* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Failure Mode Effect Analysis on Anticoagulation Across the Continuum
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
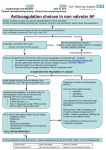
Failure Mode Effect Analysis on Anticoagulation Across the Continuum May 2, 2009 Anthony Nolosco, MS., R.Ph. Associate Director, Pharmacy Woodhull Hospital 1 RATIONALE FOR SELECTING THIS PROJECT National Patient Safety Goal (NPSG) 03:05:01 • Reduce the likelihood of patient harm associated with the use of anticoagulation therapy. 2 2 MULTIDISCIPLINARY TEAM • • • • • • • • • Medicine Nursing Pharmacy Laboratory Dietary Information Technology Quality Management Patient Safety Committee Chair Patient Safety Committee Officer 3 3 DO PLA N DO PLA N STUDY N Full implementation – (1/09) Joint Commission Pilot Testing in 8-100 and Anticoagulation Clinic- (10/08) Joint Commission •Adjustment of system for monitoring and follow up appts. in ambulatory and labs. ACT STUDY PLA ACT 3 mthStudy of the Rocess Jan - Apr •Work plan will be implemented that identifies adequate resources and a timeline for full implementation – (7/08) Joint Commission DO ACT STUDY Process/Timeline •Review Heparin, LMWH and Warfarin Protocol clinical guidelines (Draft Completed) •Five Implementation Strategies were identified to commence work on the high RPN’s from the FMEA – (4/08) •Responsibility for oversight, coordination and implementation of Requirement 03:05:01 was assigned to Dr. Gregorio Hidalgo – (4/08) Joint Commission •Additional safety measures implemented •Anticoagulation Clinic established •Multidisciplinary Team formed & FMEA Phase I (1/08) 4 5 Strategies for FMEA Process • Identified issues from the aspect of – – – – – – Item and Functions involved for each discipline Potential Failure Mode Potential Effect(s) of Failure Potential Cause(s) of Failure Current Controls Rate Potential causes of failure based on Severity, Occurrence, Detection and assigned a Risk Priority Number – Recommended Actions for improvement 5 CAUSE AND EFFECT Patient Staff Ignored alerts Compliance Barriers to learning Communication Specimen mislabeled Wrong pt. selected Wrong med ordered/dispensed/administered Wrong weight used Wrong dose, route, rate or diluent Weight not considered Pt.’s idiosyncratic response Allergy info not checked Contraindications not observed Drug interactions not evaluated Pt. does not report Signs and symptoms Indication for anticoagulation not present Pt. information not complete Order not sent Order not renewed Labs not checked/wrong lab checked Labs not ordered Adverse Outcomes Related to Anticoagulation Therapy Order sets incorrect Contraindications not checked Protocol not followed Duplicate drug therapy Infusion pump programmed incorrectly Equipment failure Drug not available Drug reference not available No monitoring occurs Safety Alerts not functioning Existing protocol is not easy To follow Lab info not available CPOE system not updated No redundancy built into the process Computer system down No safeguards built into the process Prescribing errors not identified/corrected Equipment Policies & Procedures 6 4 Analysis: High (Risk Priority Number) Potential Failure Mode Potential Effects of Failure Potential Causes of Failure Current Controls S O D RPN Recommended Actions Failure to keep follow-up appointment Incomplete management and treatment with anticoagulation Therapy Communication not received by provider Appointment provider cards provided in clinic. Staff tracks and followsup on “no shows”. 9 7 8 504 Post Discharge patient appointment in CPOE system to alert provider. Inappropriate Dispensing Inappropriate Anticoagulation Contraindication not evaluated and labs not checked Lab and pharmacy computer system interface 8 6 9 432 Institute an interactive criteria engine that will force “hard stop” based on certain values. Legend: S=Severity O=Occurrence D=Likelihood of Detection 7 6 Analysis: High (Risk Priority Number) Potential Failure Mode Potential Effects of Failure Condition and/or comorbidity undiagnosed Patient does not receive anticoagulant when indicated. Specimen misidentified. Sub-optimal patient education Potential harmful patient outcomes Failure to assess patient’s understanding of the importance of compliance Legend: Potential Causes of Failure S=Severity Current Controls S O D RPN Two patient identifiers used. 10 4 10 400 Label specimen vial immediately at patient bedside. Two specimens drawn for anticoagulation therapy. Stress the importance of medication compliance, Return demonstration required. 8 5 9 360 Educate/reeducate and monitor compliance. Engage patient/staff in the culture of safety. O=Occurrence Recommended Actions D=Likelihood of Detection 8 7 Analysis: High (Risk Priority Number) Potential Failure Mode Potential Effects of Failure Potential Causes of Failure Current Controls S O D Drug, food or herbal interactions not addressed Patient experiences Signs and Symptoms of interaction No electronic alerts/ did not check references Active patient list is reconciled with home med list. 7 4 8 Legend: S=Severity O=Occurrence RPN 224 Recommended Actions Institute electronic alerts related to Food/Herbal interactions with anticoagulants D=Likelihood of Detection 9 8 Recommended Actions Safety Measures Implemented In order to provide standardized care: 1. Interdisciplinary treatment guidelines/ protocols for anticoagulation were developed and implemented. 2. Policy and Procedure was developed and implemented 3. A comprehensive anticoagulation information package was developed for patients as well as providers. 4. CPOE Updated: a) Typical orders were built for heparin, warfarin and enoxaparin. b) A “hard stop” was designed as a forced function to obtain patient weight prior to prescribing anticoagulation therapy 10 9 Safety Measures Implemented (cont’d) Safety Measures Implemented 5. Enhancement of Pharmacy Services a) 2 clinical pharmacists were certified in Anticoagulation Therapy. b) A dedicated clinical pharmacist was assigned to the Emergency Department to monitor enoxaparin. c) A dedicated clinical pharmacist was assigned to the Anticoagulation Clinic. d) All pharmacists in OPD are trained to monitor and document INR values prior to dispensing warfarin. 11 10 Safety Measures Implemented (cont’d) Safety Measures Implemented 6. 7. 8. Drug Utilization Evaluation (DUE) done on warfarin. Cardiologist reviews every INR value > 5. Educational in-services and Town Hall trainings were held for Physicians, Nurses, Pharmacists and Allied Health Care Providers Competencies were developed and assessed 12 11 Performance Measures Per Protocol 1. Anticoagulation initiated based on diagnosis indication and laboratory values. – Baseline lab performed. – If patient is on warfarin, therapeutic INR achieved within 2 weeks. – Patient and family education/counseling on: a) Medications b) Diet – Compliance to follow-up visits in Anticoagulation Clinic. 13 12 Results of the Pilot Project [ October 1, 2008– November 17, 2008] 1) Number of cases analyzed: – Unfractionated Heparin – LMWH – Warfarin Total cases 2) Patient’s gender: -Male -Female 15 65 66 146 62 (42%) 84 (58%) 14 Results of the Pilot Project [ October 1, 2008– November 17, 2008] 3) Most common indication for initial anticoagulation: – Unfractionated heparin – LMWH – Warfarin DVT/PE ACS/Unstable Angina Atrial Fibrillation 4) Patient’s age: – <40 – 40-65 – >65 12 (8%) 65 (45%) 69 (47%) 15 Results of the Pilot Project [ October 1, 2008– November 17, 2008] 5) Condition(s) that potentially increases the risk of bleeding – Age >65 – Hypertension 70 (48%) 74 (51%) 16 Results of the Pilot Project [ October 1, 2008– November 17, 2008] 6) Adverse drug reactions to medication* – Unfractionated heparin – LMWH – Warfarin Total *Note: 0/15 (0%) 1/65 (1.5%) 5/66 (7.6%) 6/146 (4.0%) 1 patient INR (5-9) without bleeding 5 patients with epistaxis, therapeutic INR 17 JCA’s timeline • Followed Joint Commission timeline for implementation of NPSG 03:05:01 by January 1, 2009 18 13 Next Steps • Conducted a 3 month study (mid- January to mid-April) to identify the success of the processes implemented • Continue to train staff to reach 100% compliance • Data is being analyzed and will be presented to the appropriate committees 19 THANK YOU 20 14