* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download India Social Studies Grade 6 Lesson 1
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Pre-sectarian Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Enlightenment in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
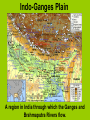
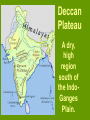
India Social Studies Grade 6 Lesson 1 Mount Everest The highest peak in the Himalayas and the tallest mountain on Earth. Indo-Ganges Plain A region in India through which the Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers flow. Indus River Valley The land surrounding the Indus River in Pakistan. Deccan Plateau A dry, high region south of the IndoGanges Plain. Western Ghats Rolling mountains west of the Deccan Plateau in southern India. Eastern Ghats Rolling mountains east of the Deccan Plateau in southern India. Subcontinent A large area of land that is separated from other countries by water and land. Monsoon Season Rainy season in monsoon climates in which winds blow from the southwest for six months. Subsistence Farming The process of growing food mainly for self-consumption. Lesson 2 Lesson 2 Harappa The site of one of the earliest civilizations in south Asia. Mohenjo- Daro An ancient city in the Indus River Valley in Pakistan. Cyrus II 585 B. C. – 529 B.C. Persian king who established the Persian Empire. Darius I 550 B.C. – 486 B.C. Persian king who expanded the Persian Empire to include India. Chandragupta Maurya 360 B.C. – 298 B.C. Soldier who started the Mauryan Empire, the first Indian empire, and later became a monk. 304 B.C. – 237 B.C. Grandson of Chandragupta Maurya, who used stone columns to mark the territory of his empire and make announcements. Ashoka brahmin A priest who held the highest position in Aryan society. sudra A serf in Hindu society. Sanskrit The main language of the Aryans. Vedas “Books of Knowledge” that contain much of the stories and songs of the Aryans. Zoroastrianism A religion founded by the Persian prophet Zoroaster based on the belief of one god as supreme and the enemy of evil. Lesson 3 Ganges River An important river in India; Hindus believe it represents purity. reincarnation The Hindu belief that the spirit or soul goes from one life to the next. caste In Hinduism, a lifelong social group into which one is born. Hinduism The main religion of India that is based on the Aryan beliefs. Rig Veda One of the best-known books of the Vedas, containing more than 1,000 hymns. Brahman Believed by Hindus to be the universal truth being, which is the source of everything. dharma In Hinduism, the order of the universe. Lesson 4 Bodh Gaya The town in northern India where Siddhartha was enlightened and became Buddha. meditation In Buddhism, a way of clearing the mind. enlightenment In Buddhism, a state of pure goodness, the goal of reincarnation. Buddhism The religion that is based on the teachings of the Buddha. the Buddha The “Enlightened One,” what Siddhartha Gautama came to be known. Four Noble Truths In Buddhism, beliefs about human suffering. The Buddhist way of living that can help Buddhists find relief from their suffering. yoga A system of exercises used to achieve mental and physical well being OM or AUM A sacred symbol representing Braham The End