* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key Elements in Warfarin Patient Education
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Intravenous therapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
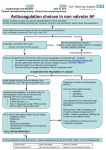
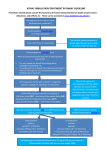
Key Patient Education Elements to Cover at Baseline – Warfarin Therapy1 Rationale for therapy How warfarin works to benefit the patient Dosing and administration (timing) Importance of adherence with dosing instructions and timely follow up What to do about missed doses Tablet identification/strength Identification of generic and brand name Visual recognition of drug/tablet strength Potential drug interaction/RX/OTC/herbals Avoidance of aspirin/NSAIDS Activities/fall prevention Dietary considerations – including alcohol use Importance of regular laboratory and clinic monitoring (INRs, CBC, FOB ect) Signs of over-anticoagulation Signs of disease recurrence What to do in case of bleeding Interruption in therapy due to surgery or dental work Keeping a log of INR results and medications Informing other healthcare professionals Women of child-bearing potential/safety in pregnancy Warfarin identification card/bracelet Emergency phone numbers and names Refill procedures Planning for trips Safe storage from children and pets. 1 Adapted from Ansell, Oertel, Wittkowsky Managing Oral Anticoagulation Therapy, Third Edition, 7:3 Major Points to Cover During Warfarin Patient Education2 General Patient Education Reason for Use: Avoid a thromboembolic event or prevent a recurrence of an event How it works What is a PT/INR? What does it mean? Duration of therapy: short term vs. long term. Frequency of visits and blood testing Importance of compliance with follow up visits Notify all health professionals that you are on warfarin Inform anticoagulation provider prior to any scheduled surgeries or dental procedures. Fall precautions, physical activity Side effects of warfarin: minor bleeding, skin rash, loss of hair Medications Name of drug: brand and generic How much to take: color, strength, number of tablets Procedure for obtaining refills – importance of not running out of medication Try to use only one pharmacy Potential for interaction with other medications Report all medication changes to the anticoagulation provider – including new and discontinued medications Verify safety of new medication with anticoagulation provider and determine if closer follow up is needed Adherence Encourage compliance with warfarin Therapy Take warfarin at the same time in the evening Keep track and report missed doses to anticoagulation provider. Do not double dose to make up for missed dose. Use a compliance method such as pill box, written dose instructions, medication calendars ect. Bleeding Signs and symptoms of bleeding; major and minor Bleeding severity: severe, sudden headache, melana, hematemesis ect Avoid risky behaviors What to do if bleeding occurs: call clinic vs go to ER Distinguish new problem from an old one (chronic nose bleeds, hemorrhoids) Disease Management Signs of disease recurrence: 2 Adapted from Ansell, Oertel, Wittkowsky Managing Oral Anticoagulation Therapy, Third Edition,7:4-7:5 PE: sudden shortness of breath and chest pain DVT: swelling, pain, heat, numbness in extremity CVA: numbness, tingling, sudden loss or change in speech, loss of consciousness, falls, sudden vertigo, facial droop, sudden weakness in a limb, visual changes or loss of sight in either eye Importance of knowing what is baseline and what is new. Diet Education on which foods are high in vitamin K Understanding of why vitamin K alters therapy Consistancy of high vitamin K containing foods Avoidance of crash diets Report problems with loss of appetite Other Factors Altering Therapy Importance of reporting to anticoagulation provider any changes: Acute illness: flu bacterial/viral illness Diarrhea Nausea/vomiting Fever Congestive heart failure Alcohol Use Do not encourage alcohol consumption Set a drinking limit per day Binge drinking: sudden increase in INR Long standing history of alcohol use/abuse: increase in liver enzymes may require higher doses in warfarin Increased risk of GI bleeding Increase risk of injury causing serious bleeding Pregnancy Do not become pregnant while on warfarin Use of birth control Explain risk of fetal harm Inform anticoagulation provider if you think you may be pregnant or are planning to get pregnant.