* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Skeletal System Gross Anatomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
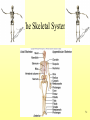
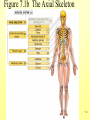
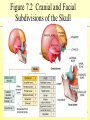
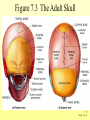
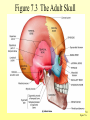
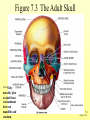
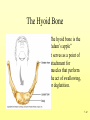
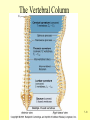
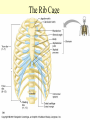
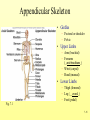
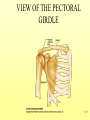
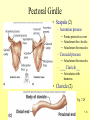
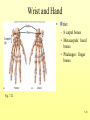
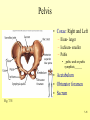
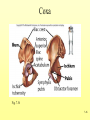
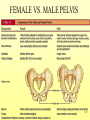
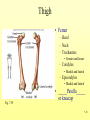
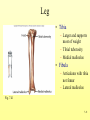
The Skeletal System 7-1 Figure 7.1b The Axial Skeleton 7-2 THE AXIAL SKELETON • The axial skeleton consists of 80 bones in three regions: – The skull – The vertebral column – The bony thorax • The axial skeleton supports the head and trunk and protects important organs. – Brain – Heart – Lungs 7-3 THE SKULL • The skull is the most complex skeletal structure consisting of 22 bones. – The cranium protects the brain – The facial bones: • • • • • Form the facial features Place for special sense organs Passages for air and food Secure the teeth Attachment sites for facial muscles • With the exception of the mandible, all skull bones are connected to each other thru sutures. 7-4 The skull • Consists of the cranium and the bones of the face – The cranium encloses cranial cavity – Facial bones surround and protect the entrances to the respiratory and digestive tracts • Superficial landmarks include the sutures – – – – Lambdoid Coronal Sagittal Squamous 7-5 Figure 7.2 Cranial and Facial Subdivisions of the Skull 7-6 Figure 7.3 The Adult Skull 7-7 Figure 7.3a, b Figure 7.3 The Adult Skull 7-8 Figure 7.3c Figure 7.3 The Adult Skull ****Only movable joint on skull bone is attachment between mandible and cranium. 7-9 Figure 7.3d Focus: The Individual Bones of the Skull Cranial Bones • one occipital bone – foramen magnum • two parietal bones • one frontal bone • two temporal bones – auditory ossicles • one sphenoid • one ethmoid – frontal sinuses 7-10 Infant Skull • Contains cartilaginous soft spots called fontanelles. • What function do fontanelles serve? 7-11 The Hyoid Bone • The hyoid bone is the “adam’s apple” • It serves as a point of attachment for muscles that perform the act of swallowing, or deglutition. 7-12 The Vertebral Column 7-13 The Rib Cage 7-14 Appendicular Skeleton • Girdles – Pectoral or shoulder – Pelvic • Upper Limbs – Arm (brachial) – Forearm (_antebrachium_) – Wrist (carpal) – Hand (manual) • Lower Limbs – Thigh (femoral) – Leg (__crural_) – Foot (pedal) Fig. 7.1 7-15 THE PECTORAL GIRDLE • The pectoral girdle is formed by the clavicle and the scapula. • Only the clavicle actually attaches to the thorax. • The scapula “floats” on the back of the ribs. • The humerus attaches loosely to the sockets formed by the scapula and clavicle. – This is good for freedom of movement. – This is not as good for stability. 7-16 VIEW OF THE PECTORAL GIRDLE 7-17 Pectoral Girdle • Scapula (2) – Acromion process • Forms protective cover • Attachment for clavicle • Attachment for muscles – Coracoid process • Attachment for muscles – ____Clavicle___ • Articulates with humerus • Clavicle (2) Fig. 7.29 7-18 THE UPPER LIMB • The upper limb consists of the: – Arm – Forearm – Hand • The upper limb contains 30 bones. 7-19 VIEW OF THE UPPER LIMB 7-20 Arm • Humerus – Head – Tubercles • Greater and lesser – – – – Intertubercular groove Capitulum Trochlea Epicondyles • Attachment of forearm muscles Fig. 7.30 7-21 Forearm • Radius – Thumb side – ___radial tuberosity_____ (biceps brachii muscle) • Ulna – – – – Little finger side Trochlear notch Olecranon process Radial notch Fig. 7.31 7-22 Wrist and Hand • Wrist – 8 carpal bones • Metacarpals: hand bones • Phalanges: finger bones Fig. 7.32 7-23 THE PELVIC GIRDLE • The pelvic girdle attaches the lower limbs to the axial skeleton. • The attachment of the pelvis to the sacrum is an incredibly stable and strong attachment, unlike the pectoral girdle. • The socket for the femur (acetabulum) is deep & holds the femur extremely well. – Less mobile ball & socket joint than the shoulder. • Each wing of the pelvic girdle is formed from a bone called the coxal bone. 7-24 Pelvis • Coxae: Right and Left – Ilium- larger – Ischium- smaller – Pubis • _pubic arch or pubic symphisis______ • Acetabulum • Obturator foramen • Sacrum Fig. 7.35 7-25 Coxa Fig. 7.36 7-26 FEMALE VS. MALE PELVIS 7-27 Female vs. Male Pelvic Girdle • What purpose do the differences between the female and male pelvic girdles serve? 7-28 THE LOWER LIMB • The bones of the lower limb must support the weight of the entire body, thus, these are the largest and heaviest of the bones. • The lower limb consists of: – The thigh – The leg – The foot • The lower limb is formed by 30 bones. – 1 patella – -1 tarsal vs carpal 7-29 Thigh • Femur – Head – Neck – Trochanters • Greater and lesser – Condyles • Medial and lateral – Epicondyles • Medial and lateral Fig. 7.39 • _____Patella_____ or kneecap 7-30 Leg • Tibia – Larger and supports most of weight – Tibial tuberosity – Medial malleolus • Fibula – Articulates with tibia not femur – Lateral malleolus Fig. 7.41 7-31 Foot • Tarsals (7) – _Talus___ (ankle bone) – _Calcaneus__ (heel) • Metatarsals: foot bones • Phalanges: toe bones Fig. 7.43 7-32 Points to Remember • Appendicular skeleton includes bones of upper and lower limbs and pectoral and pelvic girdles • Pectoral girdle and upper limb held in place largely by muscles • Pelvic girdle has strong articulation with sacrum to help support weight of body 7-33 Practice Question 1 Each of the following bones contributes to forming the orbit except the A. ethmoid bone. B. nasal bone. C. lacrimal bone. D. sphenoid bone. ****** E. frontal bone. 7-34 Practice Question 2 Each of the following bones is part of the pelvic girdle except the A. femur. ***** B. ischium. C. pubis. D. ilium. E. coxa. 7-35 Practice Question 3 In the true female pelvis, as compared to the true male pelvis, A. the bones are heavier and thicker with prominent markings. B. the distance between the anterior superior iliac spines is greater. ***** C. the ischium, ilium, and pubis remain unfused in adulthood. D. the angle formed at the junction of the pubic bones is narrow. E. the dimensions of the pelvic outlets are smaller. 7-36 Practice Question 4 The eleventh and twelfth ribs are called floating ribs because they lack A. a posterior attachment to thoracic vertebrae. B. an anterior attachment to lumbar vertebrae. C. an vertebral attachment anteriorly. D. an anterior attachment to the sternum. ***** E. an vertebral attachment posteriorly. 7-37 Practice Question 5 The bones of the forearm include the A. humerus. B. fibula. C. radius. ***** D. tibia. E. femur. 7-38 Practice Question 6 The medial bulge at your ankle is a projection from the A. femur. B. fibula. C. calcaneus. D. talus. E. tibia. ***** 7-39 Practice Question 7 Which of the following is not a part of the axial division of the skeletal system? A. Vertebral column B. Hyoid bone C. Skull D. Auditory ossicles E. Pectoral girdle ***** 7-40 Practice Question 8 At its distal end the femur articulates with the A. fibia B. tibia. ***** C. acetabulum. D. tibia and fibula. 7-41 Practice Question 9 A common injury in the winter are falls in which someone hits the back of their head on the ice. What bone is most likely to be involved in this type of fall? A. Zygomatic B. Frontal C. Temporal D. Occipital ***** 7-42 Practice Question 10 • As you proceed from the head down the vertebral column, the vertebrae become larger and heavier. True False ***** 7-43 Practice Question 11 • Damage to the temporal bone would most likely affect the sense of hearing. True False ***** 7-44 Practice Question 12 • Differences in the skeleton of males and females can best be seen in the characteristics of the pelvis. True False ***** 7-45 Practice Question 13 • Ribs that have no connection to the sternum are called the false ribs. True False ***** 7-46 Practice Question 14 • The axial skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the girdles. True False ***** 7-47 Practice Question 15 • The bones of the forearm are also called antebrachium. True False ***** 7-48 Practice Question 16 • The sacrum is composed of 5 fused vertebrae. True False ***** 7-49 Practice Question 17 • At its proximal end the humerus articulates with the ulna and radius. True False ***** 7-50 Practice Question 18 • An injury to the lateral side of your ankle would involve the tibia. True False ***** 7-51 Practice Question 19 The clavicle is part of the axial skeleton. True False ***** 7-52