* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lipids (Typed notes of Ma`am Saba by Dr. M. Hassan)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
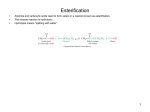
LIPIDS By Dr. M.Hassan Introduction Derived from a greek word lipos [fat] They are the substance of biomedical importance They are soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol and are sparingly soluble in H2O Chemically they are esters of different alcohols. Inaddition to alcohols and fatty acids , some of the lipids may contain phosphoric acid , nitrogenous base and carbohydrates Characteristics They are insoluble in H2O They are soluble in organic solvent Chemically they are esters glycerols with higher fatty acid CLASSIFICATION [According to Bloor] A SIMPLE Lipids These are the esters of fatty acids with various alcohols These consist of following subgroups 1.Fats [Neutral fats or Triacylglycerol] These are the esters of fatty acids with glycerol The term triacyl glycerol is being used now days rather than triglycerides 2.Waxes These are the esters of fatty acids with alcohol of higher molecular weight other than glycerol.These alcohols are monohydric B.Compound Lipids These are the esters of fatty acids containing group in addition alcohol and fatty acid These are subdivided as follows 1.Glycolipids [glyco sphingolipids] These contain sphingosine , fatty acid and a monosaccharide or oligosaccharide unit. They contain special alcohol sphingol or sphingosine , a nitrogenous base in addition to fatty acids. They does not contain phosphoric acid They are of two types A.cerebrosides B.gangliosides 2.Sulfo lipids Lipids containing sulphate group 3.Aminolipids They are also called as proteolipids They are attached with protein molecule In them the parent molecule is lipid 4.Lipoproteins In them lipids are the prosthetic group in protein The parrent is protein 5.Phospholipids These are lipids that contain a phosphoric acid , fatty acid and alcohol On the basis of type of alcohol phospholipids are of two types 1.If alcohol is glycerol>>>Glycerophospholipid 2.If alcohol is sphingosin>>>sphingophospholipid C..DERIVED LIPIDS These are obtained by the hydrolysis of simple and compound lipids These are A.[fatty acids]:may be saturated or unsaturated or cyclic B.[monoglycerides]: C:Diglyceride D:[Alcohols] straight chain alcohols obtained on hydrolysis of waxes Cholesterol and other steroids including vitamin D Vitamin A Carotenoids Glycerol D.Miscellaneous Vitamin E and Vitamin K Carotenoids Aliphatic hydrocarbon in liver fat and certain hydrocarbon in liver fat and certain hydrocarbons found in bees wax and plant wax Fatty Acids INTRODUCTION Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long chain hydrocarbons side groups They occur rarely freely in nature , but rather occur in estrified form as a major components of various lipids In higher plants and animals , predominant fatty acid residues those of the C16 and C18 species palmitic , oleic , linoleic and steric acids Fatty acids with 14 and 20 carbon atoms are uncommon Most fatty acids are even number of carbon atom because usually they are biosynthesized by catenation of C2 units Over half of the residues [fatty acids] of plants and animals lipids are unsaturated and often polyunsaturated Some important fatty acids are discussed below 1.Saturated Fatty Acids They have no double bond in their hydrocarbon chain Symbol of saturated fattyacids have two numbers 1 represent the # of carbon atoms 2 represent number of double bonds with oxygen Fatty acids with greater than 10 carbon atoms are given a systematic names e,g palmitic acid ,oleic acid etc. Palmitic and stearic acids are the two most abundant fatty acids in human being Lignoceric is component of cerebrosides 2.Unsaturated Fatty Acids They posses one or more double bonds in their hydrocarbon chain They are more reactive than saturated fatty acid Fatty acid containing one double bond is called as monoenoic/monounsaturated>>oleic and palmitoteic acid Fatty acids containing more than one double bond called as polyenoic/polyunsaturated >2 double bond dienoic >3 double bond trienoic Physical Properties Of Fatty Acids 1.Melting Point A. Saturated Fatty Acids The melting point of saturated F.acids increase with the increase in chain length Melting Point Of Unsaturated Fatty Acids It decrease with increase in unsaturation Because fatty acid double bond almost have cis configuration.This put a rigid 30 degree bend in the hydrocarbon chain of unsaturated fatty acids that interferes with their efficient packing to fill space E,g oleic acid---14 degree centigrade[1 double bond] Linoleic acid----5 degree centigrade[2 double bonds] Linolenic acid--- -10 degree centigrades[3 double bonds] Vegetable oils---room temp—liquid---unsaturated 2.On hydrogenation under pressure and in the presence of Ni catalyst these oils are soldified 2.Solubility Of Fatty acids 1.Anionic group provides hydrophillic property to the fatty acids making them H2O soluble. 2. At physiological pH carboxyl group (COOH) ionizes becoming COO-. 3.Hydrocarbon chain being hydrophobic tend to make fatty acid hydrophobic. 4.Chain length of hydrocarbons determine the solubility of fatty acids into H2O. 5.As the chain length increass it decreases the solubility of fatty acids into H2O. 6.E.g CH3COOH has only one methyl group i.e it has short hydrocarbon chain length so, it is completely miscible with H2O. 7.Unsaturation also increases the solubility. 8.E.g palmitoleic acid more soluble than palmitic acid. Isomerism in Fatty Acids (a). Saturated Fatty Acids.They does not show isomerism. They may be straight chain or branched. (b).Unsaturated Fatty Acids.Due to the presence of double bond they show isomerism.(i.e cis and trans configuration) 1.All naturally occuring unsaturated fatty acids of mammals are of cis configuration. Cis bond does not permit rotation around C=C and thus introduce rigid bend or kink. 2.Trans bond occur naturally and are also produced when unsaturated fatty acids are hydrogenated. NOTE Trans bonds have high ,melting point than cis bonds.