* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cycles of Matter
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
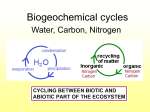
• Matter is constantly recycled through the biosphere in biogeochemical cycles – Hydro cycle moves water – Carbon cycle moves organic and inorganic carbon molecules – Nitrogen cycle moves organic and inorganic nitrogen molecules • Earth is a closed system which follows the Law of Conservation of Matter – Energy is the ONLY part of the cycle that enters and leaves the system of Earth Cycles of Matter • The Water (hydro) Cycle moves water between solid, liquid, and gaseous states. – Processes: • Evaporation… liquid water entering a gaseous state at the surface of a liquid • Transpiration… liquid water entering a gaseous state through openings (stomata) in leaves of plants • Condensation… formation of clouds from gaseous water vapor in the atmosphere • Precipitation… transformation of gaseous water to a solid or liquid that falls back to Earth • Runoff, percolation (seepage)…the movement of liquid water back to the groundwater system Water Cycle Nutrient Cycles Carbon • The carbon cycle is a biogeochemical cycle – Sources of carbon • Organic… most all organic molecules • Inorganic… calcium carbonate (CaCO3) deposits & CO2 – Processes: • Photosynthesis… fixes CO2 into organic molecules • Cellular respiration… uses organic molecules for energy producing CO2 • Decomposition… break down of complex carbon molecules into simpler forms – Burial & compression… leads to formation of coal and oil • Combustion & igneous activity… converts organic sources to atmospheric CO2 • Absorption… CO2 • that enters lakes and oceans may become concentrated into mineral deposits • Nutrient Cycles Nitrogen is an important element in DNA – Nitrogen & and every protein molecule in your body – Phosphorous is essential as it is also part of DNA and ATP Phosphorus – Both Nitrogen and phosphorous cycle between inorganic and organic sources in biogeochemical cycles – Sources of Nitrogen: • Atmospheric gas (N2), organic molecules, ammonia (NH3), nitrates (NO3-) , nitrites (NO2-) and ammonium (NH4+) – Processes: • Denitrification… the release of nitrogen gas from organic molecules through decomposition • Nitrogen fixation… the process of changing ammonia and nitrogen gas to a form useful to plants (nitrates and nitrites) – Through bacteria in the soil and on the roots of certain plants (legumes) • Assimilation… transformation of inorganic nitrogen in the soil into organic compounds • Primary production in an ecosystem reflects an ecosystems new dry biomass added per area per unit time (g/m2/yr) – Net primary production is limited by the nutrients available – Not based on biomass but on new material – Ecologist use to describe the carrying capacity of an ecosystem • The amount and type of organisms that can be supported Primary Production • Replacing limiting nutrients; – Fertilization • N, P, K – Crop rotation • Adds nutrients back to soil as different types of plants utilize nutrients in different quantities Limiting Nutrients • Process that creates abnormal algal and cyanobacteria blooms from sewage and fertilizer runoff – Can rob a lake ecosystem of resources due to over utilization of resources for primary production • Decreases aquatic species – Phosphorus is the limiting reactant in eutrophication • Water quality controls and using phosphate-free detergents are steps that are helping mediate this problem Eutrophication Drought • Santa Barbara has estimated that they will run out of fresh water by 2017! – The national average for individual water use is between 60 and 100 gallons per person per day. Goleta is at 66 gallons per person per day; Santa Barbara at 86; and Montecito at 290. – With California state water at its lowest allocation in history, the snowpack at 18 percent of its average and reservoirs at half their normal levels, shortages are around the corner, according to the scientists, but people continue to think of water as a limitless resource. – In California, agriculture accounts for 80 percent of water use, with the remaining 20 percent going to urban areas. – Recycling! • Right now, we’re recycling 10 to 15 percent of the water in the state — “showers to flowers” • Making our gardens look more like the climate that we live in!!!!