* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of hearing disorders
Telecommunications relay service wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
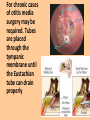
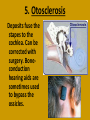
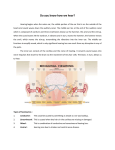
• The following presentation concerns the 4 types of hearing losses. You will need a set of speakers or headphones to listen to the audio lecture concerning certain types of disorders. The audio lecture begins with slide # 11. Four types of hearing disorders A.Conductive B.Sensorineural C.Central D.Conversion A. Conductive loss • Conductive losses occur in either the outer or middle ear. Generally these types of disorders interfere with the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. 1. Microtia This is the absence or malformation of the pinna. It can be either unilateral (one-sided) or bilateral (both sides). 2. Auditory canal atresia The auditory canal is either missing or extremely narrow. 3. Swimmer’s ear This is an infection of the auditory canal. Usually treated with antibiotic drops. 4. Otitis media AKA middle ear infection. Usually caused when the Eustachian tube doesn’t drain the middle ear well. For chronic cases of otitis media surgery may be required. Tubes are placed through the tympanic membrane until the Eustachian tube can drain properly. 5. Otosclerosis Deposits fuse the stapes to the cochlea. Can be corrected with surgery. Boneconduction hearing aids are sometimes used to bypass the ossicles. B. Sensorineural hearing loss The second category of hearing loss occurs in the inner ear and involves nerve damage. Sensorineural loss is permanent. Other symptoms may include tinnitus (ringing) or vertigo (dizziness). Causes of sensorineural hearing loss • • • • • • Genetics- passed down from a parent Auditory trauma (loud noise)- Ronald Reagan Head trauma- I. King Jordan Ototoxic drugs- Heather Whitestone High fever- Laurent Clerc and Helen Keller Viral diseases- Marlee Matlin Other causes of sensorineural loss • Rubella-virus that attacks the fetus in the womb. • Tumors-benign (non cancerous) or malignant (cancer) • Usher’s syndrome- genetic condition where child is born deaf and becomes blind • Meniere’s disease (hearing loss with vertigo)Coach Nave. More Sensorineural causes • Presbycusis- loss from due to age • Anoxia- “blue baby” lack of oxygen •Waardenburg syndromepigmentation issues •Auto-immune-Rush Limbaugh C. Central loss This type of hearing loss occurs when the brain doesn’t interpret sound correctly. May involve auditory hallucinations or problems with word recognition. D. Conversion disorder This type of loss is a psychological problem. The patient’s hearing ability is not physically impaired but the patient believes he is deaf.