* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell - Tri-City
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
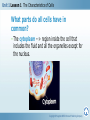
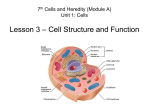
Cells Cells and Heredity Module Characteristics of Cells Explore Describe the nerve cell. Describe the plant cell. Describe the paramecium. Describe the red blood cell. Describe the animal cell. Describe the volvox. Describe euglena. Characteristics of Cells Notes Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells What is a cell? • Cell --> smallest functional and structural unit of all living organisms • Organism --> any living thing that carries out its own life processes. • Robert Hooke was the first to describe cells. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells Why are most cells small? • Cells are small because their size is limited by their outer surface area. • The surface area-to-volume ratio of a cell is the ratio of the outer surface to the cell’s volume. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells Cell Hall of Fame What is the cell theory? • All organisms are made up of one or more cells. • The cell is the basic unit of all organisms. • All cells come from existing cells. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells What is the cell theory? • Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first to describe living cells. • Matthias Schleiden concluded that all plants are made of cells. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells What is the cell theory? • Theodor Schwann determined that all animal tissues are made of cells. • Rudolf Virchow proposed that cells could form only from the division of other cells. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells What is the cell theory? • unicellular organisms = one cell • multicellular organisms = more than one cell are Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells What are the two types of cells? • Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. ○ DNA is in the cytoplasm. ○ They have ribosomes. ○ Some have hairlike structures called flagella that help them move. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells What are the two types of cells? • Eukaryotes are organisms made up of cells that contain DNA in a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and ribosomes. ○ Animals, plants, protists, and fungi are eukaryotes. ○ Most eukaryotes are multicellular but some are unicellular. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells On the Cellular What parts do all cells have in common? • A cell membrane --> protective layer that covers a cell’s surface and controls materials moving into and out of the cell. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells What parts do all cells have in common? • The cytoplasm --> region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 The Characteristics of Cells • An organelle is a small body in the cytoplasm that is specialized to perform a specific function. • The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains DNA. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company