* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physiology of Hearing Talk
Survey
Document related concepts
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
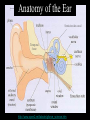
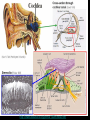
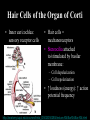
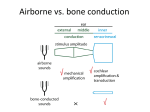
Hearing and Deafness Sarah Todd BIO 313 22 February 2006 http://www.drawingpower.org.uk/Themes04/Themes2004.htm Sense of Hearing • Sound physics – Sound energy transmitted through gaseous/liquid/solid medium – Vibration of medium’s molecules – Sound wave • ↑ amplitude: ↑ loudness • ↑ vibration: ↑ pitch • 1000-4000 Hz http://www.bananasontoast.org/?cat=12 • Physiology of: – External, middle, inner ear – Nerves of the brain – Processing of acoustic information by brain parts http://www.engr.uconn.edu/~esc abi/DynamicAuditoryStimuli.html Sound Transmission in the Ear • External Ear: – External auditory canal→ tympanic membrane • Middle Ear: – Tympanic membrane → middle ear: malleus → incus → stapes → oval window membrane • Inner Ear: – Middle ear → inner ear: scala vestibuli → cochlear duct → organ of Corti → stereocilia → action potential along cochlear nerve • Nerves of the Brain: – Cochlear nerve → brainstem (interneurons) → thalamus → auditory cortex (temporal lobe) Anatomy of the Ear Semicircular canal Temporal bone http://www.open2.net/labrats/gforce_science.htm http://www.acoustics.org/press/140th/noca.htm Hair Cells of the Organ of Corti • Inner ear/cochlea: sensory receptor cells • Hair cells = mechanoreceptors • Stereocilia attached to/stimulated by basilar membrane: – Cell depolarization – Cell repolarization • ↑ loudness (energy): ↑ action potential frequency http://anatomy.iupui.edu/courses/histo_D502/D502f04/lecture.f04/Earf04/Ear.f04.html Organ of Corti http://ourworld.compuserve.com/homepages/dp5/evod3.htm Neural Pathways in Hearing Cochlear nerve fibers ↓ interneurons (brainstem) ↓ multineuron pathway ↓ thalamus ↓ auditory cortex (temporal lobe) http://www.iurc.montp.inserm.fr/cric/audition/english/corti/hcells/transd/transd.htm http://www.rockefeller.edu/labheads/hudspeth/graphicalSimulations.php Loss of Hearing Exposure to high-intensity noises + Exposure to chronic noise levels ↓ Hair cells easily damaged/destroyed • 20 million Americans – 1/12 Americans – 8.6% population • Causes: – Heredity (50%) – Accidents/Illness (50%) • Hearing aids • Cochlear implants http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/scotland/1803505.stm Bibliography Widmaier, E.P., Raff, H., Strang, K.T. Vander’s Human Physiology: The Mechanisms of Body Function. 10th ed. Boston: McGraw-Hill, 2005. Lynch, E.D., Lee, M.K., Morrow, J.E., Welcsh, P.L., Leon, P.E., King, M.-C. 1997 Nonsyndromic Deafness DFNA1 Associated with Mutation of a Human Homolog of the Drosophila Gene diaphenous. Science. 278:1315-1318. Laurent Clerc National Deaf Education Center, Gallaudet University. “Information of Deafness.” 2006. <http://clerccenter.gallaudet.edu/about/faq.html#deaf3 >. Images/Animations from Google.com