* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CFA #2 Study Guide Name: Class: ______ Kinetmatics Review 1. A
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
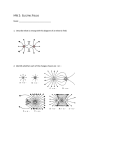
CFA #2 STUDY GUIDE NAME: ___________________________ CLASS: _____________ KINETMATICS REVIEW 1. A ball is in free fall. Its acceleration is: a. downward during both ascent and descent b. downward during ascent and upward during descent c. upward during ascent and downward during descent d. upward during both ascent and descent e. downward at all times except at the very top, when it is zero 2. The graph below shows the variation with time t of the displacement d of a body moving along a straight-line. Which graph best represents the variation with time t of the velocity v of this body? 3. The diagram represents the straight line motion of a car. Which of the following statements is true? a. b. c. d. e. The car accelerates, stops, and reverses The car accelerates at 6 m/s2 for the first 2 s The car is moving for a total time of 12 s The car decelerates at 12 m/s2 for the last 4 s The car returns to its starting point when t = 9 s 4. At the instant a ball is thrown horizontally with a large force, an identical ball is dropped from the same height Which ball hits the ground first? a. The horizontally thrown ball b. The dropped ball c. Neither -- they both hit the ground at the same time. 5. A ball is thrown into the air at some angle. At the very top of the ball's path, its velocity is: a. entirely vertical. b. entirely horizontal. c. both vertical and horizontal. d. There's not enough information given to determine. 6. A boy on the edge of a vertical cliff 20 m high throws a stone horizontally outwards with a speed of 20 m/s. It strikes the ground at what horizontal distance from the foot of the cliff? Use g = 10 m/s2 a. 10 m b. 40 m c. 50 m d. e. none of these 7. A giraffe, who stands 6.00 m tall, bites a branch off a tree to chew on the leaves, and he lets the branch fall to the ground. How long does it take the branch to hit the ground? 8. The Essex county sheriff is trying to determine the speed of a car that slid off a small bridge on a snowy New England night and landed in a snow pile 4.00 m below the level of the road. The tire tracks in the snow show that the car landed 12.0 m measured horizontally from the bridge. How fast was the car going when it left the road? FORCES REVIEW 1. The block shown moves with constant velocity on a horizontal surface. Two of the forces acting on the block are shown. A frictional force exerted by the surface is the only other horizontal force acting on the block. The frictional force is: a) 0 b) 2 N, leftward d) slightly more than 2 N, leftward c) 2 N, rightward e) slightly less than 2 N, leftward 2. Two forces, one with a magnitude of 3 N and the other with a magnitude of 5 N, are applied to an object. For which orientations of the forces shown in the diagrams is the magnitude of the acceleration of the object the least? 3. A car travels east at constant velocity. The net force on the car is: a) east b) west c) up d) down e) zero 4. An 1.5 N ball is thrown at an angle of 30 above the horizontal with an initial speed of 12 m/s. At its highest point, the net force on the ball is: a) b) c) 9.8 N, 30 below horizontal zero 9.8 N, up d) 9.8 N, down e) 1.5 N, down 5. A physics textbook is suspended on a spring scale in an elevator. Of the following, the scale shows the highest reading when the elevator: a) b) c) moves upward with increasing speed moves upward with decreasing speed remains stationary d) e) moves downward with increasing speed moves downward at constant speed 6. Two point masses m and M are separated by a distance d. If the separation d remains fixed and the masses are increased to the values 3m and 3M respectively, how does the gravitational force between them change? a) The force will be one-third as great. b) The force will be one-ninth as great. c) The force will be three times as great. d) The force will be nine times as great. e) It is impossible to determine without knowing the numerical values of m, M, and d. 7. Two satellites of different masses are in the same circular orbit about the earth. Which one of the following statements is true concerning the magnitude of the gravitational force that acts on each of them? a) The magnitude of the gravitational force is zero newtons for both satellites. b) The magnitude of the gravitational force is the same for both satellites, but not zero newtons. c) The magnitude of the gravitational force is zero newtons for one, but not for the other. d) The magnitude of the gravitational force depends on their masses. e) The magnitude of the gravitational force varies from point to point in their orbits. 8. A 2.0-N force acts horizontally on a 10-N block that is initially at rest on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is 0.50. I. What is the magnitude of the frictional force that acts on the block? a) 0 N b) 2 N c) 5 N d) 8 N e) 10 N II. Suppose that the block now moves across the surface with constant speed under the action of a horizontal 3.0-N force. Which statement concerning this situation is not true? a) The block is not accelerated. b) The net force on the block is zero newtons. c) The frictional force on the block has magnitude 3.0 N. d) The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.30. e) The direction of the total force that the surface exerts on the block is vertically upward. 9. Block A, with a mass of 10 kg, rests on a 30 incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20. The attached string is parallel to the incline and passes over a massless, frictionless pulley at the top. Block B, with a mass of 8.0 kg, is attached to the dangling end of the string. The acceleration of B is: 10.A 15-N net force is applied for 6.0 s to a 12-kg box initially at rest. What is the speed of the box at the end of the 6.0-s interval? 11. A 70 N block and an 35-N block are connected by a string as shown. If the pulley is massless and the surface is frictionless, the magnitude of the acceleration of the 70-N block is: 12. Two blocks weighing 250 N and 350 N respectively, are connected by a string that passes over a massless pulley as shown. The tension in the string is: 13. A 10-kg block is connected to a 40-kg block as shown in the figure. The surface on which the blocks slide is frictionless. A force of 50 N pulls the blocks to the right. a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the 40-kg block? b) What is the magnitude of the tension T in the rope that connects the two blocks? Work, Energy, Impulse, & Momentum Review 1. A variable force acts on an object. The force causes the object to move along a line parallel to the line of action of the force. The graph below shows how the force varies with distance. 3 force /N 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 distance /m The work done by the force is approximately A. 2.5 J B. 4.5 J C. 8.5 J D. 20.5 J 2. A ball of mass 2.0 kg falls vertically and hits the ground with speed 7.0 ms-1 as shown below. The ball leaves the ground with a vertical speed 3.0 ms-1 . The magnitude of the change in momentum of the ball is A. zero. B. 8.0 N s. C. 10 N s. D. 20 N s. 3. A 0.2 kg rubber ball is dropped from the window of a building. It strikes the sidewalk below at 30 m/s and rebounds up at 20 m/s. The magnitude of the impulse due to the collision with the sidewalk is: a. 10 N × s c. 2.0 N × s e. 9.8 N × s b. 6.0 N × s d. 19.6 N × s 4. An 81 kg football player moving 6.5 m/s tackles and collides with a stationary 140 kg football player. What speed will the football players have the moment after impact? a. 0 m/s b. 4.8 m/s c. 2.4 m/s d. 3.8 m/s 5. A 740 kg car traveling 19 m/s comes to a complete stop in 2.0 s. What is the force exerted on the car during this stop? a. 85 N b. 850 N c. 7000 N d. 9200 N 6. The momentum of a 225 g softball moving at 35 m/s is a. 7.9 kg m/s b. 3.5 N c. 5.0 m/s d. 2.1 kg m/s 7. The purpose of an airbag in an automobile is a. to prolong the time of impact for a given change in momentum thereby reducing the force of impact b. to deliver a greater force to the car occupant upon impact c. to shorten the time of impact d. to reduce the momentum of the vehicle 8. What is the velocity of car "B" after the collision? (Define motion to the right as being positive.) A. -1 m/s B. 3 m/s C. 5 m/s D. 8 m/s E. 0 m/s 9. A 2-kg object accelerates as a net external force is applied to it. During the 5-second interval that the force is applied, the object’s velocity changes from 3 m/s east to 7 m/s west. 5 seconds later: 3 m/s 7 m/s A student states: “The change in momentum of this object during these 5 seconds was 8 kg·m/s so the impulse applied to this object during these 5 seconds was 8/5 kg·m/s.” What, if anything, is wrong with this statement? If something is wrong, identify and explain how to correct all errors. If this statement is correct, explain why. 10. A 10-kg box, initially at rest, moves along a frictionless horizontal surface. A horizontal force to the right is applied to the box. The magnitude of the force changes as a function of time as shown. Force (Newtons) 3 2 1 Time (seconds) 2 4 6 8 10 A student calculates that the impulse applied by the force during the first 2 seconds is 4 N·s and that the impulse applied during the following 3 seconds is 6 N·s. What, if anything, is wrong with these calculations? If something is wrong, identify it and explain how to correct it. If these calculations are correct, explain why. 11. A 10-kg box, initially at rest, moves along a frictionless horizontal surface. A horizontal force to the right is applied to the box. The magnitude of the force changes as a function of time as shown. Force (Newtons) 3 2 1 Time (seconds) 2 4 6 8 10 Rank the impulse applied to the box by this force during each 2-second interval indicated below. A. 0 to 2 s B. 2 to 4 s Greatest C. 4 to 6 s D. 6 to 8 s E. 8 to 10 s 1 _______ 2 _______ 3 _______ 4 _______ 5 _______ Least OR, The impulse applied to the box during each of the intervals is the same but not zero. ___ OR, The impulse applied to the box during each of the intervals is zero. ___ OR, We cannot determine the ranking of the impulse applied to the box during the intervals. ___ 12. 13. A concrete block is pulled 7.0 m across a frictionless surface by means of a rope. The tension in the rope is 40 N; and the net work done on the block is 247 J. What angle does the rope make with the horizontal? 14. The graph shows the force component along the displacement as a function of the magnitude of the displacement. Determine the work done by the force during the interval from 2 to 10 m. 15. A bullet of mass 0.01kg is moving at 500ms-1 when it hits a wall. How much work is done by the wall on the bullet if the bullet penetrates 0·1m into the wall? 16. A parachutist with a mass of 50.0 kg jumps out of an airplane at an altitude of 1.00 103 m. After the parachute deploys, the parachutist lands with a velocity of 5.00 m/s. Using the work–kinetic energy theorem, find the energy that was lost to air resistance during this jump. (g = 9.81 m/s2.) 17. Two boxes are connected to each other as shown. The system is released from rest and the 1.00-kg box falls through a distance of 1.00 m. The surface of the table is frictionless. What is the kinetic energy of box B just before it reaches the floor? 18. An escalator is 30.0 meters long and slants at 30.0° relative to the horizontal. If it moves at 1.00 m/s, at what rate does it do work in lifting a 50.0 kg man from the bottom to the top of the escalator? 19. How much power is needed to lift a 75-kg student vertically upward at a constant speed of 0.33 m/s? 20. Frank, a San Francisco hot dog vender, has fallen asleep on the job. When an earthquake strikes, his 300-kg hot-dog cart rolls down Nob Hill and reaches point A at a speed of 8.00 m/s. How fast is the hot-dog cart going at point B when Frank finally wakes up and starts to run after it? 21. A bullet with a mass of 5.00 x 10–3 kg is loaded into a gun. The loaded gun has a mass of 0.52 kg. The bullet is fired, causing the empty gun to recoil at a speed of 2.1 m/s. What is the speed of the bullet? 22. A swimmer with a mass of 75 kg dives off a raft with a mass of 500 kg. If the swimmer’s speed is 4 m/s immediately after leaving the raft, what is the speed of the raft? 23. A clay ball with a mass of 0.35 kg strikes another 0.35 kg clay ball at rest, and the two balls stick together. The final velocity of the balls is 2.1 m/s north. What was the first ball’s initial velocity? 24. Car One is traveling due north and Car Two is traveling due east. After the collision shown, Car One travels due east. Which of the numbered arrows is the only one that can represent the final direction of Car Two?