* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infectious Diseases
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
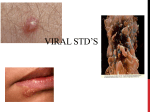
Infectious Diseases Diseases caused by a virus, bacterium, protist or fungus and are spread from an infected organism or the environment to another organism Biological Vector: disease carrying organism (rats, birds, dogs, cats, mosquitoes, fleas, flies) People can be carriers too! Louis Pasteur • French Chemist • Realized that microorganisms could cause diseases in humans. • Pasteurization: the process of heating a liquid to a specific temperature to kills most bacteria. • Virus: a minute piece of genetic material surrounded by a protein coating that infects and multiplies in host cells • The connection between viruses and disease transmission was not understood until the late 1800’s and early 1900’s Surgery Through History • Past: bloody aprons, dirty tools and street clothes were commonplace • Present: disinfectants, sterilized tools, antiseptics and protective (sterile) clothing. • Joseph Lister: one of the first surgeons to promote keeping things clean during surgery. CDC • Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – An arm of the US Department of Health – Monitor the spread of diseases in the US and worldwide. – Located in Decatur, GA (east of Atlanta near Emory University) – Study known pathogens for improved treatments – Working to be prepared for emerging health threats – Provide health and safety information to the public – www.cdc.gov Sexually Transmitted Diseases STD’s • Infectious diseases that are passed from person to person through sexual contact • Bacterial STD’s - treated with antibiotics – Gonorrhea – Chlamydia – Syphilis • Viral STD’s – treated with antiviral drugs – Genital Herpes – HIV Bacterial STD’s • Gonorrhea and Chlamydia – May be present for some time before symptoms appear. – Symptoms: painful urination, genital discharge and genital sores. – Usually respond to antibiotics – Left untreated, they can leave patients sterile or with permanent damage to reproductive organs • Syphilis: caused be a spiral shaped bacterium – Has 3 stages: 1. Sores on mouth or genitals (10 to 14 days) 2. Involve rash, fever and swollen lymph glands (up to a year) 3. Affects cardiovascular and nervous systems Viral STD’s • Genital Herpes – Lifelong viral STD – Causes painful blisters on sex organs – Can be transmitted through sexual contact or from mother to child in childbirth – Goes dormant and then flairs up suddenly – No cure and no vaccine, but can be treated with antiviral medicines • Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) HIV • Exists in blood and other body fluids • Can hide in the body’s cell for years • Transmitted by having unprotected sex, and reusing infected hypodermic needles • Early on was transmitted through blood transfusions but now the blood supply is screened to prevent this. • Can be transmitted from mother to child through the placenta. • The virus cannot multiply outside the body • Cannot be transmitted through casual contact such as touching an infected person or objects that they have touched. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) • Attacks the body’s immune system – Enters the T-cells and multiplies – Infected Helper T cells burst and infect more T-cells – When T-cells are destroyed, not enough B-cells are activated to produce antibodies – The body can no longer fight invading antigens and is unable to fight HIV and other pathogens – Most AIDS patients die from other diseases such as TB, pneumonia or cancer. – The is no known cure but we have developed a series of medicines that interfere with the way the virus multiplies in the host cell (called AZT) Fighting Disease • Washing wounds with soap and water is the first step to disease prevention • Cleaning with and antiseptic and covering with a sterile bandage are other steps • Washing hands (and entire the body) can help prevent the spread of disease • Regular flossing and brushing teeth can also prevent the spread of disease • Healthy habits (nutrition, sleep, exercise) can make the body less susceptible to disease