* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types and Causes of Peripheral Hearing Loss
Telecommunications relay service wikipedia , lookup
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
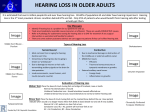
TYPES AND CAUSES OF PERIPHERAL HEARING LOSS TYPES OF HEARING LOSS Conductive – Cochlea and auditory neural systems OK, problem with sound transmission through the ear canal and/or middle ear. Sensorineural – Ear canal and middle ear OK, cochlea or auditory neural system not fully functioning. Mixed – A combination of conductive and sensorineural. COMMON CAUSES OF PERIPHERAL HEARING LOSS CONDUCTIVE Wax blockage in ear canal; middle ear infections (otitis media), glue ear (otitis media with effusion OME), perforated eardrum; no or malformed ear canal (atresia/stenosis of canal). Middle ear problems such as otitis media, partly due to Eustachian Tube dysfunction/abnormality, may often occur in children with Down’s syndrome and cleft palate. SENSORINEURAL Inherited causes (family history of hearing loss alone), in-utero infections (eg, CMV), hearing loss as part of a syndrome (eg, Pendred’s), neurodegenerative disorders (eg, neurofibromatosis), need for post natal or later intensive care with effects on the cochlea and auditory nerve (eg, prematurity and jaundice, meningitis). Some causes of hearing loss are associated with sudden loss (such as the presence of an enlarged vestibular aqueduct or occurrence of a perilymph fistula), or a gradual decline in hearing. MIXED Most commonly occurring due to an ear infection present in a child who normally has a sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL). Can be present permanently in children with hearing loss as part of CHARGE Association. Hearing thresholds become temporarily elevated due to the conductive overlay caused by a middle ear infection. For many young children with SNHL, the degree of hearing loss may fluctuate repeatedly as a result of ear infections. Further Reading; Northern JL and Downs MP “Hearing in Children” (5th ed). Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, MD. 2002