* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DOWNLOAD The Digestive Dysfunction Map
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
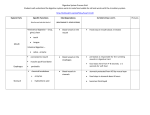
Digestive Dysfunction Stomach Pancreas Chart The principle functions of the stomach are the initiation of protein digestion and the breakdown of minerals for absorption in the small intestine. The most important elements in the stomach are hydrochloric acid and pepsin. Without these two elements, in sufficient quantity, protein digestion and mineral digestion are incomplete. The pancreas uses its digestive enzymes to further break down carbohydrates, protein, and fat. It is also responsible for producing insulin and regulating glucose. Symptoms: Symptoms: Bad breath (halitosis) Loss of taste for high protein (meat, etc.) Gas shortly after eating Indigestion 1/2 to 1 hour after eating Acidic or spicy foods upset stomach Chronic asthma, airborne or food allergies H-Pylori infection and/or intestinal parasites Crave sweets or coffee in afternoon or mid-morning Hungry between meals or excessive appetite Eat when nervous Irritable between meals Inability to tolerate fruits and vegetables, especially lettuce Particles of undigested fruits and vegetables seen in stool Get “shaky” or light-headed if meals missed Fatigue, eating relieves Heart palpitations if meals missed or delayed Awake after a few hours of sleep, hard to get back to sleep Gall Bladder/Liver The gall bladder stores bile produced in the liver. Bile is released when fat enters the small intestine and the bile is responsible for emulsifying the fat and neutralizing the acid produced from protein digestion Small Intestine The small intestine is where most Symptoms: nutrients from ingested food are Lower bowel gas and/or bloating sev- absorbed after breakdown in the stomach and emulsification by bile eral hours after eating Feet burn and pancreatic enzymes Whites of eyes (sclera) are yellow Dry skin, itchy feet and/or skin peels on feet Brown spots or bronzing of the skin Bitter metallic taste Blurred vision or headache over eyes Feel nauseous, queasy, or gag easily Color of stools light brown or yellow Greasy or high fat foods cause distress Pain between shoulder blades Dark circles under eyes “Acid” breath History of gall bladder attacks or gallstones Gall Bladder removed Symptoms: Inability to handle carbohydrates Food allergies Intestinal cramping Gas/bloating Gluten/casein sensitivity Large Intestine (Colon) The colon is responsible for storing waste, reclaiming water, and absorbing some nutrients. Symptoms: Coated tongue or “fuzzy” debris on tongue Pass large amounts of foul smelling gas Irritable bowel or mucous colitis Constipation, diarrhea, or stools alternate from soft to watery Bowel movements painful or difficult, and/or laxatives used Burning or itching anus