* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution as Theory and Fact
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
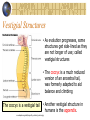
Evidence of Evolution The Tree of Life • All living things share a common ancestor. • We can draw a Tree of Life to show how every species is related. • Evolution is the process by which one species gives rise to another and the Tree of Life grows en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Phylogenetic_tree.svg Evolution as Theory and Fact • Confusion sometimes arises as to whether Evolution is a theory or a fact. Actually it is both! • The theory of Evolution deals with how Evolution happens. Our understanding of this process is always changing. • Evolution is also a fact as there is a huge amount of indisputable evidence for its occurrence. Rodin’s “The Thinker” Theories of Evolution Origin Myths/Cosmologies Genesis (Western example) Carl Sagan’s Universe Calendar 24 days = 1 billion years 1 second = 475 years “Big Bang” Milky Way Solar System Life on Earth Humanlike Primates January 1 May 1 September 9 September 25 Milky Way December 31, 10:30pm Theories of Evolution Darwin and Wallace, 1850s Evolution theory holds that existing species of plants and animals have emerged over millions of years from simple organisms. Darwin, On the Origin of Species, 1859 Charles Darwin Theories of Evolution Darwin’s principle of natural selection “Natural selection is the gradual process by which nature selects the forms most fit to survive and reproduce in a given environment.” For natural selection to work on a given population, there must be variety within that population and competition for strategic resources. The concept of natural selection argues that organisms which have a better fit within their environmental niche will reproduce more frequently than those organisms that fit less well. Theories of Evolution Random genetic drift is the loss of alleles from a population's gene pool through chance. Mutation introduces genetic variation into a breeding population. Gene flow occurs through interbreeding: the transmission of genetic material from one population to another. Gene flow decreases differences and inhibits speciation, the formation of new species. Theories of Evolution Mendel’s principle of inheritance, 1856 The science of genetics explains the origin of the variety upon which natural selection operates. By experimenting with successive generations of pea plants, Mendel came to the conclusion that heredity is determined by discrete particles, the effects of which may disappear in one generation, and reappear in the next. Other Theories Creationism accounts for biological diversity by referring to the divine act of Creation as described in the book of Genesis Catastrophism is a modified version of Creationism, which accounts for the fossil record by positing divinely authored worldwide disasters that wiped out the creatures represented in the fossil record, who were then supplanted by newer, created species. Intelligent Design states that modern physics and cosmology have uncovered evidence for intelligence in the structure of the universe and this intelligence seems to act with us in mind and that the universe as a whole shows evidence of design. Evidence of Evolution Early Primates Prosimians (65mya) Monkeys (35mya) Apes (23mya) Hominids (5mya) Early Primates - Traits Common physical primate traits: Dense hair or fur covering Warm-blooded Live young Suckle Infant dependence Common social primate traits: Social life Play Observation and imitation Pecking order Common Primate Traits Primate Family Tree Crown lemur Orangutan Born from Primates? ‘Discovering Ardi’ and ‘Ardipithecus and Human Evolution’ videos (Discovery.com) Biochemistry • The basic similarity of all living things suggests that they evolved from a single common ancestor. • As we have already seen, all living things pass on information from generation to generation using the DNA molecule. • All living things also use a molecule called ATP to carry energy around the DNA for Information organism. Transfer en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:ATP-xtal-3D-sticks.png ATP for Energy Transfer Similar Genes HUMAN CHIMPANZEE GORILLA CCAAGGTCACGACTACTCCAATTGTCACAACTGTTCCAACCGTCACGACTGTTGAACGA CCAAGGTCACGACTACTCCAATTGTCACAACTGTTCCAACCGTCATGACTGTTGAACGA CCAAGGTCACAACTACTCCAATTGTCACAACTGTTCCAACCGTCACGACTGTTGAACGA Genetic code of chimps and gorillas is almost identical to humans • If evolution is true then we might also expect that closely related organisms will be more similar to one another than more distantly related organisms. • Comparison of the human genetic code with that of other organisms show that chimpanzees are nearly genetically identical (differ by less than 1.2%) whereas the mouse differs by ≈15%. Comparative Anatomy • Similar comparisons can be made based on anatomical evidence. • The skeleton of humans and gorillas are very similar suggesting they shared a recent common ancestor, but very different from the more distantly related woodlouse… Human and Gorilla yet all have a common shared characteristic: bilateral symmetry Woodlouse en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Primatenskelett-drawing.jpg Homology The pentadactyl limb is ancestral to all vertebrates… but modified for different uses en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Evolution_pl.png Vestigial Structures • As evolution progresses, some structures get side-lined as they are not longer of use; called vestigial structures • The coccyx is a much reduced version of an ancestral tail, was formerly adapted to aid balance and climbing The coccyx is a vestigial tail • Another vestigial structure in humans is the appendix. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Illu_vertebral_column.jpg Fossil Record http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geologic_time_scale © World Health Org. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Eopraptor_sketch5.png © NASA origins bacteria complex cells dinosaurs humans The fossil record shows a sequence from simple bacteria to more complicated organisms through time and provides the most compelling evidence for evolution. Evolution of the modern horse From Eohippus (5 toes, > 1 foot, size of a cat) To Equus (1 toe, 5 feet tall) Evolution of the modern horse Transitional fossils • Many fossils show a clear transition from one species, or group, to another. • Archaeopteryx was found in Germany in 1861. It share many characteristics with both dinosaurs and birds. Archaeopteryx en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Archaeopteryx_lithographica_paris.JPG • It provides good evidence that birds arose from dinosaur ancestors Geography Marsupials • Geographic spread of organisms also tells of their past evolution. • Marsupials occur in two populations today in the Americas and Australia. • This shows the group evolved before the continents drifted apart evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/lines/IVCexperiments.shtml en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Kangaroo_and_joey03.jpg Antibiotic Resistance Antibiotic Resistance •This is an example of natural selection in action. The antibiotic acts as an environmental pressure. It weeds out those bacteria with low resistance and only those with high resistance survive to reproduce.