* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecosystems and Communities practice test
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
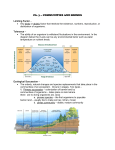
Ecosystems and Communities practice test Name: answers Score: 0 / 37 (0%) http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... [14 subjective questions not graded] Ecosystems and Communities practice test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The average year-after-year conditions of temperature and precipitation in a particular region are referred to as the region’s a. weather. c. ecosystem. b. latitude. d. climate. ANSWER: D 2. Climate is a global factor that produces a. Earth’s unique ocean and atmosphere. b. the shape and elevation of landmasses. c. a wide range of environmental conditions that shapes communities. d. solar energy within the atmosphere. ANSWER: C 3. The greenhouse effect is a. the result of an excess of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. b. a natural phenomenon that maintains Earth’s temperature range. c. the result of the differences in the angle of the sun’s rays. d. an unnatural phenomenon that causes heat energy to be radiated back into the atmosphere. ANSWER: B 4. Earth has three main climate zones because of the differences in latitude and, thus, a. amount of precipitation received. c. ocean currents. b. angle of heating. d. prevailing winds. ANSWER: B 5. Cool air over the poles will a. rise. b. sink. c. absorb heat from the equator. d. flow parallel to Earth’s surface. ANSWER: B 1 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM Ecosystems and Communities practice test http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... 6. The unequal heating of Earth’s surface a. drives wind and ocean currents. b. causes winds that transport heat throughout the biosphere. c. has important effects on Earth’s climate regions. d. all of the above ANSWER: D 7. The tendency for warm air to rise and cool air to sink results in a. global wind patterns. c. unequal heat distribution. b. ocean upwelling. d. regional precipitation. ANSWER: A 8. Why does Earth have three main climate zones? a. Warm air rises at the equator and cold air sinks over the poles causing an unequal distribution of heat over Earth. b. There are differences in latitude and, thus, the angle of heating from the sun. c. Continents and other landmasses physically interfere with global heat distribution. d. The Earth rotates and affects the major ocean currents. ANSWER: B 9. Each of the following is an abiotic factor in the environment EXCEPT a. plant life. c. rainfall. b. soil type. d. temperature. ANSWER: A 10. During a long period when there is no rainfall, a mountain lion may temporarily leave its usual hunting territory to drink from a farm pond. This behavior is probably due to a. its need to find different foods to eat. b. the change in an abiotic factor in its environment. c. its need to find a new habitat. d. the change in a biotic factor in its environment. ANSWER: B 11. An organism’s niche is a. the range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which it uses those conditions. b. all the physical and biological factors in the organism’s environment. c. the range of temperatures that the organism needs to survive. 2 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM Ecosystems and Communities practice test http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... d. a full description of the place an organism lives. ANSWER: A 12. Several species of warblers can live in the same spruce tree ONLY because they a. have different habitats within the tree. b. eat different foods within the tree. c. occupy different niches within the tree. d. can find different temperatures within the tree. ANSWER: C 13. An interaction in which one organism captures and feeds on another organism is called a. competition. c. mutualism. b. sybiosis. d. predation. ANSWER: D 14. Different species can share the same habitat, but competition among them is reduced if they a. reproduce at different times. c. increase their populations. b. eat less. d. occupy different niches. ANSWER: D 15. No two species can occupy the same niche in the same habitat at the same time a. because of the interactions that shape the ecosystem. b. unless the species require different abiotic factors. c. because of the competitive exclusion principle. d. unless the species require different biotic factors. ANSWER: C 16. A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit is a. commensalism. c. predation. b. mutualism. d. parasitism. ANSWER: B 17. The symbiotic relationship between a flower and the insect that feeds on its nectar is an example of a. mutualism because the flower provides the insect with food and the insect pollinates the flower. b. parasitism because the insect lives off the nectar from the flower. 3 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM Ecosystems and Communities practice test http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... c. commensalism because the insect does not harm the flower and the flower does not benefit from the relationship. d. predation because the insect feeds on the flower. ANSWER: A 18. The series of predictable changes that occurs in a community over time is called a. population growth. c. climax community. b. ecological succession. d. climate change. ANSWER: B 19. Primary succession can begin after a. a forest fire. c. farm land is abandoned. b. a lava flow. d. a severe storm. ANSWER: B 20. Which biome is characterized by very low temperatures, little precipitation, and permafrost? a. desert c. tundra b. temperate forest d. tropical dry forest ANSWER: C 21. Which two biomes have the least amount of precipitation? a. tropical rain forest and temperate grassland b. tropical savanna and tropical dry forest c. tundra and desert d. boreal forest and temperate woodland and shrubland ANSWER: C 22. A biome is identified by its particular set of abiotic factors and its a. average precipitation and temperature. b. characteristic ecological community. c. distance from the equator. d. specific geographical location. ANSWER: B Modified True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. 4 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM Ecosystems and Communities practice test http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... 23. Earth’s natural “insulating blanket” is the biosphere. _________________________ RESPONSE: ANSWER: F,atmosphere 24. The greenhouse effect occurs when carbon dioxide and other gases prevent heat energy from leaving the atmosphere. _________________________ RESPONSE: ANSWER: T 25. Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor trap light energy. _________________________ RESPONSE: ANSWER: F,heat 26. The amount, intensity, and duration of sunlight striking Earth vary with latitude. _________________________ RESPONSE: ANSWER: T 27. A symbiotic relationship between organisms in which one species benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed is mutualism. ______________________________ RESPONSE: ANSWER: F,commensalism 28. An existing community is gradually replaced by another community in an ecological succession. _________________________ RESPONSE: ANSWER: T 29. The temperate forest biome is typically warmer and has more rainfall than the boreal forest biome. _________________________ RESPONSE: ANSWER: T 30. The tropical rain forest is characterized by a wet season and a dry season. _________________________ 5 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM Ecosystems and Communities practice test http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... RESPONSE: ANSWER: F,dry 31. Tall, perennial grasses and herds of grazing herbivores are inhabitants of the desert biome. ______________________________ RESPONSE: ANSWER: F,tropical savanna Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 32. The energy of incoming ____________________ drives Earth’s weather and helps to determine climate. RESPONSE: ANSWER: sunlight 33. Weather differs from ____________________ in that weather can change on a daily basis and is not considered a description of year-to-year conditions of temperature and precipitation. RESPONSE: ANSWER: climate 34. Average year-after-year conditions are to climate as day-to-day atmospheric conditions are to _________________. RESPONSE: ANSWER: weather 35. Atmospheric gases that trap heat inside Earth’s atmosphere are called ____________________ gases. RESPONSE: ANSWER: greenhouse 36. Organisms within an ecosystem are ____________________ factors in that ecosystem. RESPONSE: ANSWER: biotic 37. Mild, moist air from the Pacific Ocean and giant redwood trees characterize the ______________________________. 6 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM Ecosystems and Communities practice test http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... RESPONSE: ANSWER: northwestern coniferous forest Short Answer Figure 4–1 38. Using Figure 4–1, describe a climate you might find at 10°N latitude. RESPONSE: ANSWER: The climate at 10°N latitude is most likely a hot, rainy climate, because this location is in the tropical zone. 39. Using Figure 4–1, explain why average temperatures decrease with increasing distance from the equator. RESPONSE: ANSWER: The sun’s rays strike Earth at increasingly lower angles with increasing distance from the equator, thus providing less and less direct sunlight. 40. Explain why the food that a bullfrog eats is considered a part of its niche. RESPONSE: ANSWER: A niche includes all of the physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and how the organism uses those conditions. Food is part of the biological conditions that a bullfrog uses. 41. List three biotic and three abiotic factors that determine the survival of a rabbit in a temperate forest. 7 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM Ecosystems and Communities practice test http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... RESPONSE: ANSWER: Biotic factors may include: plants the rabbit eats, predators that eat the rabbit, and other competitive species. Abiotic factors may include: temperature, rainfall, and space. 42. How is mutualism similar to and different from commensalism? RESPONSE: ANSWER: They are both symbiotic relationships. In mutualism, both species benefit from the relationship; in commensalism, only one species benefits whereas the other is neither helped nor harmed. 43. Describe an important role that pioneer species play in primary succession. RESPONSE: ANSWER: In primary succession, pioneer plants help rocks to break up in the process of soil formation and contribute organic material to the forming soil in which plants can grow. Other USING SCIENCE SKILLS Average Rainfall and Temperature of Earth’s Biomes Biome Average Yearly Average Climate Zone Rainfall Temperature Tropical rain forest 400 cm Daytime: 34ºC Tropical Nighttime: 20ºC Tropical dry forest 250–300 cm Dry season: 32ºC Tropical Wet season: 20ºC Temperate forest 75–125 cm Summer: 28ºC Mostly Winter: 6ºC temperate Boreal forest 35–75 cm Summer: 14ºC Mostly Winter: -10ºC temperate Tropical savanna 150 cm Dry season: 34ºC Mostly tropical Wet season: 16ºC Desert Less than 25 Summer: 38ºC Tropical and cm Winter: 7ºC temperate Temperate 25–75 cm Summer: 30ºC Temperate grassland Winter: 0ºC Tropical woodland Less than 50 Summer: 20ºC Temperate and scrubland cm Winter: 10ºC Tundra 30–50 cm Summer: 12ºC Temperate and Winter: -26ºC polar 8 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM Ecosystems and Communities practice test http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... Figure 4–2 44. Comparing and Contrasting In Figure 4–2, compare the average daytime temperature of the tropical rain forest with the average summer temperature of the tundra. How can you account for the difference? RESPONSE: ANSWER: The tropical rain forest has an average daytime temperature of 34°C. The tundra has an average summer temperature of 12°C. The difference is that the tropical rain forest receives almost direct sunlight all year long. The tundra receives sunlight at a much lower angle, resulting in a colder climate than the tropical rain forest. 45. Calculating What is the highest average temperature shown in Figure 4–2? The lowest average temperature? How many degrees of temperature are there between the highest and the lowest temperatures? RESPONSE: ANSWER: highest temperature = 38°C; lowest temperature = –26°C; There are 64 degrees between the highest and lowest temperatures. (38 Celsius degrees above zero + 26 Celsius degrees below zero) 46. Using Tables and Graphs Which climate zone listed in Figure 4–2 includes the most biomes? RESPONSE: ANSWER: temperate zone 47. Using Tables and Graphs Which biomes listed in Figure 4–2 include areas that have an average yearly rainfall of less than 75 cm? Which biomes include areas that have an average yearly rainfall of more than 200 cm? RESPONSE: ANSWER: Biomes that have less than 75 cm of yearly rainfall include: boreal forest, desert, temperate grassland, temperate woodland and shrubland, and tundra. Biomes that have more than 200 cm of yearly rainfall include: tropical rain forest and tropical dry forest. 48. Analyzing Data Which two biomes shown in Figure 4–2 have seasons determined by the amount of precipitation they receive at different times of the year? RESPONSE: ANSWER: The tropical dry forest and the tropical savanna each have a wet season and a dry season. 9 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM Ecosystems and Communities practice test http://cwcboe.schoolwires.net/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricit... Essay 49. Describe the greenhouse effect and explain how it maintains Earth’s temperature range. RESPONSE: ANSWER: Solar energy has an important effect on the temperature of the atmosphere. Atmospheric gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor, do not allow heat energy to pass out of the atmosphere. This natural situation in which heat is retained by these greenhouse gases is called the greenhouse effect. This effect provides a natural insulating blanket around Earth and maintains its temperature range. 50. Name and define the three main classes of symbiotic relationships. Give examples of each. RESPONSE: ANSWER: The three main classes of symbiotic relationships are mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. In mutualism, both species benefit from the relationship. For example, flowers depend on certain insects to pollinate them. The flowers provide the insects with food in the form of nectar, pollen, or other substances. In commensalism, one member of the association benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed. Barnacles attached to the skin of whales benefit from food particles in the water moving past the swimming whale, but the whale is not affected. In parasitism, one member benefits by obtaining all its nutritional needs from the host. The host can be damaged but is usually not killed. Fleas, ticks, and lice are examples of parasites that live on the bodies of mammals. 51. Describe the stages of primary succession in land environments, including lichens, mosses, grasses, shrubs, and trees. RESPONSE: ANSWER: Primary succession occurs on newly exposed surfaces, such as a fresh lava flow that destroys the previous ecosystem. The first organisms to appear are plantlike lichens that colonize the newly formed volcanic surfaces. Over several years, various species of plants including mosses and grasses establish themselves among the rocks and then take root in the thin layer of soil. Eventually, tree seedlings and shrubs sprout among the plant community. A characteristic ecological community may eventually dominate the area. 10 of 10 6/8/15 7:42 AM