* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Levels of Organization
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
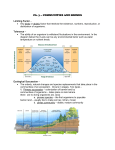
Topic: Name: ____________________________ Date:_________________________ Levels of Organization Objective: SWBAT understand the ecological levels of organization. Questions/Main Ideas: What are the cellular levels of organization? Remember the cellular levels of organization: - Atoms (Carbon) - Compounds (protein) - Organelles (ER) - Cells (stomach lining cell) - Tissue (stomach tissue) - Organ (stomach) - Organ system (digestive system) - Organism (human) What is an organism? Ecological Levels of Organization (lowest to highest): 1. Organism • An individual living thing • Ex) Powder Blue Tang What is a population? 2. Population • Group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time • Species= organisms with similar characteristics that are able to breed and produce fertile offspring • Compete for food water, mates, resources • Adaptations may lead to no competition • Ex) School of Tangs What is a community? 3. Community • Collection of interacting populations living in the same place at the same time • Change in one population affects other populations in the community • Ex) Different species of fish What is an ecosystem? 4. Ecosystem • Interactions among populations in a community and the physical surroundings (Biotic + abiotic factors) • First level that includes abiotic factors • Ex) Coral Reef • Terrestrial • Aquatic • Fresh water- ponds, lakes, streams • Salt water- 75% of earth (marine) What is a biome? 5. Biome • A group of ecosystems that share the same climate and have similar type of communities • Ex) Tropic Coastal Ocean Terrestrial Biomes Tropical Rain Forest Tropical Dry Forest Tropical Savanna Desert Temperate Grassland Temperate Woodland/ Shrubland Temperate Forest Coniferous Forest Boreal Forest/ Taiga Tundra Aquatic Biomes Coral Reef Open ocean Estuary Marsh Swamp Lakes/ ponds Rivers/ Streams What is the biosphere? Summary: Wet; most biodiversity Warm; tigers, monkeys lions and hyenas Dry; cacti and snakes Grassy; coyotes and prairie dogs Shrubs; mountain lions Deciduous trees; deer Evergreens; bears Evergreens; moose Cold; permafrost (frozen ground) Marine/ salt water; warm shallow water; high biodiversity Marine/ salt water Brackish (salt and freshwater); Ex) Chesapeake Bay Fresh; shallow water; no trees Fresh; shallow water; trees Fresh; still water Fresh; moving water 6. Biosphere • The highest level of organization that supports life • Ex) The earth