* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Solar System Inner Planets 14.3
Life on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planetary protection wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of Mars observation wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Interplanetary contamination wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
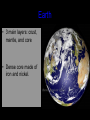
The Solar System Inner Planets 14.3 Components of our Solar System • • • • • • • • • Planets Star Comets Asteroids Satellites Space Trash Dark Matter Particles (Dust) Electromagnetic radiation (Photons) Planets • There are 8 planets: Gas Giants – – – – – – – – – Mercury Venus Terrestrial Planets Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus (YOOR uh nus) Neptune Pluto Inner Planets • Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are called the inner planets • The four inner planets are small and dense and have rocky surfaces • They are often called the terrestrial planets Earth • Atmosphere extends 100+km above the surface. • Atmosphere is 78% Nitrogen; 21% Oxygen • Earth is unique in our solar system in having liquid water on its surface • 70% of Earth’s surface is covered in water. Earth • 3 main layers: crust, mantle, and core • Dense core made of iron and nickel. Mercury • Closest to the sun • Similar in size to the Earth’s moon (smallest planet) Why is it difficult for astronomers to learn about Mercury? Mercury • Very little atmosphere, causing the environment to be extreme – Day time temp: 600 degrees Celsius (840o F) – Nighttime temp: -200 degrees Celsius (-300o F) • Made up mainly of dense metal irons and nickel. Venus • Similar in size to Earth (Earth’s twin) • Venus’s density and internal structure are similar to Earth’s • Takes about 7.5 Earth months to revolve around the sun • Takes 8 months to rotate on its axis • Rotates from east to west (retrograde rotation) Venus • Very thick atmosphere, never has a sunny day (clouds= sulfuric acid) • Pressure of Venus’ atmosphere is 90x greater than that of the Earth’s • Atmosphere= mostly CO2 • Surface temp: 600 degrees Celsius due to the greenhouse effect. HOT ENOUGH TO MELT LEAD!!!!!! Mars • Called the “red planet” due to it’s reddish hue. • Atmosphere: 95% CO2 and only has 1% of the pressure of Earth’s atmosphere. Mars • Temperatures range from -140oC to 20oC • Some water remains in the form of ice at its north pole. • Scientists think that water flowed on Mars’s surface in the past Mars • Has seasons just like Earth because of it’s tilt. • The largest volcano in our solar system is on Mars: Olympus Mons – it is three times the height of Everest and covers the state of Missouri • Mars has 2 small moons: Phobos (27 km diameter) and Deimos (15 km diameter) Homework • Read Section 3, Chapter 14 • Do the review questions on page 559