* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pathological Conditions: The Heart and Blood Vessels
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
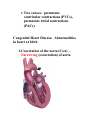
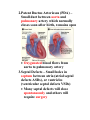
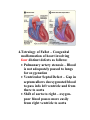
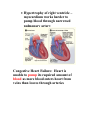
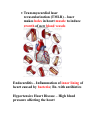
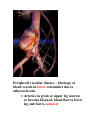
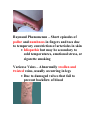
Pathological Conditions: The Heart and Blood Vessels Medical Terminology Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms Types of arrhythmias: 1.Heart block or atrioventricular block: * Failure of proper conduction of impulses through the AV node to the Bundle of His. Damage to SA node can cause impulses to be too weak to activate AV node which means that impulses fail to reach ventricles If failure occurs only occasionally causing heart to miss beat at regular intervals – partial heart block No impulses reach AV node from SA node means ventricles contract slower than the atria and are not coordinated – complete heart block RX: cardiac pacemaker – establish normal rhythm. 2.Flutter Rapid but regular contractions of atria or ventricles Heart rhythm may reach up to 300 beats per minute (BPM) 3.Fibrillation Rapid, random, ineffectual, and irregular contractions of the heart; 350 bpm or more Atrial fibrillation: wave of excitation passes through atrial myocardium more quickly than in atrial flutter. Defibrillator is used to reverse abnormal rhythm; aka cardioversion Automatic Implantable Cardioverter/Defibrillator (AICD) – implanted into chest wall to sense arrhythmias and correct them Radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFA): nonsurgical treatment used to treat arrhythmias; catheter placed in blood vessels leading up against heart muscle , delivers a high-frequency current to burn a small portion of muscle, aka ablation 4.Cardiac Arrest Sudden and often unexpected stoppage of heart movement 5.Palpitations Uncomfortable sensations in chest associated with different types of arrhythmias Not necessarily indicate of a serious condition. Two causes: premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), premature atrial contractions (PACs) Congenital Heart Disease: Abnormalities in heart at birth 1.Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) – Narrowing (coarctation) of aorta 2.Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) – Small duct between aorta and pulmonary artery which normally closes soon after birth, remains open Oxygenated blood flows from aorta to pulmonary artery 3.Septal Defects – Small holes in septum between atria (atrial septal defects ASDs), or ventricles (ventricular septal defects VSDs) Many septal defects will close spontaneously and others will require surgery 4.Tetralogy of Fallot – Congenital malformation of heart involving four distinct defects as follows: Pulmonary artery stenosis – Blood is not adequately passed to lungs for oxygenation Ventricular Septal Defect – Gap in septum allows deoxygenated blood to pass info left ventricle and from there to aorta Shift of aorta to right – oxygenpoor blood passes more easily from right ventricle to aorta Hypertrophy of right ventricle – myocardium works harder to pump blood through narrowed pulmonary artery Congestive Heart Failure: Heart is unable to pump its required amount of blood as more blood enters heart from veins than leaves through arteries Coronary Artery Disease: Dz of arteries surrounding the heart Three large vessels that arise from aorta and supply oxygenated blood to heart Atherosclerosis: deposition of fatty compounds on inner lining of coronary arteries Narrowing causes inflexibility and plugging up of vessel; roughened lining of artery may rupture or cause thrombotic occlusion Blood flow decreased = ischemia leading to necrosis; Area of dead myocardial tissue is infarction Angina pectoris – temporary difference between supply and demand of oxygen to heart muscle Rx – CABG Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) – catheterization with balloons and stents Transmyocardial laser revascularization (TMLR) – laser makes holes in heart muscle to induce growth of new blood vessels Endocarditis – Inflammation of inner lining of heart caused by bacteria; Rx. with antibiotics Hypertensive Heart Disease – High blood pressure affecting the heart Caused by contraction of arterioles leading to increased pressure in arteries Heart has to pump more vigorously to overcome increased resistance in arteries Vessels lose elasticity, become like solid pipes and place increased burden on heart to pump blood through body Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP) – Improper closure of mitral valve when heart is pumping blood *Antibiotics are given at time of dental procedures to prevent valve from becoming infected. Murmur – extra heart sound heard between normal beats Pericarditis – Inflammation of membrane surrounding heart Caused by virus, bacteria, or idiopathic May need pericardiocentesis to remove excess fluid Rheumatic Heart Disease – Heart disease caused by rheumatic fever Rheumatic fever – occurs usually in childhood, can follow a few weeks after a streptococcal infection Damages heart valves (esp. mitral valve); become inflamed and scarred BLOOD VESSELS Aneurysm – Ballooning out of artery caused by weakness in arterial wall or breakdown of wall due to atherosclerosis Danger is rupture Rx. Depends on location of vessel Small vessels in brain – occlusion of vessel with small clips Larger arteries – resection of vessel with synthetic graft Peripheral vascular disease – blockage of blood vessels in lower extremities due to atherosclerosis Arteries in groin or upper leg narrow or become blocked, blood flow to lower leg and foot is reduced Raynaud Phenomenon – Short episodes of pallor and numbness in fingers and toes due to temporary constriction of arterioles in skin Idiopathic but may be secondary to cold temperatures, emotional stress, or cigarette smoking Varicose Veins – Abnormally swollen and twisted veins, usually occurring in legs Due to damaged valves that fail to prevent backflow of blood