* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Feedback - NHS Networks
Telecommunications relay service wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Hearing aid wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
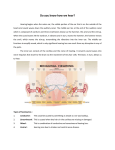
Introduction to Audiology Ed Brown Consultant Clinical Scientist (Audiology) South of Tyne NHSP Local Director Royal Hospital Sunderland SR4 7TP 0191 569 9001 [email protected] Audiology Newborn Hearing Screening Paediatric Screening Paediatric Hearing Assessment Adult Diagnostic Testing Hearing Aid Provision Bone Anchored Hearing Aid Provision Adult Rehabilitation Hearing Therapy Tinnitus Rehabilitation Balance Assessment Balance Rehabilitation Auditory Implants (including Cochlea Implants) Measurement of Hearing School-age children and adults can have their hearing assessed by audiometry Pure tone sounds are presented through headphones Frequencies from 250-8000 Hz are typically tested Threshold is found at each frequency in dB HL Results (dB HL versus frequency) are plotted on an Audiogram Audiometry Low pitched humming Very Quiet Normal Conversational Voice Mild Moderate Severe Very Loud High pitched whistling Profound Anatomy & Physiology Types of Hearing Loss There are two main types of hearing Loss: Anything which prevents or reduces the vibrations through the external or middle ears will produce a conductive deafness If the cochlea or nerve is affected it will result in a sensorineural deafness Conductive Hearing Loss (CHL) Typical CHL Audiogram CHL Summary Due to an abnormality in middle or outer ear Ear canal completely blocked with wax Fluid in the middle ear cavity “glue ear” Chronic middle ear disease Abnormality in the middle ear bones (e.g. otosclerosis) Trauma (things stuck in the ear) Incidence is high (quite common) over 4 out of 5 children may have an episode Management can be conservative or surgical e.g. grommet insertion Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SNHL) Typical SNHL Audiogram Sensorineural Hearing Loss Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by a problem in the cochlea (because the hair cells of the cochlea are not working properly) or with the hearing nerve. Sensorineural hearing loss is permanent Generally a child with sensorineural hearing loss will use amplification (hearing aids and/or a cochlear implant) Causes of SNHL Inherited (genetic) even with no previous family history of deafness Syndromic Congenital Infection (eg CMV) Ototoxic medication Severe jaundice Lack of oxygen at birth Meningitis SNHL Summary Due to an abnormality in cochlea/ auditory nerve Can be present at (or shortly after) birth Can be acquired (e.g. meningitis) Incidence is very low (it is quite rare) Approximately 1.3 per 1000 live births - 0.1% Management is early provision of amplification Early detection is therefore essential Better outcomes if identified < 6 months That’s why we’re doing NHSP ! Newborn Hearing Screening NHSP Follow Up Assessment First Appointment within 28 days of referral Up to 120 minute appointment Tone Pip ABR (e.g. 1 & 4 kHz) Tells us more about hearing across pitches Bone Conduction ABR Can help identify Conductive versus SNHL Tests for other conditions Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder Tympanometry Can help identify OME (Glue Ear) NHSP Follow Up Assessment Diagnostic Assessment by 6 weeks of age Identify if there is a hearing impairment Conductive or Sensorineural Mild, Moderate, Severe or Profound Results to Parents, GP, Link HV, Child Health, SALT, Paediatrics, (Education/Sensory Support) Provide appropriate habilitation Amplification (Hearing Aids) Family Friendly Approach Links with Education/Early Support As soon as appropriate (typically by 6 months of age) Newborn Hearing Assessment Oto Acoustic Emissions (OAE) Transient Evoked OAE (TEOAE) most common Emission elicited by brief acoustic stimuli (click) Response 4 to 15 ms after the stimulus (“echo”) Present in almost all normal ears Response is abolished if hearing loss > 25 dB HL Quick and non-invasive Does not provide threshold information Only indicates healthy hair cell population Use includes neonatal screening (well babies) Equipment (AOAE/AABR) Auditory Brainstem Response Objective test of hearing Assesses function of cochlea and auditory nerve Does not assess higher auditory function Use Tone-Pip (Frequency Specific) sounds 1 kHz (low pitch) and 4 kHz (high pitch) Use Bone Conduction Identify SNHL versus CHL Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder (OAE/CM present ABR absent/abnormal) Assessing hearing in newborn babies ABR Waveforms Children’s Hearing Assessment Visual Reinforcement Audiometry(VRA) Children aged 6 to 30 months (or older) Child sits erect on the parent's knee facing forward Front distracter engages child in simple play activity Sounds through loudspeaker system Warble tone or narrow band noise employed Frequencies in the range 0.25-4.0 kHz are tested Child conditioned to respond when sound heard Visual reward (animated toy) Once conditioned then test procedure begins Levels decreased to find "minimum response" =< 25 dBnHL consistent with (near) normal hearing Visual Reinforcement Audiometry (Age 5 months to 2 Years) Performance/Play Audiometry(age 2 years to 4 years) Tympanometry Otoscopy use otoscope to visualise ear drum Identify contraindications for tympanometry Tympanometry probe placed in child’s ear assesses middle ear function assesses mobility of ear drum can help to identify Otitis Media with Effusion Tympanometry Assesses Middle Ear Function Typical Tympanogram ECV MEP MEC Normal Range Shown = 0.9 ml ECV Baseline Adjusted = -70 DaPa = 1.1 ml = normal Glue Ear Normal Glue Thick Glue Other Conditions Normal Otosclerosis Perforation Children’s Hearing Aid Provision Hearing Aids High Quality Digital Instruments Wide Dynamic Range Compression Quiet sounds amplified more Loud sound amplified less Speech presented at comfortable level Reduces need for volume control Fitted using a prescriptive approach Desired Sensation Level 5.0 Real Ear Measurement Children’s Hearing Aid Provision Hearing Aids Technology Connectivity Outcomes Hearing vs Hearing Impaired Balance Assessment & Rehabilitation Balance System Balance Assessment Assessment of Visual Pathways Vestibular Myogenic Evoked Potentials Balance Rehabilitation Balance Rehabilitation Auditory Implants Cochlear Implant Bone Anchored Hearing Aid