* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
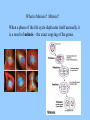
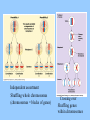
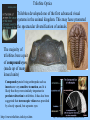
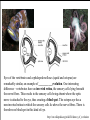
DIVERSITY OF LIFE Current species are classified into 3 Domains and/or 5-6 Kingdoms Kingdoms 1. Prokaryotes 2. Protists 3. Plants 4. Fungi 5. Animals Domains 1a. Archaebacteria 1b. Eubacteria Archaea Bacteria Eukarya Major groups are related All alive today All equally “evolved” But also represent different depths of branching, time since shared common ancestor Diversification also involved a series of innovations that added new forms of life Older modes persisted, possibly largely unchanged “advanced” vs. “primitive” Diverse species appeared then went extinct Current diversity is a slice of a continuing process 3-1 1. Prokaryotes (bacteria) single celled DNA, lack nucleus no organelles motility, incl. flagella closest to early life? Prokaryotes No sexual reproduction (meiosis) per se, but various modes of genetic exchange The real “tree” of life? Prokaryotes Much of biochemistry evolved in this group Both respiration and photosynthesis started here __________ (“self feeding”) – use CO2 as carbon source chemoautotroph – energy from chemicals (e.g. H2S) photoautotroph – energy from sun - photosynthesis ___________ (“other feeding”)– use organic molecules for carbon and energy anaerobic – respiration without O2 aerobic – respiration with O2 Prokaryotes Cyanobacteria (“blue-green algae”) are free living and photosynthetic contain chlorophyll a, ancestor of __________ Prokaryotes Some bacteria and cyanobacteria can also fix ________ In aquatic and terrestrial systems Even in some plant roots Also involved in other Nitrogen transformations (discussed later) Important as ________________ and Pathogens Often closely related species Prokaryotes Archaea – extreme environments – salty, high temperature Prokaryotes “Black smoker” (hydrothermal vent) http://www.ocean.udel.edu/kiosk/bsmoker.html Archaea – “ancient”, origin of life? Eukaryotes – Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals _________ and Endomembrane Organelles – mitochondria and chloroplasts Sexual reproduction (meiosis) Multicellularity (tissues, organs) Sociality 2. Protists – mostly small, single celled & multicellular - Eukaryotes – true nucleus (containing DNA) and endomembrane - Many are heterotrophs, aquatic – highly diverse - Various parasites (e.g., amoebas, malaria, helminths) Endosymbiotic origin of organelles Mitochondria - ___________ Chloroplast - ___________ Key biochemistry done by bacteria or their descendants Protists Includes true ALGAE – single and multicellular forms that are photosynthetic, and mainly ________(main “producers” in _________ systems) Unicellular algae - contain chloroplasts - chlorophyll a, b, & c Multicellular algae – “___________” - various differentiated structures, food conducting systems - not rooted - holdfast (nutrients from water) Complex life cycles & Sexual Reproduction Both diploid and haploid phases Sexual (meiosis) and asexual (mitosis) components Brown Alga (Laminaria) Green Alga (Ulva) – haploid & diploid equivalent What is Diploid? Haploid? Life cycles often switch between these two states. ___________ are haploid and fuse to form diploid zygotes. The zygote is “diploid” because it contains two complete sets of genes, one “haploid” set from each parent. This means two copies of genes of each gene type (“locus”). The two copies need not be identical (alternate “alleles” are common at each locus) What is Meiosis? Mitosis? When a phase of the life cycle duplicates itself asexually, it is a result of mitosis – the exact copying of the genes. Meiosis Sexual reproduction results from a much stranger process, where the diploid produces haploid cells by meiosis. The genes replicate once, then divide twice, creating (four) cells with only one set of genes each (haploid). Both haploids and diploids can replicate asexually (mitotically) too “Water Mold” (Oomycota) – mostly diploid Malaria (Plasmodium) mostly haploid Recombination – the real point? At least as important as the production of haploid cells, is the recombination of alleles in meiosis. Before making haploid cells, the dividing cells undergoing meiosis essentially “shuffle” the two parental genotypes, creating new genotypes that are mixtures of the parents. Often, the resulting recombinant haploid gametes are fused with gametes from other individuals (___________) to make the zygotes. This creates new genetic variation. The offspring are different from each other and from either parent. Independent assortment Shuffling whole chromosomes (chromosomes = blocks of genes) Crossing over Shuffling genes within chromosomes The paradox of sex - why meiosis? We have emphasized that evolution favors organisms (autocatalysts) that are good at transforming resources into more self – but here is a widespread mode of reproduction that seems designed to create offspring that are different from the parents, that are deliberately NOT self. Why? It is assumed there are good reasons, we just don’t know what they are for sure. But of course there have been many proposed explanations (hypotheses). This is another good example of the difficulty of verifying functional explanations. The Main Contenders 1. a. b. 2. a. b. 3. 4. 5. 3. Plants - primarily terrestrial, multicellular - evolved from ________________ - photosynthetic (chloroplasts), rooted in soil (nutrients) - extensive _____________ tissue - widespread, diverse Mosses and related species Ferns and others Includes tree ferns, once dominant Petro future here Coal Age – Carboniferous 290-360 MYBP How long will current oil supplies last? = _______ years http://www.eia.doe.gov/oiaf/ieo/oil.html Gymnosperms (conifers and others) Ginko Cycad Welwitschia Read Sacks Conifers Angiosperms – flowering plants Include most plants that dominate landscapes today 4. Fungi - eukaryotic, diverse ____________ - unicellular (yeast) and multicelled (mushrooms) - with bacteria, the most important _________ (nutrient releasers) in aquatic and terrestrial systems Read Sacks 4. Fungi - important __________, plant root fungal symbionts that enhance nutrient and water uptake - many fungi are plant & animal pathogens (mostly plants) 4. Fungi- include photosynthetic _______ – a symbiotic association of a fungus and a green algae. Fungus gets carbohydrates for photosynthesis of algae. Live on bare substrate (rock, bark), tolerate drying. Largest organism? Blue Whale Giant sequoia Aspen clone (Populus tremuloides) – one genotype Honey mushroom (Armillaria ostoyae) – one genotype 5. Animals - evolved from ________ - multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes - 35 “body plans”, most invertebrates, many marine - highly elaborated tissue and organ systems - herbivores, carnivores, parasites Sponges Jelly Anemone Chiton (Mollusk) Rotifer Scallop (Bivalve) Sea Slug (Gastropod) Sea Star Cephalopods: Nautilus & Octopus Leech (Annelid) Corals - _______________ - have a symbiotic association with “zooxanthellae” which are themselves a symbiosis of a dinoflagellate (protist) and photosynthetic cyanobacteria (prokaryote). Arthropods Trilobite (extinct) Barnacle Shrimp Horseshoe Crab Lobster Trilobite Optics Trilobites developed one of the first advanced visual systems in the animal kingdom. This may have promoted the spectacular diversification of animals. The majority of trilobites bore a pair of compound eyes (made up of many lensed units) Compound eyes in living arthropods such as insects are very sensitive to motion, and it is likely that they were similarly important in predator detection in trilobites. It has also been suggested that stereoscopic vision was provided by closely spaced, but separate eyes http://www.trilobites.info/eyes.htm http://ebiomedia.com/gall/eyes/octopus-insect.html Some Trilobites “lost” vision, as have many existing species crayfish Astaynax Yamamoto Y, Stock DW, Jeffery WR (2004) Hedgehog signalling controls eye degeneration in blind cavefish. Nature 431:844-847. The eyes of the Octopus and Squid (Cephalopods) are very similar to ours in structure and function, with lens and image forming retina. Read Williams Eyes of the vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs (squid and octopus) are remarkably similar, an example of ___________evolution. One interesting difference – vertebrates have an inverted retina, the sensory cells lying beneath the nerve fibers. This results in the sensory cells being absent where the optic nerve is attached to the eye, thus creating a blind spot. The octopus eye has a non-inverted retina in which the sensory cells lie above the nerve fibres. There is therefore no blind spot in this kind of eye. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evidence_of_evolution The Blind Spot The blind spot is the area on the retina without receptors that respond to light. Therefore an image that falls on this region will NOT be seen. It is in this region that the optic nerve exits the eye on its way to the brain. In the next two images, close your right eye. With your left eye, look at the numbers on the right side, starting with the number "1." You should be able to see the "sad face" (top image) or the gap in the blue line (bottom image) in your peripheral vision. Keep your head still, and with your left eye, look at the other numbers. The sad face should disappear when you get to "4" and reappear at about "7." Similarly the blue line will appear complete between "4" and "7.“ This is because your brain is "filling in" the missing information. Here is another image to show your blind spot. Close your right eye. With your left eye, look at the +. You should see the red dot in your peripheral vision. Keep looking at the + with your left eye. The red dot will move from the left to the right and disappear and reappear as the dot moves into and out of your blind spot. http://staff.washington.edu/chudler/chvision.html Arthropods – Spiders and Insects Vertebrates (Chordates) Animals - Sociality End Part 3 End