* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy Notes organ systemspp 12
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
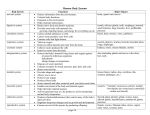
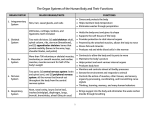
Anatomy Notes pp 12-14, Organ Systems. Human organism consists of several organ systems. Each system includes a set of interrelated organs, working together to provide a specialized function that contributes to homeostasis. Body Coverings Integumentary system: Organs: Skin Accessory organs-hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands Function Protect underlying tissues, regulate body T, sensory receptors, and synthesize certain products. Support and Movement Skeletal System Organs: bones, ligaments, cartilages Function: framework, shields, prod. Rbc, & store inorganic salts. Muscular System Organs: muscles Funtion: movement and support Integration and Coordination Nervous System: Organs: brain, sc, nerves, sense organs Nerves cells w/in organs communicate with each other and with muscles and glands using electrochemical signals- nerve impulses. Impulse has a short-term effect on target. Specialized sensory receptors detect changes inside and outside of body. Other nerve cells rec. messages. Other nerve cells carry impulses. From brain or sc to muscles of glands. For the body to act as a unit it must be integrated and coordinated. Endocrine System: Organs: All the glands that secrete hormones (chemical messengers) Hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands ovaries, testes, pineal gland, and thymus Particular hormone affects only a particular group of cells. (Target cells). Hormone alters metabolism of target cell. Comp to nerve impulse, hormone effects last along time. Transport Cardiovascular System: Organs: heart, arteries, veins, capillaries and blood. Function: Heart: muscular pump that helps force blood thru the blood vessels. Blood- transports gases, nutrients, hormones and wastes. Carries oxygen from the lungs and nutrients from the digestive organs to all body cells. - Also transports hormones and carries wastes from body cells to excretory organs where the wastes are removed from the blood and released to the outside. Vessels- pipes Lymphatic System: Closely related to cv system Organs: lymphatic vessels, lymph fluids, lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen. Function: transports some tissue fluids back to the bloodstream and carries certain fatty substances away from the digestive organs and bloodstream. Cells of lymphatic system are called lymphocytes- defend body against infections; remove disease causing microorganisms and viruses from tissue fluid. Absorption and Excretion Organs in several systems absorb nutrients and oxygen and excrete various wastes. Digestive System Organs: mouth, tongue, teeth, pharynx, salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, gall bladder, liver, pancreas, si, li. Functions: break down food molecules into simpler forms that can pass through cell membranes and be absorbed. Material not absorbed is transported back outside and eliminated. Other digestive organs prod hormones and are also part of the endocrine system. Respiratory System Moves air in and out and exchange gases between the blood and air. Oxygen-from air in lungs-into blood- carbon dioxide leaves the blood and enters the air. Organs: nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Urinary system Organs: kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Function: Kidneys- removes waste from blood and helps maintain the body’s water and salt concentrations. (Electrolytes). Product-urine. Other portions of the urinary system store urine and transport it outside the body. Reproduction Process of prod offspring- progeny. Produces whole new organism like self. Male reproductive system- scrotum, testes, epididymides, ductus deferentia, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral glands, penis and urethra, Prod and maintain sperm cells and transfer sperm into female reproductive tract. Female Reproductive system: Organs: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, clitoris, and vulva Function: Produce and maintain female sex cells (egg cells or oocytes). Transport female sex cells w/in female reproductive system. Can receive sperm cells. Supports dev of embryos, carries fetuses to term and functions in the birth process. Know the medical and applied science terms on pp 17-19.