* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy terminology etc
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
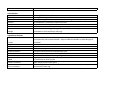
Bones
Physiology and structure of bones
Long bones
Short bones
Flat bones
irregular bones
sesamoid bones
Osteokinematics
Component movement
Arthrokinematics
Joint Types
Moveable
Non-moveable
calcified connective tissue consisting of osteocytes (bone cells) in a matrix of ground
substance and collagen fibers
longer than they are wide, include the clavicle, humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, fibula,
metacarpals, and phalanges
are found in the wrist and ankle and are shaped like cuboids
include ribs, sternum, scapulae, and bones in the vault of the skull
include bones of mixed shapes, such as bones of the skull, vertebra, and coxal bones
develop in certain tendons, and worik to reduce friction on the tendon, thus protecting
from excessive wear
voluntary movements (flexion, abduction, rotation, etc.)
accompany active motion, but are not voluntary (i.e. upward rotation of the scapula,
clavicular rotation that occurs with shoulder fllexion, rotation of the fibula that occurs with
ankle motion, etc.)
aka joint play between joint surfaces as well as distendibility ("give") in a joint capsule
(distraction, sliding, compression, rolling, spinning of joint surfaces)
Pivot
also known as Synovial/Diarthroidal
joined by fibrous connective tissue or caritlage
one bone has a ball, the other has a "cave" for the ball. Movement in all directions - Hip or
Shoulder
one convex surface meets a concave surface. Movement in one plane (flexion/extension) elbow or knee
a process when on bone fits into a ring structure on another, Rotational movement whre
the atlas meets the axis
Sliding/Gliding
both surfaces are essentially flat. Limited movement - Rib/vertebrae or scapula/clavicle
Condyloid
oval-shaped process of one bone fits into the elliptical cavity of antoher. Movement in two
places (flexion/extension & abduction/adduction) - Writs or Atlas/occiput
Ball and socket
Hinge
Saddle
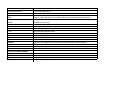
Axial Skeleton
7 cervical vertebrae
12 Toracic vertebrae
5 Lumbar vertebrae
Scacrum
Coccyx
Sternum
Ribcage
both surfaces are saddle shaped. Movemtn in two planes. - Thumb joint
C1 through C7 C1 = Atlas, C2 = Axis
T1 though T12 Larger than cerivcal vertebrae, articulate with ribs
L1 though L5 Largest vertebral bodies. Support the weight of the upper body
five fused bones. The posterior side of the pelvis
Three to five fused bones, aka tail bone
anterior area of the chest where rib cage comes together with collar bone
scapulae sit on the ribcage, moving about it, home of the diaphragm (that works with the
intercostals to assist repiration) and lungs
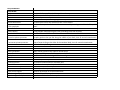
Appendiclar Skeleton
Clavicle
Scapula
Subscapular fossa
spine
Acromion process
Coracoid process
Glenoid cavity
Femur
Greater trochanter
Lesser trochanter
the collar bone - connects thte scapula to the sternum and forms tow joints
sternoclavicular and acromioclavicular - helps to hold the shoulder in place during arm
moveemtn
the anterior surface of the scapula
the prominent edge of the posterior surface of the scapula
joins with clavicle to form acromioclavicular joint
site of muscle attachment for shoulder joint
oval hole on lateral scapula forming the glenohumeral joint
longest/heaviest bone in body. The smooth rounded head articulates with acetabulum of
the coxal bone to form hip joint
upper lateral process of the femur
lower medial process of the femur. The distal end has medial and lateral condyles that
articulate with lower leg.
Patella
Patellofemoral joint
Tibiofemoral joint
fits into a groove between the 2 condyles of the femur.
patella meets with femur
femur meets with tibia
Tibia
Fibula
larger of 2 lower leg bones on the medial side, prosimal end articulates with femur.
thin, twisted bone on the lateral side, articulates with tibia but not femur and makes the
rounded bump of ankle.
Bones of the Foot - 26 bones
7 tarsal Bones
Talus
Calcaneu
5 Metatarsal bones
14 Pedal phalanges
form ankle
articulates with tibia and fibula
heel bone, distributes the weight of the body through the foot
#1 big toe, #5 pinky toe
make up toes - two in big toe, three in others
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
long boen of the upper arm, head is the ball of the shoulder's ball and socket
one of two main forearm bones which rotates around the ulna
the fixed bone of the two main forearm bones
Bones of the Hand 27 bones
8 Carpal bones
5 Metacarpal bones
14 Phalanges
form wrist
form the palm
make up the fingers - 2 in thum, 3 in others
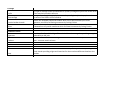
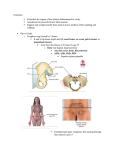
Bony Landmarks
Pelvic Girdle
Pelvis
ASIS
PSIS
Iliac Crest
Ischial tuberosities
Pubic symphysis
Spine
Spinal column
Vertebral bodies
composed of scarum, ilium, ischium, pubis and coccyx
anterior superior iliac spine
posterior superior iliac spine
the outward and upward flaring ridge of the hip
the lower back end of the coxal bones aka "the sit bones"
the lower front portion of the coxal bones connected by a cartlagenous disc aka "the pubic
bone"
strong flexible rod supporting the trunk, extending from skull to pelvis
the round flattened surfacw which interfaces with the intervertebral discs
Posterior spinous processes
the spiny portion that you feel along the middle of your back, sites of muscular attachment
Transverse spinous processes
Sacrum
Coccyx
Femur
Great Trocahnter
Lesser Trochanter
Condyles
Shoulder Girdle
Acromion
Coracoid process
Glenoid fossa
Acromioclavicular joint
Sternoclaviclar Joint
Spine of the scapula
Inferior angle of Scapula
Superior angle of scapula
flaps of bone sticking to the sides of the vertebral body, sites of muscular attachment
the back of the pelvic ring
the tail bone
upper lateral process of the superior end of femur
the lower medial process fo the superior end of the femur
medial and lateral articulating with the lower leg
point of scapula that joins with the calvicle
site of muscle attachment for shoulder joint
oval hole on the scapula that joins with the humerus
shoulder blade/collar bone joint
sternum/collar bone joint
posterior protrusion for muscle attachment
inferior border of the scapula
superior-medial border of the scapula
Cartilage
Synovial tendon sheaths
this type of cartilage unites synchondroses or pirmary cartilaginous joints such as the union
of the manubrium and the sternum
this type of cartilage joins symphysis or secondary cartilaginous joints by a plate usch as
the union of the bodies of the vertebrae
tubular sacs wrapped around the tendons which occur where tendons pass under
ligaments, retinacula, facilitating movement by limiting friction
Bursa
a flattened sac of synovial membrane which facilitates movement by limitng friction
Hyalin
Fibrocartilage
Connective Tissue
Ligaments
Tendons
Fascia
Superficial
Deep
dense bundles of parallel collagen fibers that hold two bones together, providng strength
and stability to the joint
the extension of a muscle into a long fibrous cord that blends into the periosteum of a
bone - connects muscle to bone.
loose connective tissue between the dermis and the deep fascia
sheet of fibous tissue that invests the muscles and helps to support them by serving as an
elastic sheath providing origins and insertions for the muscles and fibrous sheaths or the
tendons
Muscles
Muscles of Respiration
Levator costarum
the floor of the thorax, the priamy muscle of respiration which elevates lower rivs
increasing width of rib cage, elevates upper ribs increasing depth of rib cage.
muscles between adjacent ribs which contract during deep, forced respiration. Help
maintain the correct shape of the rib cage.
insert proximally on trasverse processes of lower five cervical vertebrae and distally on
upper surface of primay two ribs. Active during quiet respiration. Lift sternum and
primary two ribs in "pum handle" action causing upward/outward action of upper portion
of rib cage.
runs from thoracic vertebrae to the back of a rib one or two notches below. Assists in the
rotation of the spine and elevation of ribs
Transversus abdominus
pelvic floor
deepest of four abdominal muscles which reduces diameter of abdomen, increases
lordosis of the lumbar spine, supports the internal organs, and acts as stabilizer with sidebending. This muscle exhibits a pre-anticipatory contraction in health
the ischiococcygeus and the pubococcygeus aka the "kegel muscles".
Diaphragm
Intercostals
Scalenae
Muscles of the Spine
Spine Extensors
Erctor spinae
Quadratus lumborum
Mutifidi
Trapezius
Rhomboids
3 divisions (iliocostalis - lateral, longissimus - middle, spinalis - medial) running all the way
from head to bottom of rib cage producing extension, side-bend and rotation
runs from back of iliac crest to the bottom rib and the spianl processes along the way, side
bending of lumbar spine, elevation of pelvis
multisegmental deep spinal muscles, completing the "corset" begun by the transverses
abdominus.
runs from occiput through T12 to the superior scapula and Clavicle producing extesniosn,
side-bend, rotation of neck.
run from the back of C7 through T5 to the medial scapula, lateral shift of vertebrae, sidebend or rotation of neck
Spine Flexors
Rectus abdominus
External obliques
internal obliques
transversus abdominus
crest of pubic symphysis to xyphoid process and cartilage of ribs 5-7. Funciton includes
compression of abdomen and spinal flexion.
front of ribs 5 - 12 to lenea alba and inguinal ligament. Produces flexion, compression of
abdomen, unilateral side-bend, contralateral rotation.
iliac crest, inguinal ligament, thoracolumbar fascia to lower ribs. Produces compression of
abdomen, flexion, ipsilateral side-bend, rotation
deepest of our, compression of abdomen, increase lumbar lordosis, stabilizes spine and
pelvis before movement.
Muscles of the Neck
Subocciptal muscles
Longus colli
sternocleidomastoid
Muscles of the Shoulder
Serratus anterior
Trapezius
Pectoralis major and minor
Rhomboids
Deltoids
Levator scapulae
Latissimus dorsi
Coracobrachialls
Rotator cuff
Subscapularis
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
teres minor
muscles which attach to the external surface of the occipt anteriorly and posteriorly
deep 3-part muscle (longitudinal - C2-T3 to C4-C7, superior oblique - C1 to C3-C6, inferior
oblique - T1-T3 to C5-C7). Flexion of head, straighten cervical spine, side-bend, rotation
largest anterior neck muscle, runs bilaterally from sternum/clavicle to mastoid process.
Elevation of sternum, side-bend, roation or flexion of head.
scapular depression, abduction, upward rotation
scapular elevation, adduction, upward rotation. Diamond-shaped, from occipital bones and
primary 18 vertebrae to acromion process and spine of scapulae
shoulder flexion, adduction, internal rotation
scapular elevation, adduction, downward rotation
shoulder flexion and internal rotation (anterior). Extension and external rotation
(posterior), abduction (medial).
scapular elevation, downward rotation
shoulder extension, adduction, internal rotation
flexion and adduction
4 muscles that combine to pull the head of the humerus medially, stabilizing the joint
during movement
shoulder internal rotations
shoulder abduction
shoulder external rotations
shoulder extension, adduction, rotation
Muscles of the Arm
Biceps brachii
triceps brachii
Brachialis
Muscles of the Hand
Extensor carpi radialis
primary arm flexor
primary arm extensor
elbow flexor
extensor digitorum
extednds and adducts wrist
from anterior/medial ulna, splits into 4 tendons running through carpal tunnel to distal
phalnages of fingers, producing flexion of all finger joints
from elbow, splits into 4 tendons, each splitting into 3 bands, to the posterior second and
first knucles, producing extension of all finger joints and wrist
Pollicis
Flexor: from radius to thumb, bends thumb inward toward palm, Abductor: from ulna and
radius to lateral base of thumb, brings entire thumb toward palm, Extensor: from posterior
radius to first and second knuckles of thumb, causing thumb extension
Flexor digitorum
Muscles of the Hip
Hip Flexors
Psoas major
Iliacus
Tensor fascia latae
Iliotibial band
Sartorius
Rectus femoris
large, thick muscle deep in abdomen. From vertebral bodies and discs at T12-L5 to the
inguinal ligament and anterior part of hip jiont capsule.
primarily a hip flexor and stabilizer. Poor flexibility may increase lumbar lordosis, anterior
pelvic tilt and a hip-flexed posture.
from anterior iliac crest to the IT band, producing abduction, flexion and medial rotation of
thigh
from iliac crest to superolateral tibia and head of fibula
longest muscle of body running ASIS to superomedial tibia producing flexion, lateral
rotation, abduction of femur
2 joint muscle, crossing hip and knee
Hip Extensors
Gluteus maximus
Biceps femoris
Semimembranosis
Semitendonosis
thigh extension from 45 degrees down to 0 degrees of flexion.
part of hamstrings
part of hamstrings
part of hamstrings
Hip Rotators
Lateral rotators
Medial Rotators
Piriformis, Obturator internus, Obturator externus, Gemellus inferior, Gemellus superior,
Quadratus femoris
Gluteus minimus, Gluteus medius (anterior fibers), Tensor fascia latae, Gracilis
Hip Adductors
Adductor magnus
Adductor brevis
Adductor longus
Pectineus
Gracilis
largest and strongest of adductors
hip adduction
anterior to adductor brevis
from lateral pubis to pectineal line connecting lesser trochanter to linea aspera
long, thin superficial hip adductor
Hip Abductors
Gluteus medius
Gluteus minimus
Tensor fascia latae
Sartorius
Muscles of the lower leg
Knee extensors
Knee flexors
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Anterior Tibialis
Peroneus brevis
peroneus longus
Flexor hallucis longus
Flexor digitorum longus
Tibialis posterior
superior to gluteus maximus, abducts and medially rotates thigh. Secondary job is hip
flexion
anterior to gluteus medius, reinforces action of anterior portion of gluteus medius
(abduction and flexion of hip). Secondary job is hip flexion.
from anterior iliac crest to the IT badn, producing abduction, flexion and medial rotation of
thigh
flexes, laterally rotates and abducts hip
Quadriceps, vastus medialis, vastus intermedlu, vastus lateralis, rectus femoris
Semimenbranosis, semintendonosis, biceps femoris, popliteus, plantaris, gracillis
located on back of leg (calf), extend foot, inserts on heel by achilles tendon
located on back of leg (calf), extend foot, inserts on heel by achilles tendon
located on front of leg, flexes foot
located on lateral leg, everts foot
located on lateral leg, everts foot
from posterioinferior fibula under foot to last joint of thumb toe, pointing of foot/toes and
ankle inversions
from posteromedial tibia under foot to last joints of 4 toes, pointing of foot and toes
deepest of calf muscles producing plantar flexion and inversion, support of arches, works
with peroneus longus forming sling for mid-foot
Muscles of the Foot
Instrinsic
Flexion of the Arm
Extensin of the Arm
Abduction of the Arm
Adduction of the Arm
Lateral Rotation of the arm
Medial Roation of the Arm
provide support of arches during gait, and stability in standing
anterior deltoid, pectoralis major, coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, subscapularis
posterior deltoid, latissimus dorsi, teres major
deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, Long head of biceps
Latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major, Teres Major, Teres minor, Short head of biceps,
Coracobrachialis
Infraspinatus, teres minor, Posterior deltoid
Subscapularis, Latissimus dorsi, Pectoralis major, Teres Major, Anterior Deltoid
Lateral Rotation of the Hips
Psoas, Iliacus, Rectus femorsi, Tensor fascia Latae, Gluteus minimus and medium, Sartorius,
Pectineus, Gracilis
Gluteus maximus, Biceps femoris, Semimembranosus, Semitendinosus, Gluteus medius,
Adductor magnus
Gluteus medius, Gluteus minimus, Tensor fascia latae, Gluteus maximus, Piriformis,
Obturaors, Gemelli, Sartorius
Adductor magnus, Adductor longus, Adductor brevsi, Pectineus, Gracilis, Psoas, Iliacus,
Biceps femoris, Gluteus maximus
Gluteus Medius, Gluteus minimus, Tensor fascia latae
Gluteus maximus, Piriformis, Obturators, Gemelli, Quadratus femoris, Biceps femoris,
Sartorius
Flexion of the Knee
Extension of the Knee
Medial Rotation of the Knee
Lateral Rotation of the Knee
Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus, Biceps femoris, Popliteus, Gastrocnemius, Sartorius,
Gracilis
Rectus femoris, Vastus lateralis, Vastus intermedialis, Vastus medialis
Sartorius, Semitendinosus, Semimbranosus, Gracilis, Popliteus
Tensor fascia latae, Gluteus maximus, Biceps femoris
Flexion of the Hip
Extension of the Hip
Abduction of the Hip
Adduction of the Hip
Medial Rotation of the Hip
Planes of Motion
Sagittal Plane
Frontal/Coronal
Transverse
divides body into right and left - flexion and extension
divides body into front and back - abduction and adduction
Divides body into top and bottom - medial and lateral rotation
Anatomical Terms
Proximal
Distal
Anterior
Posterior
Medial
lateral
nearer center of body
farther from center of body
front
back
toward Midline
away from midline
Movement Terms
Adduction
Abduction
Flexion
extension
lateral flexion
medial rotation
lateral rotation
circumduction
Axial Elongation
Elevation
depression
protraction
retraction
superior rotation
interior rotation
pronation
supination
Plantar flexion
Dorsiflexion
Toward midline
away from midline
forward from anatomical position
backward from anatomical position
side-bending
spiraling inward toward center
spiraling outward from center
triplanar movement of the hip joint, usually indicates abnormal gait
grwong taller in the spine
toward the superior
toward the inferior
lateral movement
medial movement
upward
downward
flattening of the arch
peeling the medial foot away from the ground
pointing the foot
flexing the foot
Muscle Function Terms
Agonist
Antagonist
Synergetic
Muscle Contraction Terms
Isotonic
Isometric
Concentric
Eccentric
Origin
Insertion
produces a given movement
produces the opposite movement
muscles that work together to produce the same movement
force of contraction is constant - muscle shortens
force of contraciton changes - muscle length remains the same
an overall shortening of the muscle occurs as it generates tension and contracts against
resistance
an overall shortening of the muscle occurs as it generates tension and contracts against
resistance
typically one of two muscle attachment "sites" which is fixed in some way. This is often the
proxiaml bone.
the other "site" of the muscle attachment which moves as a result of muscle contraction.
This is oftent he distal bone.