* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download a forward look
Data Protection Act, 2012 wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
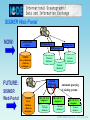
State-of-the-art tools and practices for marine data and information management – a forward look Lesley Rickards British Oceanographic Data Centre (BODC) Chair, International Oceanographic Data and Information Exchange (IODE) Committee MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 What are we aiming for? • Simple access to all types of marine data (and information) on an appropriate time scale • A virtual or distributed data centre • Data available on CD-ROM/DVD • End to end data management Where are we now? • A collection of separate centres with a wide variety of remits, skills and data • Made up of NODCs, RNODCs and WDCs • Sometimes work together in groups for individual projects MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Data Management and Communication System for the coastal module of GOOS MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Data management practices: • ‘Best’ rather than ‘state of the art’ • Compliance with IOC Data Exchange Policy • Proper collaborative efforts, building on existing standards and practices – not reinventing the wheel each time a new project comes along • Cooperation – partnership – collaboration MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Timely, efficient and open access to the best possible data, metadata & associated products • Metadata Standards • Discovery • Accompanying data (position, date/time, etc) • Data Documentation (qc history) • Quality Control • Automatic tests • ‘Scientific’, delayed-mode • Data dissemination • CD-ROM/DVD • On-line access • Long term stewardship of data MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Data management tools - METADATA • Metadata is all the descriptive information necessary to allow • • • • • • • users to find (discover), access, manipulate, process (request) and extract (recover) data, information and products Standards • • • ISO19115 Dublin Core MEDI, GCMD, EDMED, FGDC, ANZLIC, (EDIOS), (CSR), etc, etc. Mappings between standards available (cross-walks) ** Compliance with ISO19115 ** Various controlled vocabularies Links with XML (schemas/DTDs) MEDI Authoring Tool All have search tools • geospatial location, temporal information, keywords, controlled vocabulary items, “free text” MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 eXtensible Markup Language (XML) • XML is being widely used as a basis for both dynamic web page development and more generally as a data exchange mechanism • Data exchange aspects of XML include the ability to define flexible data structures that utilise the terminology of the subject area • Data to be exchanged is packaged in a form more intuitive to the user. • Extensive availability of free software for manipulation and transformation of the XML data stream • Allows developers to easily develop, populate, exchange and transform data streams. MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 MarineXML EU MarineXML “… demonstrate how XML technology can be used to develop a framework that improves the interoperability of data for the marine community and specifically in support of marine observing systems. The project will develop a prototype of an XML-based Marine Mark-up Language (MML).” ICES-IOC SGXML “… utilize or establish international standards to promote the seamless exchange of data from distributed data sources, by using a single parameter dictionary, well-defined and explicitly tagged metadata, and a common XML data structure, packaging all content and providing to the client datasets and software tools that are platform independent or web enabled” MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Quality Control • • (Real-time) automatic tests (but do not rely on them) Quality flags Data visualisation tools • to include comparison with other data collected in the same place or nearby, climatology; different ways of looking at the same data • Ocean Data View • Ncbrowse (for netCDF files) • EPIC (management, display and analysis of oceanographic and meteorological data) • Sea Level data • POL TASK2000 package + on-line tidal analysis • University of Hawaii JASL software • ESEAS – working towards new package • Document QC (e.g. audit trail, data history) • Use existing standards/guidelines where available • ICES data type guidelines, WOCE standards MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Ocean Data View (ODV) • Interactive exploration and graphical display of oceanographic and other geo-referenced profile, sequence or gridded data • Runs on Windows (9x/NT/2000/XP), Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X • Data collection and configuration files are platform independent • Interactive browse through large sets of station data MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Ocean Data View (ODV) • High-quality station-maps, general propertyproperty plots of one or more stations, scatter plots of selected stations, property sections along arbitrary cruise tracks and property distributions on general iso-surfaces • Display of original scalar and vector data by coloured dots, numerical data values or arrows • Fast gridding algorithms allow colour shading and contouring of gridded fields along sections and on iso-surfaces • Derived quantities calculated dynamically, displayed and analysed MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Development of distributed systems OPeNDAP (DODS) • Data servers for making local data accessible at remote locations • Free software for download Live Active Server (LAS) • Best for large, gridded environmental data sets • Dynamically generated graphics • Compare variables from distributed locations (using DODS) Thematic Real-time Environmental Data Distributed Services (THREDDS) • Access to large collection of real-time and archived data sets from a variety of data sources • Analysis and display software MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Other examples of distributed systems • • • • • • • US GLOBEC (US JGOFS) NOAA Coastal Directory Russian ESIMO NERC Data Grid IFREMER/SISMER Data Portal SeaSearch Common Data Index Distributed Generic Information Retrieval (DiGIR) – protocol for retrieving structured information from multiple heterogeneous databases • etc. MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 SISMER Web Portal NOW: SISMER WEB interface SISMER Server Database « Datasets catalogues » SISMER Server Database « Data sets catalogues » WEB interface i Thematic database i Thematic database 1 Thematic database 2 SISMER WEB portal FUTURE: SISMER Web Portal WEB interface 1 WEB interface 2 XML / ISO 19115 integrator 1 Thematic database 1 Automatic querying of existing systems XML / ISO 19115 integrator 2 Thematic database 2 XML / ISO 19115 integrator i Thematic database i MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 ARGO STATUS (Jan 27, 2004) 1037 Active Floats Target: 3000 floats by 2006 MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Argo Data Management • • • • • Data transmitted in real-time by satellite Transferred to data centres Messages decoded Automatic real-time quality control tests Data passed to global centres (GDACs) for dissemination • Delayed-mode quality control and calibration • Replacement version sent to GDACs • Regional centres for further quality control and products MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Location of Argo float profiles 01 – 27 Jan2004 No. of profiles: 2139 Data available for download: Profiles Trajectory Metadata Technical info From: • US GODAE • CORIOLIS MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS) • • • • Web-based provider Global geo-referenced information Accurately identified marine species Expert species level and habitat level databases • Variety of spatial query tools for visualizing relationships among species and their environment. • Strives to assess and integrate biological, physical, and chemical oceanographic data from multiple sources. • Users, including researchers, students, and environmental managers, gain a dynamic view of the multi-dimensional oceanic world Part of the Census of Marine Life (CoML) MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Gulf of Maine Biogeographic Information System (GMBIS) • Regional implementation for CoML • Partner with OBIS • Integrated into the Gulf of Maine Ocean Observing System (GoMOOS) • Designed to assimilate and integrate marine ecosystem and fisheries data, as well as natural-history information • Included is an advanced oceanographic geographic information system (GIS) MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Gulf of Maine Biogeographic Information System (GMBIS) • Access to biological, physical, chemical and geological data and information • Enhance understanding of biological patterns and their changes through time • “Aggregation server” providing access, rapid visualization and data download capabilities • Server will rely on a combination of archived (local access) data as well as dynamic access to remote data providers • Visualisation and other interactive software will be designed to help the user evaluate what data are available, combine data layers and download data MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 Gulf of Maine Biogeographic Information System (GMBIS) Access to: • historical data • taxonomic collections • geological base maps • modern remote sensing data • • • (buoys, CODAR, satellite) modelling products broad-scale survey data (e.g. living marine resources) other monitoring programs (e.g. COASTWATCH, Continuous Plankton Recorder) MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 GMBIS uses Environmental Analysis System (EASy) • Storage, dissemination, analysis, integration, and dynamic • • • display of spatially referenced series of oceanographic data PC-based Aids interfacing of multivariate oceanographic data Both data and model outputs can be imaged in time through diverse kinds of displays • Including vector, contour, and false-colour imagery • Vertical structures can be depicted along line transects or point• • sampling stations Time series can also be visualised Patterns in the spatial distribution or organisms to be visualized and compared to other spatial distributions • • Including both biological and other oceanographic variables Even when characterised by different scales of sampling and different degrees of resolution MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004 CONCLUSIONS • Use of modern IT techniques in a transparent manner to improve service to users (internet, web, distributed systems, XML, etc.) • Setting the standards (metadata, data quality control, data stewardship) • Working collaboratively whilst responding to national remit • Increasing data diversity (many different parameters being measured) • Developing systems to deliver (near) realtime data MAMA MD&IM Workshop - 28 January 2004