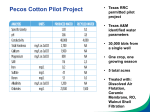
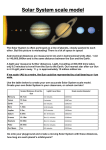
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sustainable Engineering Certificate Technical Track 1. GEO 416
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Sustainable Engineering Certificate Technical Track 1. GEO 416 Global Warming (Fall 2010) Educate the student about climate change, including its causes and impacts, mitigation measures, climate policy, energy alternatives and carbon footprinting. Global warming refers to contemporary changes to the surface temperature of the Earth which are occurring in large part due to changes in the carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere as a result of our consumption of fossil fuels 2. ME 483 Alternative Energy Engineering (Sp 2010 MW 2:00- 3:15) Solar radiation characteristics. Solar energy collection and conversion devices. Design and analysis of passive and active solar energy systems. Solar electric power production. Wind energy conversion. Economic analysis. 3. MSE 415 ( Every Fall) Product Design and Development is a project-based course that covers modern tools and methods for sustainable product design and development. The cornerstone is a project in which teams of management, engineering, and industrial design students conceive, design and prototype a physical product. Class sessions are conducted in workshop mode and employ cases and hands-on exercises to reinforce the key ideas. Topics include identifying customer needs, concept generation, industrial design, and design-for-manufacturing. 4. MSE 304 Engineering Economics/ Env Economics (Every Sp and Fall) Systematic evaluation of the economic benefits and cost of projects involving engineering design and analysis. Economic decision-making in an environment of limited resources and uncertainty. 5. PS 461 Env Policy ( Sp 2010 T Th 12:30-1:45) The political processes that govern environmental policymaking in the U.S. are examined. It begins by laying the groundwork of an evaluation of the current state of environmental affairs by exploring the history of American environmentalism. It then presents a theoretical framework for understanding environmental problem and their policy solutions. Finally, it encourages students to critically analyze environmental cases, with specific attention focused on issues surrounding energy and climate change, air, and water pollution, land use, and hazardous and toxic waste. 6. CMT 336/L Fundamentals of Green Buildings and Lab The purpose of this course is to give the students an overview of design process and construction delivery systems for high performance green buildings. The US Green Building Council (USGBC) Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) will be studied in some detail. Sustainability evaluation systems will be reviewed. The course will provide an understanding of the concept of high performance green buildings and sustainability, the physical limitations of the materials used and the issues involved in selecting green building materials. Sustainable landscapes, energy usage and indoor environmental quality factors will be discussed. Students will learn to reduce the footprint of construction operations and become familiar with green building commissioning. 7. MSE 556 Nanomaterials and nanotechnology (Every Even Spring) Introduction to nanotechnology and types of nanomaterials that have been synthesized for applications in nanotechnology (mechanics, electronics, optoelectronics, energy and biomedical sciences. Illustration of novel synthesis methods of various nonmaterials. 8. CE 487 Water Pollution Control (Fall 2010) Principle of water and waste-water purification processes. Design of engineering systems for treatment of water and municipal waste-water. 9. ECE 411 Electric Power Systems Review of basic principles such as complex power, nuclear, hydroelectric and fossil power plant generation. Transmission line parameters, flux linkage, impedance, line capacitance. Design of transmission lines, V-I relationships, wave analysis, models and power handling capabilities. Transformer and generator analysis at the power system level. Per unit system analysis. Two port analysis and design of power transmission lines. Use of software such as Matlab, C, Visual Basic and Excel for simulation, design and homework. 10. Principles of Recycling and Municipal Solid Waste Management Designed for those new to the recycling and solid waste management industry, this introductory course covers the nature and composition of municipal solid waste as well as the current “integrated waste management approach” and the practices of waste reduction, recycling, and transformation/disposal of solid waste. A broad overview of the legal and regulatory framework that governs the industry and various technologies utilized will be discussed. Sustainable Practice Certificate Non-Technical Track 1. GEO 416 2. ME 122 Energy and Society Energy use and its impact on society. Energy production and consumption at all levels from personal to global. Conventional and alternative energy sources, their costs, and their environmental impacts. Understanding and participating in public discussions of energy. Designed for non-majors. Regular written assignments are required. 3. MSE 415/MAE 188 4. CMT 336/L 5. MGT 466 A humanly inhabitable earth is in danger: global warming, ozone depletion, drought, deforestation, species extinction, etc. We can trace the source of these problems to economic activity, population growth, technology, and our collective failure to adequately address these problems. In this course, we will examine these issues and study how business can play a major role in attempting to create a sustainable economy. 6. PS 461 7. Principles of Recycling and Municipal Solid Waste Management