* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document 3883624
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
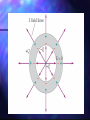
Coulomb’s Law The force between a charge q and another charge Q a distance r apart is given by qQ FE k 2 r Where k = 9 x 109 Nm2/C2 Action-at-a-distance Coulomb’s Law describes the force between two charges. What happens to the force on q if Q is suddenly moved? How quickly does q realize the change in force? What is it that q and Q interact with? Michael Faraday (1830s) Faraday proposed the concept of the “Electric Field” Charges create a “force field” surrounding themselves Charge q would interact directly with the field created by charge Q – it wouldn’t interact with Q directly Charge Q would likewise interact with the field created by q – not q directly If Q were suddenly moved, q would still react to the field that already exists in that region… The change would move at the speed of light (the change in the field actually IS light!) Mapping a mine-field Send disposable robots to different points in the field – if they blow up, put a marker at that spot BOOM! Mapping an E-field Place positive test charges at different points in the field – measure the force (magnitude and direction) acting on the charge at that point E-field around positive point charge E-field around positive charge points outward Spacing of lines represents strength of field Arrows point in the direction of the force that would act on a positive charge placed in the field E-field around negative point charge E-field around negative charge points inward Spacing of lines represents strength of field Arrows point in the direction of the force that would act on a positive charge placed in the field Definition of E-field F E q E-field is measured in N/C E-field around a point charge Combine E = F/q with Coulomb’s Law to get Q Ek 2 r E-field around a charge follows an inverse-square law Field around multiple charges Field around multiple charges is the vector sum of the field at each point around the charges The electric field obeys a superposition principle. The total field at any point is the vector sum of all fields at that point. E-field between parallel plates The E-field between two oppositely charged plates is uniform (constant) A charge placed anywhere between the plates will feel the same magnitude of force E-field inside a conductor When an E-field passes though a conductor, charges will move around until the E-field inside the conductor is zero (an equilibrium is established)