* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download February 16, 2017 Cardiovascular System
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
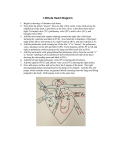
February 16, 2017 ▶ ▶ Objective: ◦ Identify the structures within the heart ◦ Trace the movement of blood through the heart Journal: ◦ Do you know any parts of the heart? If so, which ones? Cardiovascular System Major Components ▶ ▶ ▶ Heart: pumps blood throughout the system Blood: connective tissue made of plasma, cells, and other substances Blood Vessels: vessels that carry blood around the body ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Heart Overview ▶ ▶ ▶ Size of your fist Surrounded by protective layers Slightly left of the center of your chest and above your diaphragm Heart Protective Layers = Pericardium ▶ ▶ ▶ Fibrous Pericardium –outer layer Parietal Pericardium – middle layer Visceral Pericardium – inner protective layer that attaches directly to the heart surface Three Layers of the Heart Wall: ▶ Epicardium – outer layer ◦ Made up of visceral pericardium ▶ Myocardium – middle layer ◦ Made up of cardiac muscle ▶ Endocardium – inner layer ◦ Epithelium lining of the heart Heart Structure ▶ Base ◦ Top of the heart ◦ Tilted towards the head ▶ Apex ◦ Bottom of the heart ◦ Points away from the head Chambers of the Heart ▶ ▶ ▶ ▶ Right Atrium: Collects blood returning to the heart from circulating around the body Left Atrium: Collects blood returning from the pulmonary circuit Right Ventricle: Pumps blood through the pulmonary circuit Left Ventricle: Pumps blood throughout the rest of the body Valves ▶ Tricuspid Valve - aka AV valve ◦ Between right atrium and right ventricle ▶ Bicuspid Valve – aka mitral valve ◦ Between left atrium and left ventricle Separation of the Chambers ▶ Septum: walls of the heart that separate the chambers ◦ Interatrial Septum: separates the two atria ◦ Interventricular Septum: separates the two ventricles Vessels Around the Heart ▶ ▶ ▶ ▶ ▶ Superior vena cava: brings blood back to the heart from above the heart Inferior vena cava: brings blood back to the heart from below the heart Aorta: artery that blood travels from the left ventricle to the rest of the body Pulmonary Veins: carries blood back from the lungs Pulmonary Arteries: carries blood to the lungs February 22, 2016 ▶ Journal: What is the function of the left atrium? Cardiac Cycle Phases ▶ The cardiac cycle has two phases: ◦ Systole: contracting phase ◦ Diastole: resting phase Steps of the Systole Phase Step 1 ▶ Blood enters the right atrium of the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava ◦ The tricuspid valve is closed and blood collects in the right atrium Step 2 ▶ The tricuspid valve opens and the blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle ◦ Then the tricuspid valve closes to prevent blood from flowing backwards into the right atrium Step 3 ▶ The right ventricle contracts causing the blood to flow through the pulmonary semilunar valve into the pulmonary trunk Step 4 ▶ The blood divides into the left and right pulmonary arteries which bring the blood to the capillaries in the respective lung ◦ While at the lungs, the blood gives up carbon dioxide and picks up a fresh supply of oxygen ** Note: The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood. Step 5 ▶ The blood flows from the capillaries through increasingly larger blood vessels until it reaches the left and right pulmonary veins. **Note: The pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood. Step 6 ▶ The pulmonary veins meet and pour the oxygenated blood into the left atrium. Step 7 ▶ Once the left atrium is full, blood flows through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle. ◦ Once the left ventricle is full the bicuspid valve closes so blood cannot flow back into the left atrium. Step 8 ▶ The left ventricle then contracts and blood is pumped through the aortic semilunar valve into the aorta, from which the blood will be sent around the body. Diastole Phase ▶ While the atria fill with blood the heart rests before contracting again. Timing ▶ ▶ ▶ Both atria fill at the same time Both ventricles fill at the same time Both ventricles eject blood at the same time when the heart contracts ◦ Contraction begins at the apex and travels upward to ensure all the blood is expelled from the heart