* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOSPHERE Chapter 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
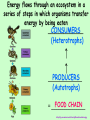
Energy Flow in the Biosphere, Chapter 3-1 & 3-2 http://www.geog.uni-heidelberg.de/~ttavk/weltkarten/globen/1997-1998-biosphere-Nasa.jpg REMEMBER CELL BIO INTEREST GRABBER- THINK BACK TO CHAPTER 7 ATOMS ________ MOLECULES __________ ORGANELLES ___________ IMAGE SOURCES: see last slide CELLS TISSUES ____________ ____________ Similar cells working together IMAGE SOURCES: see last slide ORGAN ORGANS SYSTEMS ___________ __________ Different tissues working together ORGANISM ___________ Different organs working together IMAGE SOURCES: see last slide ORGANISMS POPULATIONS COMMUNITY ___________________________________ SAME SPECIES LIVING TOGETHER IN AN AREA Ex: “herd” DIFFERENT POPULATIONS LIVING TOGETHER IN AN AREA BIOLOGY; Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall;2006 ECOSYSTEMS BIOMES BIOSPHERE _______________________ _____________ All the organisms that live in a place together with their NON-living environment Group of ecosystems that have same climate and similar communities The portion of the planet in which all life exists IMAGE SOURCES: see last slide Organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce SPECIES fertile offspring = _____________ http://suedafrika.net/bluegifs/twooryx.jpg http://environnement.ecoles.free.fr/Site-chevaux/images/etalon_quarter_horse_genuine_redskin.jpg http://www.caribbeanart.com/art/j-portrait-donkey.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mule EX: Horse X donkey = mule 64 chromosomes 62 chromosomes 63 chromosomes Horses and donkeys are different species. If you breed them, the result is a mule which can NOT have offspring! The scientific study of interactions of organisms with each other and with their environment = ECOLOGY ______________ The portion of the planet in which all BIOSPHERE life exists = _________________ (includes land, water, atmosphere) Extends from about 8 km above the Earth’s surface to 11 km below the ocean’s surface http://jaeger.earthsci.unimelb.edu.au/Images/Topographic/Whole_Earth/Earth_100.jpg WHAT SHAPES AN ECOSYSTEM? __________________ BIOTIC FACTORS All the living things an organism interacts with ABIOTIC FACTORS __________________ All the non-living things that affect an organism Ex: climate, temperature, sunlight soil, humidity, wind Images from: Pearson Education Inc; Publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall HABITAT __________________ = The area where an organism lives A rattlesnake lives in a desert in the American Southwest http://animals.timduru.org/dirlist/snake/animalwild089-RattleSnake-FaceCloseup.jpg http://www.rvstogophx.com/images/arizona_desert_sm.jpg NICHE _____________ = place it lives PLUS the abiotic biotic _____________ & ______________ interactions it has in that place NICHE includes: Where it lives PLUS . . . What it eats? What eats it? Where in the habitat it lives? In a tree, in a pond, underground Its actions… hibernating, migrating, etc When & how it reproduces? http://www.electricwomen.com/hunterspoint/images/21-street-sign-moreell.jpg HABITAT vs NICHE? Habitat is like an organism’s address ____________ Niche is like an OCCUPATION organism’s ______________ http://resmedicinae.sourceforge.net/logos/doctor.png http://www.michcampgrounds.com/yogibears/yogi-picnic-cartoon.jpg http://www.formaui.org/kamalii/critters.htm NO TWO SPECIES CAN SHARE THE SAME NICHE ! Competitive exclusion principle = ______________________________ BIOLOGY; Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall; 2006 ALL LIVING THINGS USE ENERGY The Earth is SOLAR POWERED! SUNLIGHT _____________ is the main source of energy for life on Earth. http://www.animation-station.com/smileys/index.php?page=17 ALL LIVING THINGS USE ENERGY AUTOTROPHS = PRODUCERS Can make their own food PHOTOSYNTHESIS Most autotrophs use _______________ to capture solar energy Main producers on land = green plants In water = algae BIOLOGY; MIller and Levine; Prentice Hall; 2006 Some autotrophs can make own food in the absence of light ____________________ They use energy stored in chemical bonds ________________ of INORGANIC MOLECULES ______________________to produce CHEMOSYNTHESIS carbohydrates = ___________________ Ex: Bacteria that live in HOSTILE places Like volcano vents, hot springs, marshes BIOLOGY; MIller and Levine; Prentice Hall; 2006 CONSUMERS HETEROTROPHS = ____________ Get energy from consuming other organisms http://www.epa.gov/region5/superfund/ecology/images/fishcartoon.gif HETEROTROPHS = CONSUMERS HERBIVORES = ________________ eat only plants CARNIVORES = ________________ eat only animals OMNIVORES ________________ = eat both plants & animals http://gallery.hd.org/_exhibits/natural-science/_more2003/_more09/elephant-eating-greenery-in-Addo-Park-Eastern-Cape-South-Africa-2-WL.jpg http://personal.ecu.edu/wuenschk/rabbit-wolf.gif http://www.rodsguide.com/bears/eating.jpg HETEROTROPHS = CONSUMERS DETRITIVORES = ________________ feed on plant & animal remains EX: mites, earthworms, snails, crabs DECOMPOSERS = ________________ break down and absorb organic matter EX: bacteria & fungi http://montereybayphotos.com/images/nature/2.jpg http://www.fwnp.com/bracket-fungi.htm Energy flows through an ecosystem in a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by being eaten ________________ CONSUMERS (Heterotrophs) ↑ ↑ PRODUCERS _________________ (Autotrophs) FOOD CHAIN = _________________ http://fig.cox.miami.edu/Faculty/Dana/foodchain.jpg Pearson Education Inc, Publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall In most ecosystems feeding relationships are more complex A ______________ links ALL the food chains in FOOD WEB an ecosystem together. Each step in a food chain or web = TROPHIC LEVEL _______________ ______________ PRODUCERS ALWAYS make up the ________ FIRST trophic level. http://home.insightbb.com/~g.mager/Pond/Ecosystem.htll Lower levels must be bigger to support the level above. 10% of Only about_____ the energy from each level is passed on. http://home.insightbb.com/~g.mager/Pond/Ecosystem.htll Some energy is used for life processes such as growth, development, movement, metabolism, transport, and reproduction. The rest is HEAT lost as ________ http://home.insightbb.com/~g.mager/Pond/Ecosystem.htll WHAT DO CELLS USE ENERGY FOR ? ACTIVE TRANSPORT Na+ - K + PUMP Endocytosis Exocytosis Animation from: http://www.lionden.com/cell_animations.htm See a movie Animation from: http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/cell-movement.html WHAT DO CELLS USE ENERGY FOR ? Movement Synthesis of biomolecules Meiosis: http://www.tokyo-med.ac.jp/genet/anm/ Cilia: http://www.sk.lung.ca/content.cfm?edit_realword=hwbreathe Replication: http://www.beyondbooks.com/lif71/4c.asp Transcription:http://www.wappingersschools.org/RCK/staff/teacherhp/johnson/visualvocab/mRNA.gif Translation: Growth and Development REPRODUCTION Family image from: http://babyhearing.org/Parenet2Parent/index.asp http://www.mark-ju.net/wildlife/images/monkey03.jpg http://www.dimijianimages.com/Aggression-defense-page4/vultures.jpg WAYS ORGANISMS INTERACT 4-2 http://www.epa.gov/region5/superfund/ecology/images/fishcartoon.gif http://www.uark.edu/depts/agripub/Publications/Agnews/mosquito.jpg Ways organisms interact ______________________ COMPETITION Between SAME and DIFFERENT kinds of organisms Compete with each other for available resources PREDATION __________________________ Between DIFFERENT kinds of organisms Hunt and kill other organisms to supply their energy needs COOPERATION __________________________ Between SAME kind of organisms Live together and help each other SYMBIOSIS __________________________ Between DIFFERENT kinds of organisms live in close association with another kind of organism WHAT IS A RESOURCE? Anything needed by an organism for life ____________________________________________ Examples: Nutrients, water, light, space ________________________ COMPETITION Organisms in an ecosystem have to compete with each other for available resources. FOOD http://www.knology.net/~sgoswald/Eating.jpg http://www.harcourtschool.com/glossary/science/images/gr3/community3.jpg COMPETITION Organisms in an ecosystem have to compete with each other for available resources: shelter http://www.dpiw.tas.gov.au/inter.nsf/Images/LBUN-5K538R/$File/fox_adultandcub.jpg http://www.gdccc.org/Records/EOY2004/NSEOY.htm COMPETITION Organisms in an ecosystem have to compete with each other for available resources mates http://www.wasatchcomputers.net/gallery/elk_fight.jpg http://www.biocrawler.com/w/images/thumb/3/34/200px-Peacock_courting_peahen.jpg COMPETITION Organisms in an ecosystem have to compete with each other for available resources: space/territory http://www.elise.com/weblog/photos/prairie-dogs.jpg Prairie dogs - 5 to 35 per acre Mountain lion- 1 male per 50-300 sq. mi http://www.rilanationalpark.org/gr.phtml?dir=../../pictures/in_text&img=/65_1180.jpg COMPETITION Organisms in an ecosystem have to compete with each other for available resources: LIGHT http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/chloroplasts.html http://www.csjbacau.ro/gallery/images/Beech%20Tree%20Forest%20in%20Slanic%20Moldova.jpg Ways organisms interact PREDATION ___________________ Between DIFFERENT kinds of organisms Hunt and kill other organisms to supply their energy needs http://www.epa.gov/region5/superfund/ecology/images/fishcartoon.gif PREDATION Organisms in an ecosystem that capture and eat other organisms to supply their energy needs http://personal.ecu.edu/wuenschk/rabbit-wolf.gif http://www.aphis.usda.gov/lpa/pubs/images/wspred_6.jpg INTERDEPENDENCE All living and non-living things in an ecosystem are interconnected and changing even one thing impacts the whole ecosystem. When one tugs at a single thing in nature, he finds it attached to the rest of the world. ~John Muir, naturalist, Sierra Club founder COMPETITION If resources are scarce, some organisms will starve and populations will decrease. If resources become more plentiful, populations will increase. Competition in nature often results in a winner and a loser . . . with the loser failing to survive! SHORT SUPPLY If a nutrient is in _____________ CYCLES SLOWLY OR __________________ it will LIMIT the growth of the population LIMITING FACTOR = _____________ During this drought, there was not enough food available and many kangaroos starved. http://www.wspa-international.org/exhibition/gallery/large_DeadKenyan%20droughtSPANA.jpg REMEMBER: EVERYTHING IS CONNECTED ! BIOLOGY; MIller and Levine; Prentice Hall; 2006 A decrease in the prey population means some predators will starve. Fewer predators mean prey population will increase. Increase in prey means more food for predators. Predator population will increase until there is not enough food . . . and the cycle repeats itself. LIMITING NUTRIENT The short supply of a limiting nutrient keeps the population in check. http://www.greenfacts.org/images/glossary/algae-bloom.jpg When an ecosystem receives a LARGE input of limiting nutrient (ie.,fertilizer runoff) the BLOOM population increases dramatically = ALGAL ___________ Ways organisms interact COOPERATION __________________ Between SAME kind of organisms Live together and help each other http://www.mark-ju.net/wildlife/images/monkey03.jpg COOPERATION Same species live together in groups EX: herds, packs, colonies, families, etc Share food & childcare responsibilities Groom each other Take care of sick http://www.kenyatravelideas.com/african-elephants.html http://www.sphoto.com/medium/meercats37.jpg http://people.uleth.ca/~d.rendall/groom4.jpg COOPERATION Same species live together in groups EX: herds, packs, colonies, families, etc Hunt in packs Provide protection http://www.knology.net/~sgoswald/Eating.jpg http://rosswarner.com/zebras1.jpg Ways organisms interact SYMBIOSIS __________________________ Between DIFFERENT kinds of organisms Live in close association with another kind of organism http://www.zahnersatz.com/english/library/symbiosis.jpg 3 KINDS of SYMBIOSIS ______________________ MUTUALISM Both organisms benefit COMMENSALISM ______________________ One organism benefits; Other is neither harmed nor helped _____________________ PARASITISM One organism benefits; Other is harmed in some way MUTUALISM “Good for me - Good for you” Birds eat parasites living on the hides of giraffes and rhinos while enjoying protection from predators. Groomed animals lose their pests. http://www.imbt.org/science.htm http://www.hugheshome.net/jon/africa02/images/rhino_bird_JPG.jpg MUTUALISM “Good for me - Good for you” Insects transfer pollen between plants as they gather nectar for food. http://www.providence.edu/bio/faculty/adams/LECTUREProvCollegeMutualism.html http://www.yksd.com/DistanceEdCourses/YKSDbiology/lessons/SecondQuarterLessons/Chapter5/5-5/images/3-way-mutualism.jpg MUTUALISM “Good for me - Good for you” Clown fish gets protection from enemies by hiding out in poisonous sea anemones Sea anemone gets scraps of leftover food dropped by fish http://www.zahnersatz.com/english/library/symbiosis.jpg COMMENSALISM “Good for me - Doesn’t bother you” http://www.geology.wmich.edu/gillespie/g322/Chapters/C16shark.gif Pilot fish receive scraps of food dropped by shark; Shark is neither harmed nor helped COMMENSALISM “Good for me - Doesn’t bother you” http://www.abyssal.com/meeks/images/hermit_crab.jpg Hermit crabs make homes in shells abandoned by snails; Snail is not harmed by crab PARASITISM “Good for me - Hurts you” http://www.geology.wmich.edu/gillespie/g322/Chapters/C16parasitism.whale.gif Barnacles are crustaceans that attach to the surface of whales and feed on their skin and fluids; Whale is harmed PARASITISM “Good for me - Hurts you” http://www.dogbreedinfo.com/guineafowltickphotos.htm Tick feeds on dog’s blood; Dog has discomfort, can get diseases/infection from bite PARASITISM “Good for me - Hurts you” Tapeworms absorb food by living inside host intestine; host is harmed http://www.biology.ucok.edu/AnimalBiology/Platyhelminthes/tapeworms.jpg SOUTH DAKOTA CORE SCIENCE STANDARDS LIFE SCIENCE: Indicator 3: Analyze how organisms are linked to one another and the environment. 9-12.L.3.1. Students are able to identify factors that can cause changes in stability of populations, communities, and ecosystems. • • Define populations, communities, ecosystems, niches and symbiotic relationships. Predict the results of biotic and abiotic interactions. Examples: Dormancy and migration Fluctuation in available resources (water, food, shelter) Biogeochemical cycles Energy flow Cooperation and competition in ecosystems SOUTH DAKOTA CORE SCIENCE STANDARDS LIFE SCIENCE: Indicator 3: Analyze how organisms are linked to one another and the environment. 9-12.L.3.1. Students are able to identify factors that can cause changes in stability of populations, communities, and ecosystems. • Define populations, communities, ecosystems, niches and symbiotic relationships. • Predict the results of biotic and abiotic interactions. Examples: Fluctuation in available resources (water, food, shelter) Energy flow Core High School Life/Earth Science Performance Descriptors High school students performing at the ADVANCED level: High school students performing at the PROFICIENT level: predict the effect of an interruption in a given cycles High school students performing at the BASIC level: given pictorial representations of the H20 and C cycles explain how elements and compounds move between living and nonliving systems describe one factor that may affect global climate predict how life systems respond to changes in the environment; explain how H20, N, C, and O cycle between living and non-living systems; describe how various factors may affect global climate; IMAGE BIBLIOGRAPHY http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/summer2004/lect02.htm Paint image by Riedell Paint image by Riedell http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookCHEM2.html#Organic%20molecules http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/evo101/images/dna_bases.gif http://bioweb.wku.edu/courses/BIOL115/Wyatt/Biochem/Carbos/Carb_poly.gif http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/golgi.html http://www.science.siu.edu/plant-biology/PLB117/JPEGs%20CD/0076.JPG http://classes.kumc.edu/som/bioc801/lectures/images/mem01-08.gif http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_nucleus.html http://www.biologyclass.net/mitochondria.jpe http://www.ncu.edu.tw/~ls/graph/faculty_pictures/whole_time/SLC/SLC_lab-1.jpg http://www.kufm.kagoshima-u.ac.jp/~anatomy2/BON/1016A03.jpg http://www.carolguze.com/text/102-19-tissuesorgansystems.shtml http://academic.pg.cc.md.us/~aimholtz/AandP/206_ONLINE/Immune/Innate_Images/cilia.jpg http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookAnimalTS.html http://www.agen.ufl.edu/~chyn/age2062/lect/lect_19/147b.gif http://www.proctitispages.force9.co.uk/ http://vilenski.org/science/safari/fungus/fungus.html http://www.harrythecat.com/graphics/ http://bestanimations.com http://www.inclusive.co.uk/downloads/images/pics2/tree.gif http://people.eku.edu/ritchisong/homepage.htm http://sps.k12.ar.us/massengale/animal%20dissections.htm