* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch55Test - Milan Area Schools
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
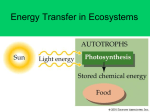
Communities and Ecosystems: Chapter 55 Name: Block: Fill in the Blank 1. The total amount of ______________ assimilated by photosynthesis is called gross primary production. 2. A ____________________ is defined as all organisms that get their energy from a common source (e.g., all herbivores) 3. Detritivores reduce the remains of other organisms to mineral nutrients that can be taken up by plants. An example of these are _________________. 4. The introduction of organisms where there were previously none due to a disturbance is called ___________________. 5. Animals that eat primary producers are called ___________. 6. Organisms such as the beaver have a larger than expected impact on their ecosystems. These are called __________________. 7. If decomposers where removed from an ecosystem all the minerals and energy would _____________ in dead matter. 8. Only about ______________% of the energy present at one trophic level makes it to the next trophic level. 9. A food web better explains what occurs in ecosystems because most organisms ______________ more than one other organism 10. ___________________ and __________________ drive the amount of primary production found in an area. Multiple Choice 11. Which of the following statements about food chains and energy flow through ecosystems is false? a. A single organism can feed at several trophic levels. b. The lower the trophic level at which an organism feeds, the more energy is available. c. Detritivores feed at all trophic levels except the producer level. d. Food webs include two or more food chains. e. All organisms that are not producers are consumers. 12. Assume that the energy transfer efficiency between trophic levels is 10 percent. How much grain would be required to produce 70 kg of human biomass if the grain is eaten by cows and the cows are eaten by humans? a. 210 kg b. 700 kg c. 2,100 kg d. 7,000 kg e. 70,000 kg 13. If the removal of a species from a community has a greater effect on the structure and functioning of the community than one would have predicted from the species’ abundance, then that species is most likely a(n) a. keystone species. b. carnivore. c. herbivore. d. early successional species. e. mimic of another species. 14. The sea star Pisaster ochraceous is an abundant predator on the rocky intertidal communities on the Pacific coast of North America. The sea star feeds preferentially on the mussel Mytilus californianus. In the absence of the sea star, the mussel is a dominant competitor. Predation by the sea star, however, creates bare areas. For this reason, a. the number of species will be changed by the presence of the sea star, but the direction of change cannot be predicted. b. the variety of species will be unaffected by the presence or absence of the sea star. c. the variety of species will be greater when the sea star is present than when it is absent. d. the variety of species will be smaller when the sea star is present than when it is absent. e. Mytilus will go extinct when the sea star is present. 15. Which of the following could not be used as an example of succession? a. A landslide exposes bare rock. Eventually a forest is reestablished on the site. b. An alien weed is introduced into the Hawaiian Islands. Eventually it displaces a native plant, driving the native plant to extinction. c. A freshly killed mouse decomposes. d. A tree falls in the forest. Eventually a new tree replaces it. 16. The greatest amount of energy loss in ecosystems occurs through a. photosynthesis. b. respiration. c. herbivory. d. excretion. e. digestion. 17. Photosynthetic plants are considered to be a. heterotrophs. b. consumers. c. autotrophs. d. detritivores. e. predators. 18. Organisms that obtain their food from both primary consumers and another trophic level are called a. herbivores. b. omnivores. c. detritivores. d. producers. e. autotrophs. 19. All of the following are detritivores except a. insects. b. fungi. c. wolves. d. insects. e. bacteria. 20. This type of energy drives almost all biological systems. a.Solar b.Chemical c.Physical d.Mechanical e.Electrical