* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transposition Complexes
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
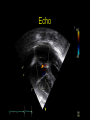
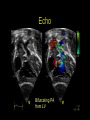
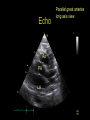
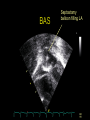
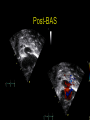
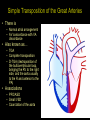
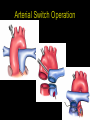
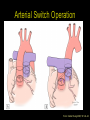
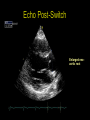
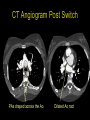
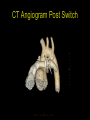
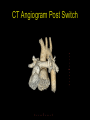
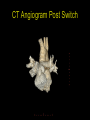
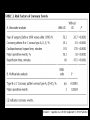
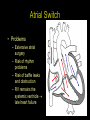
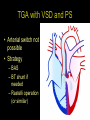
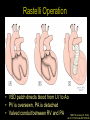
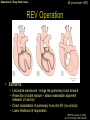
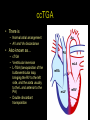
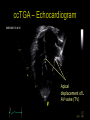
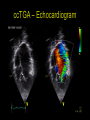
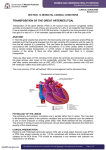
“Everything you need to know about transposition” Paediatric Cardiology for Paediatricians Birmingham Sept 2010 Dr Dirk G Wilson Consultant Paediatric Cardiologist University Hospital of Wales Remit “Simple” transposition of the great arteries (TGA) Transposition of the great arteries with ventricular septal defect and pulmonary stenosis (TGA/VSD/PS) Congenitally-corrected transposition of the great arteries (ccTGA) • Natural history • Operative approach • Long-term outcomes and surveillance Sequential Segmental Analysis Systemic veins Pulmonary veins Atrial arrangement Atrio-ventricular connection Ventricular arrangement Ventriculo-arterial connection Arterial arrangement Terminology • Connections may be – Concordant • The expected, appropriate connection – e.g. the morphologic LA connects to the morphologic LV – e.g. the morphologic LV connects to the aorta – Discordant • The connection is inappropriate – e.g. the morphologic LA connects to the morphologic RV – e.g. the morphologic LV connects to the PA So… • Atrial situs solitus, A-V concordance, V-A discordance Simple TGA • Atrial situs solitus, A-V discordance, V-A discordance Congenitally-corrected TGA (ccTGA) Simple Transposition of the Great Arteries Case • 41+1/40 • Cyanosis from birth – no response to oxygen • Taken to local NICU (Swansea) – Intubated – Ventilated Case • Found to be hypoxic, hypotensive and acidotic • Treated with – Fluids – Bicarbonate – Inotropes (dopamine, dobutamine, adrenaline) Case • Local echo performed • Commenced on PGE • Saturations remained low despite escalating doses of PGE (up to 160 ng/kg/min) Echo Echo Bifurcating PA from LV Echo Ao PA LA Parallel great arteries long axis view Echo Ao PA Ao anterior and to R of PA on short axis view PDA flow Echo Hmm • What is your assessment? – What is the underlying diagnosis – Why is the baby so compromised? – What is exacerbating the situation • What needs to be done? BAS Septostomy balloon filling LA Post-BAS Simple Transposition of the Great Arteries • There is – Normal atrial arrangement – AV concordance with VA discordance • Also known as… – TGA – Complete transposition – D-TGA (dextroposition of the bulboventricular loop, bringing the RV to the right side, and the aorta usually to the R and anterior to the PA) • Associations – PFO/ASD – Small VSD – Coarctation of the aorta TGA • Natural history – Average life expectancy for a newborn with transposition is 0.65 years – Survival • At 1 year ~10% • Dependent on adequate mixing between the two circulations – Atrial – Ventricular – Arterial TGA – Modern Management • Prostaglandin E administration • Balloon atrial septostomy • Arterial switch operation – Described by Jatene (1975) – Widely practised in most UK centres from the early 1990s • Survivors now entering ACHD services Arterial Switch Operation Arterial Switch Operation From: Cardiol Young 2008; 18:124–34 ASO - Survival • 30 day survival = 99.2% • 1 year survival = 96.9% • Complications – RV outflow tract distortion – Coronary artery stenosis or occlusion – Reintervention for • • • • Branch PA stenosis Aortic root enlargement (“neo-aortic dilatation”) Aortic regurgitation Coronary complications CCAD.org Echo Post-Switch Enlarged neoaortic root CT Angiogram Post Switch PAs draped across the Ao Dilated Ao root CT Angiogram Post Switch CT Angiogram Post Switch CT Angiogram Post Switch Post Switch – Clinic Assessment • History – – – – Exercise performance Chest pain Palpitation Syncope • Examination – Expect ESM ULSE referred to back – Listen for AR murmur Post Switch – Clinic Assessment • ECG • Echo – – – – – Function Regional wall motion abnormalities AR Branch PAs TR velocity (surrogate for branch PS) • Exercise test – Before high school sports participation – To investigate symptoms Post Switch – Clinic Assessment • Consider need for – MRI or CT angiogram – Myocardial perfusion scan – Coronary angiography • 324 patients undergoing coronary angiography post ASO • ~7% had coronary obstruction (>50% of lumen) Circulation. 2003;108:II-186 In Practice • Investigate coronaries if – Exertional chest pain – Unexplained LV dysfunction • Encourage “heart healthy” lifestyle in all patients Simple TGA – Historical Management • Atrial switch procedure – Senning operation (1958) – Mustard operation (1963) • • • • Systemic venous blood baffled to MV Pulmonary venous blood baffled to TV Senning – autologous material Mustard – Dacron baffles Atrial Switch • Problems – Extensive atrial surgery – Risk of rhythm problems – Risk of baffle leaks and obstruction – RV remains the systemic ventricle late heart failure Atrial Switch • Only a small number of these patients are in the paediatric age group • Adult congenital clinics will have to deal with this legacy TGA with VSD and PS TGA with VSD and PS • Arterial switch not possible • Strategy – BAS – BT shunt if needed – Rastelli operation (or similar) Rastelli Operation • VSD patch directs blood from LV to Ao • PV is oversewn, PA is detached • Valved conduit between RV and PA MMCTS (January 23, 2009). doi:10.1510/mmcts.2007.003046 Rastelli Operation • Advantage: LV is the systemic ventricle • Problems – Conduit degeneration and stenosis – Risk of atrial and ventricular arryhthmias – Risk of sudden death, especially with conduit degeneration Réparation à l'Etage Ventriculaire 25 yr survival = 80% REV Operation • Elements – LeCompte manoeuvre - brings the pulmonary trunk forward – Resection of outlet septum – allows reasonable alignment between LV and Ao – Direct implantation of pulmonary trunk into RV (no conduit) – Lower likelihood of reoperation MMCTS (January 23, 2009). doi:10.1510/mmcts.2007.003046 TGA with VSD and PS • OPD Surveillance – – – – – – Exercise capacity Palpitations ECG (QRS duration) RV pressure, size and function RVOT status (obstruction, PR) Timing of conduit replacement Congenitally Corrected Transposition of the Great Arteries CCTGA • Rare - <1% of CHD • Heterogeneous population – Clinical features are variable – May present at any age • Fetus • Child • Adult ccTGA • There is – Normal atrial arrangement – AV and VA discordance Ao • Also known as… – cTGA – Ventricular inversion – L-TGA (laevoposition of the bulboventricular loop, bringing the RV to the left side, and the aorta usually to the L and anterior to the PA) – Double discordant transposition PA mLA mRA mLV mRV ccTGA • Associations – – – – Dextrocardia VSD (70%) – usually perimembranous Pulmonary stenosis (40%) – often subvalvar Tricuspid (systemic) valve abnormalities (90%) • Significant leak in up to 90% of patients • Valve may be “Ebstein-like” with displacement towards the cardiac apex – Rhythm • AV node + His bundles displaced – course is elongated • Dual AV nodes may be present • Risk of heart block 1-2% per year (+ increased risk with surgery) ccTGA - Variants ccTGA – Presentation • Murmur ± cyanosis – due to associated lesions • CCF – due to – VSD – Systemic ventricular failure • Heart block • Incidental finding • NB – may present from fetus to mature adult ccTGA – ECG • • • • R&L bundles are inverted along with ventricles Septal activation occurs R to L Q waves in R precordial leads, but not in V5/V6 Heart block may be present ccTGA – Echocardiogram Apical displacement of L AV valve (TV) ccTGA – Echocardiogram ccTGA – Echocardiogram Parallel great arteries ccTGA – Clinical Challenges • Systemic ventricular failure • Systemic AV valve regurgitation (SAVVR) • Heart block ccTGA – Heart Failure • “Simple” ccTGA – 1/3 have CCF by the 5th decade of life • “Complex ccTGA (associated lesions) – 2/3 have with CCF by 5th decade despite medical and surgical interventions ccTGA – Heart Failure • Factors – RV performing systemic workload – RV coronary supply – attenuated coronary reserve • Effect of volume load (shunt, AV valve leak) – Pacing ccTGA – Heart Failure • Treatment – ACE inhibitor – -blockers – use with caution (heart block) – Surgery to improve SAVVR ccTGA – SAVVR • Contributing factors – Tricuspid valve bears the systemic load – Altered RV geometry (affecting leaflet apposition) – Ebstein-like malformation ccTGA – SAVVR • Treatment – – – – ACE inhibitor -blockers – use with caution (heart block) Surgery Repair or replacement of SAVV • Intervention is needed before significant SV dysfunction sets in • High risk of heart block ccTGA – Heart Block • Risk is 1-2% per year • Pacing may be required • Risk of worsening SV function (?due to shift of septum, ??V-V interaction, →effect on TV) ccTGA – Surgical Strategy • ccTGA with no associated lesions – Consider double switch in younger patients – requires “training” of LV with PA band – needs to be a clear indication for intervention • ccTGA with VSD – Consider VSD closure – Consider double switch • ccTGA with VSD and PS – Consider Rastelli–Senning operation ccTGA – Surgical Intervention • Double Switch – Paris Group (Planché) – 20 patients – Actuarial survival at 10 years was 100% – Freedom from reoperation at 5 and 10 years were 93% and 77.4%, respectively EJCTS 2009;35:879-884 – All patients class I or II Transposition Complexes • Summary – Varied anatomical spectrum – Varied management – Simple TGA • Modern management should produce good outcomes • Concern about atrial switch outcomes – TGA with VSD and PS • “Like a bad ToF with a conduit” – ccTGA • “Like MR with a bad ventricle” and a high risk of heart block