* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
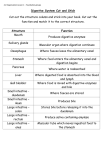
NAME: ______________________________________________ DATE: __________ BLOCK: ____ 1. anus – outside and end opening of alimentary canal 2. ascending colon – begins at cecum and continues upward 3. bile – yellow-green liquid secreted from hepatic (liver) cells and contains bile salts, bile pigments (bilirubin and biliverdin), cholesterol, and electrolytes 4. bile salts – break fat globules into smaller droplets (emulsification), and enhance absorption of fatty acids, cholesterol, and fat-soluble vitamins 5. cecum – pouch-like structure at the beginning of large intestine which leads to rest of intestine of to appendix 6. chyme – mixture of food particles and gastric juice 7. descending colon – follows the transverse section downward 8. digestion – mechanical and chemical break down of foods, and the absorption of the resulting nutrients by cells 9. duodenum – first 25 cm of small intestine 10. epiglottis – a flap-like structure attached to larynx that closes off the trachea so that food does not enter it 11. esophageal sphincter or cardiac sphincter – the thickened wall that prevents stomach contents from regurgitating into the stomach 12. esophagus – a straight, collapsible tube about 25 cm long connecting the pharynx to the stomach 13. feces – undigested and unabsorbed materials; also includes water, mucus, shed intestinal cells, and bacteria 14. gastric glands – found in stomach and secrete gastric juice 15. gastric juice – includes mucus, digestive enzymes, intrinsic factor, and hydrochloric acid 16. hepatic duct- transfer bile from liver into the small intestine 17. ileocecal sphincter – distal end of small intestine where it joins the large intestine; opens to let chime pass into large intestine 18. ileum – third and remaining section of the small intestine 19. intestinal villi – tiny projections of the inner wall of the small intestine and greatly increase the surface area for absorption 20. intrinsic factor – in gastric juice and helps aid in B12 absorption 21. jejunum – second portion of small intestine and includes about 2/5 of total length 22. lacteal – lymphatic vessel in each villus that helps carries nutrients to the body 23. large intestine – larger in diameter than the small intestine; absorbs water and electrolytes from chyme and forms and stores feces 24. liver – large, reddish-brown organ that has many functions; main digestive function is the production and secretion of bile 25. mouth – receives food and begins digestion mechanically; mixes food with saliva 26. pancreas – an endocrine gland that secretes pancreatic juice 27. pancreatic duct – a tube that carries pancreatic juice from pancreas to duodenum 28. pancreatic juice – contains enzymes that break down carbohydrates (pancreatic amylase), lipids (pancreatic lipase), nucleic acids (nucleases), and proteins (trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase) and bicarbonate to neutralize acidity of chyme 29. pepsin – most important gastric enzyme which breaks down protein (inactive form is called pepsinogen) 30. peristalsis – wavelike movements that moves food down the canal 31. pharynx – connects nasal and oral cavities with the larynx and esophagus 32. pyloric sphincter – the thickened wall that controls gastric emptying into the small intestine 33. rectum – attached to the sacrum and leads to anal canal and anus 34. salivary amylase – enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch and glycogen 35. salivary glands – secrete saliva; include the parotid, submadibular, and sublingual 36. sigmoid colon – the S-shaped section after the descending colon and ends in the rectum 37. small intestine – tubular organ that extends from stomach to large intestine; completes digestion, absorbs products of digestion, and transports leftover residues to large intestine 38. stomach – a J-shaped pouch and can hold about 1 liter or more; receives food from the esophagus, beings protein digestion, and carries on limited absorption 39. transverse colon – begins after ascending and crosses the abdomen horizontally