s stages of cognitive development. 4. Describe the influence of temperament and other social factors on attachment. 5. Summarize and evaluate Kohlberg’s stages of moral development 6. Summarize and evaluate Erikson’s stages of social development 7. Explain and compare the major events of adolescence, adulthood, and the changes associated with aging. 8. Describe how sex and gender influence socialization and other aspects of development. 9. Summarize Kubler-Ross’s research on death and dying. Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Compare the interaction of nature and nurture in the determination of behavior. Multiple Choice & Free Response 2. Summarize physical and motor development of the neonate and infant. 3. Summarize and evaluate Piaget’s stages of cognitive development. 4. Describe the influence of temperament and other social factors on attachment. 5. Summarize and evaluate Kohlberg’s stages of moral development 6. Summarize and evaluate Erikson’s stages of social development 7. Explain and compare the major events of adolescence, adulthood, and the changes associated with aging. 8. Describe how sex and gender influence socialization and other aspects of development. 9. Summarize Kubler-Ross’s research on death and dying. Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Personality Brief Description: Length of Course (Days/Weeks): Essential Questions: Theories of human personality development and description 9 days 1. Describe how Freud’s life shaped the theory of Psychoanalysis 2. Summarize Freud’s work — levels of consciousness, structure of personality, stages of development, defense mechanisms (define & explain all), therapy, & dream analysis 3. Compare/Contrast the Neo-Freudians (Jung, Horney, Adler, Erikson) 4. Describe & critique other methods of explaining personality a. The Humanistic/Phenomenological Perspective (Maslow, Rogers) b. Trait perspective (Allport, Eysenck) c. Social-Cognitive Perspective (Bandura, Rotter, Seligman) 5. Define & describe different personality assessment techniques (from each perspective) Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Describe how Freud’s life shaped the theory of Psychoanalysis Multiple Choice & Free Response 2. Summarize Freud’s work — levels of consciousness, structure of personality, stages of development, defense mechanisms (define & explain all), therapy, & dream analysis 3. Compare/Contrast the Neo-Freudians (Jung, Horney, Adler, Erikson) 4. Describe & critique other methods of explaining personality a. The Humanistic/Phenomenological Perspective (Maslow, Rogers) b. Trait perspective (Allport, Eysenck) c. Social-Cognitive Perspective (Bandura, Rotter, Seligman) 5. Define & describe different personality assessment techniques (from each perspective) Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Psychological Disorders & Treatment Brief Description: Psychological disorders and methods of treatment Length of Course (Days/Weeks): 10-12 days Essential Questions: 1. Define contemporary & historical conceptions of what constitutes a disorder. 2. Explain the ways we diagnose disorders, including the use of the DSM-IV. 3. Explain classifications of disorders and appropriate therapies. 4. Summarize explanations for disorders according to the major theoretical perspectives. 5. Compare/contrast different therapies according to the major theoretical perspectives Content Standards: STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) 1. Define contemporary & historical conceptions of what constitutes a disorder. Multiple Choice & Free Response 2. Explain the ways we diagnose disorders, including the use of the DSM-IV. 3. Explain classifications of disorders and appropriate therapies. 4. Summarize explanations for disorders according to the major theoretical perspectives. 5. Compare/contrast different therapies according to the major theoretical perspectives Instructional Unit Name of Unit/Big Idea: Social Psychology Brief Description: Length of Course (Days/Weeks): Essential Questions: Content Standards: Common Core State ELA or Math Standards: Influence of social interaction on human thought and behavior 8-10 days 1. Define Attribution theory & describe the ways in which people explain behavior. Explain how the fundamental attribution error can affect our analysis of behavior 2. Summarize & describe how attitudes and actions may influence each other. Explain key terms relating to attitudes & actions. 3. Define Conformity. Describe experiments associated with conformity. Summarize factors that may influence conformity. 4. Define Obedience. Describe experiments associated with obedience. Summarize factors that may influence obedience. 5. Summarize the influence of the group. Define & explain key terms associated with group influence (facilitation, loafing, deindividuation, polarization, groupthink). 6. Identify & define components of prejudice. Summarize factors that may influence prejudice. 7. Describe aggression, research done on aggression, and summarize factors that may influence aggression. 8. Summarize findings on attraction, describe factors that may influence attractions, explain the different types of love. 9. Summarize & define altruism. Describe factors that influence altruism. Define & explain key terms associated with altruism (bystander, social exchange/norms) STATE GOAL 18: Understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. B. Understand the roles and interactions of individuals and groups in society. C. Understand how social systems form and develop over time. Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. Students will need to know . . . (content objectives) Students will be able to . . . (skill objectives) Resources and assessments (common to all like classes) Multiple Choice & Free Response 1. Define Attribution theory & describe the ways in which people explain behavior. Explain how the fundamental attribution error can affect our analysis of behavior 2. Summarize & describe how attitudes and actions may influence each other. Explain key terms relating to attitudes & actions. 3. Define Conformity. Describe experiments associated with conformity. Summarize factors that may influence conformity. 4. Define Obedience. Describe experiments associated with obedience. Summarize factors that may influence obedience. 5. Summarize the influence of the group. Define & explain key terms associated with group influence (facilitation, loafing, deindividuation, polarization, groupthink). 6. Identify & define components of prejudice. Summarize factors that may influence prejudice. 7. Describe aggression, research done on aggression, and summarize factors that may influence aggression. 8. Summarize findings on attraction, describe factors that may influence attractions, explain the different types of love. 9. Summarize & define altruism. Describe factors that influence altruism. Define & explain key terms associated with altruism (bystander, social exchange/norms)