* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1260_86892301f9dd00dd15644fada8f66d4d
Jurisprudence wikipedia , lookup
Alasdair MacIntyre wikipedia , lookup
Consequentialism wikipedia , lookup
Moral development wikipedia , lookup
Antinomianism wikipedia , lookup
Catholic views on God wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Moral disengagement wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg's stages of moral development wikipedia , lookup
Ethical intuitionism wikipedia , lookup
Morality throughout the Life Span wikipedia , lookup
Moral relativism wikipedia , lookup
Christian views on the Old Covenant wikipedia , lookup
Divine command theory wikipedia , lookup
School of Salamanca wikipedia , lookup
Morality and religion wikipedia , lookup
Euthyphro dilemma wikipedia , lookup
Moral responsibility wikipedia , lookup
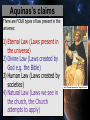
NML is An ethical theory based on a sense of duty / rules or obligations Learn this word! NML is The view that there are universal moral norms which apply in all situations and at all times to all people; the view that certain actions are always good or evil, regardless of the context or situation in which the act is performed. Learn this word! Aristotle ancient Greek Philosopher, (384-322 BC) (he was also the tutor to Alexander the Great!) There are Natural Moral Laws because: Everything has a purpose The natural world has a design Fulfilling that design is the greatest good or ‘superior aim’. Thomas Aquinas (1225-1274) Medieval Theologian Catholic Priest Claimed people could find a rational basis for Christian morality using ‘Natural Law’ Therefore people could discover what is morally good without the use of the Bible, Church, divine Revelation etc… Aquinas’s claims There are FOUR types of law present in the universe: 1) Eternal Law (Laws present in the universe) 2) Divine Law (Laws created by God e.g. the Bible) 3) Human Law (Laws created by societies) 4) Natural Law (Laws we see in the church, the Church attempts to apply) • God had established the world and had established an order and pattern which reflects His will. • Everything was created for a purpose. Human reason, reflecting on that purpose, can judge how to act. • An act does not depend upon its consequences for its moral justification (an act can be considered ‘morally good’ even if it leads to suffering!) • NML can be used by anyone (even if they are not religious) because it is based on REASON not REVELATION. Humans are tempted by the (that which can seem to be good or pleasurable in a personal way but does not always achieve anything good) to ignore the (That which is based upon God’s will and restores the right relationship with Him. This requires REASON) Original sin was the result of Adam and Eve being tempted away from the real good (God’s instructions) to follow that which seemed to be apparently good (eating the fruit of the tree of knowledge – disobeying God). Humans need to apply Natural Moral Law to moral dilemmas to see if they are acceptable or not. An act which is SEEN must also have a good motive. For example, helping an old lady across the road is a good exterior act. If it is done to show off, it is bad. If the motive is to genuinely help, out of love or concern, it is a good INTERIOR act. Is an action taken for the right reason? For example, a doctor who performs an abortion to save a woman’s life (good) also takes away the life of the foetus (Bad). BUT the intention of the doctor’s actions is to SAVE life. Aquinas used Aristotle’s four cardinal virtues Practising these is a way to live a life that flourishes. Life would be happy and . the person would be closer to happiness. The three ‘revealed’ virtues – based upon St. Paul’s First letter to the Corinthians. (rules of life according to Aquinas) Worship God Order society Reproduce Learn Defend the weak What would NML say about…. ABORTION CONTRACEPTION SEX OUTSIDE OF MARRIAGE Cohabitation HOMOSEXUAL SEX DIVORCE MARRIAGE FERTILITY TREATMENT SEX BEFORE MARRIAGE Do these moral dilemmas conflict with the 5 Primary Precepts? • Does the dilemma contradict any of the PRIMARY PRECEPTS? (Remember W.O.R.L.D!) • Apply (these are arguments for or against a dilemma based on the Primary Precepts and REASON. E.g. is something being done for the right reason; how does a moral question back up or go against the Primary Precepts) This decides whether a moral dilemma is right or wrong. Attractions of NML It provides CLEAR ANSWERS to an ethical dilemma (It tells it as it is) It is POSITIVE in what it promotes (e.g. it promotes life, religion, defending the weak etc) It is based upon a belief in God (which appeals to religious people) It provides a standard set of principles for all to live up to. It uses REASON and HUMAN EXPERIENCE Not everybody believes in God It is UNCOMPROMISING It does NOT attempt to provide happiness in all cases It assumes that everybody has the same moral values. It has too many rules It does not allow for other ethical theories to be followed