* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download aldehydesketonescarb..
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
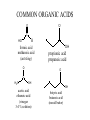
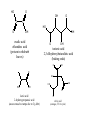
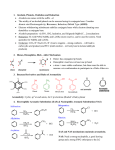
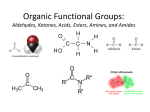
ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS ALDEHYDES AND KETONES • Aldehydes and ketones both contain the carbonyl group (C=O). • In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is attached to the end carbon. Example O H butanal • In ketones, the carbonyl group is attached to a carbon that is not on the end. Example O butanone Physical Properties • Like the hydroxyl group, the carbonyl group is polar but does not allow for hydrogen bonding. • Compare the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones to corrresponding alkanes and alcohols. NAMING ALDEHYDES 1. Take the longest chain containing the carbonyl group, remove the “e” and add “al” as the ending. 2. Any substituents are numbered using the lowest sum. Examples: H O O H C C C H H methanal formaldehyde H Cl O H ethanal acetaldehyde 2-chloro-4-ethyl-1-hexanal NAMING KETONES 1. Take the longest chain containing the carbonyl group, remove the “e” and add “one” as the ending. 2. If necessary indicate the position of the carbonyl using the lowest numerical coefficient. 3. Any substituents are numbered so the sum is the lowest. Examples O O O C C CH3 CH 3 CH 3 propanone acetone H 3C C O 2,3-butadione 3-Ethyl-2-pentanone CARBOXYLIC ACIDS • Contain the carboxyl functional group O C OH • Since the carboxyl group is polar, carboxylic acids contain dipole-dipole forces and are able to hydrogen bond. • How does the carboxyl group affect the physical properties of these compounds? • They are weak acids that will ionize slightly in water. • The H on the –OH is the acidic hydrogen and leaves when the acid is ionized. NAMING CARBOXYLIC ACIDS 1. Identify the longest chain containing the carboxyl group, remove the “e” and add “oic” acid. Examples O O C H methanoic acid HO C H 3C OH ethanoic acid COMMON ORGANIC ACIDS O O C H formic acid methanoic acid (ant sting) HO O OH propionic acid propanoic acid O C H 3C OH acetic acid ethanoic acid (vinegar 3-4 % solution) OH butyric acid butanoic acid (rancid butter) HO O C OH O C HO O OH oxalic acid ethandioc acid (poison in rhubarb leaves) OH O OH tartaric acid 2,3-dihydroxybutandioic acid (baking soda) O OH O HO HO OH OH HO O lactic acid 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (causes muscle cramps due to O2 debt) O citric acid (oranges, TCA cycle) HOMEWORK • • • • Pg 48 #1-5 Pg 51 #1-3 Pg 52 # 4 Pg 60 # 1, 2