* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (17) Digestive system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
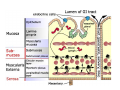
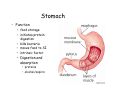
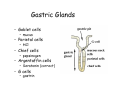
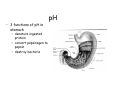
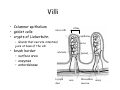
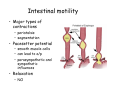
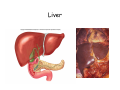
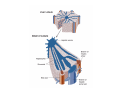
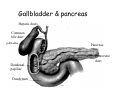
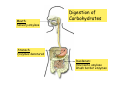
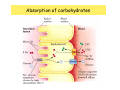
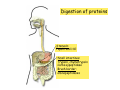
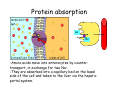
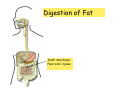
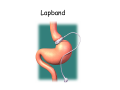
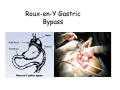
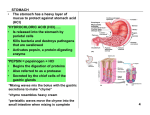
Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions • Motility – – – – ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis • Secretion – exocrine – endocrine • Digestion • Absorption Tunics Innervation • Autonomic nervous system • Parasympathetic (vagus nerve) – motility – secretion • Sympathetic – decreases peristalsis – secretion – contraction of sphincters Esophagus • Collapsible tube • first 1/3 – Skeletal muscle • last 2/3 – Smooth muscle • gastroesophageal sphincter Stomach • Function – food storage – initiates protein digestion – kills bacteria – moves food to SI – intrinsic factor – Digestion and absorption • proteins • alcohol/aspirin Gastric Glands • Goblet cells – mucus • Parietal cells – HCl • Chief cells – pepsinogen • Argentaffin cells – Seratonin (correct) • G cells – gastrin pH • 3 functions of pH in stomach – denature ingested protein – convert pepsinogen to pepsin – destroy bacteria Protective mechanisms • Impermeability of gastric mucosa to CO2 and NH3 • alkaline mucus • tight junctions • rapid cell division and replacement • protective effects of prostaglandins • In doudenum – bicarbonate from pancreatic juice – Brunner’s glands • Secrete mucinous alkaline solution Peptic ulcers – Gastric ulcers • Weakened defense mechanisms – Duodenal ulcers • Increased acid and pepsin production – Helicobacter pylori • Major factor in both types • Present in 100% of gastric ulcer patients and 95% of duodenal ulcer patients – Exceptions: Those whose ulcers are the result of overuse of NSAIDS = inhibits prostaglandin production • Produces NH3 and urease – damages epithelium and allows H+ to permeate • Also linked to increased acid secretion Small intestines • Length • 3 divisions – duodenum – jejunum – ileum • absorption – doudenum + jejunum – ileum • system of folds – microvilli, villi, plicae circularis Villi • Columnar epithelium • goblet cells • crypts of Lieberkuhn villus microvilli capillaries – Glands that secrete intestinal juice at base of the villi • brush border – surface area – enzymes – enterokinase nerve arteriole Lymph duct lacteal vein Muscularis artery mucosa Intestinal motility • Major types of contractions – peristalsis – segmentation • Pacesetter potential – smooth muscle cells – can lead to a/p – parasympathetic and sympathetic influences • Relaxation – NO Large Intestine • Structure • Haustra • Fluid and electrolyte absorption – 90% in SI – passive osmosis – water secretion • Defecation Liver Liver lobules: functional unit Functions of liver • • • • • • • Exocrine Endocrine Clotting functions Plasma proteins Organic metabolism Cholesterol metabolism Excretory and degradative functions Exocrine & Endocrine • Synthesis and secretion of bile salts – 250-1500ml/day • Adds bicarbonate rich solution to bile • Secretes IGF-1 = promotes cell division • Forms T3 from T4 • Secretes Angiotensinogen • Metabolizes hormones • Secretes immune cytokines Clotting and Plasma proteins • Produces prothrombin & fibrinogen • Produces bile salts needed for vitamin K absorption • Produces plasma albumin, acute phase proteins, binding proteins, and lipoproteins Organic metabolism • Converts plasma glucose to glycogen and triglycerides • Converts amino acids to fatty acids • Produces triglycerides and secretes them as lipoproteins • Gluconeogeneisis and glycogenolysis • Converts fatty acids into ketones • Produces urea Cholesterol metabolism/excretory & degradative functions • Synthesizes cholesterol • Secretes plasma cholesterol into bile • Converts plasma cholesterol into bile salts • Secretes bile pigments • Excretes toxins via bile • Destroys old erythrocytes • …and lots, lots more! Gallbladder & pancreas Hepatic ducts Common bile duct gallbladder Pancreas Pancreatic duct Duodenal papillae Doudenum Pancreas • Endocrine = islets of Langerhans – insulin and glucagon, etc. • Exocrine = pancreatic acini – pancreatic juice – composition • water • bicarb • digestive enzymes – role of enterokinase Neural and endocrine regulation • Long reflex – preconditioning • Short reflex – more local • GI hormones • Extrinsic controls – 3 phases (cephalic, gastric, intestinal) • some events without neural or endocrine control GI hormones • • • • Gastrin Secretin CCK glucose-dependent insolinotropic peptide (GIP) • Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) • Guanylin Gastrin • endocrine cell location – antrum of stomach • stimulus for release – amino acids, peptides in stomach parasympathetic nervous system • actions – stimulates secretion of HCl and pepsinogen Secretin • Endocrine cell location – small intestine • stimulus for release – acid in small intestine • action – stimulate pancreatic bicarbonate secretion – potentiate CCK-stimulated pancreatic enzyme secretion Cholecystokinin (CCK) • Endocrine cell location – small intestine • Stimulus for release – amino acids, fatty acids in small intestine • Action – contraction and emptying of the gall bladder – stimulates release of pancreatic enzymes – (in the brain: acts as satiety hormone) Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) • Endocrine cell location – small intestine • Stimulus for release – glucose, fat in the small intestine • Action – inhibits gastric emptying – potentiates insulin release Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) • Endocrine cell location – ileum and colon • Stimulus for release – oral ingestion of nutrients – glucose, fats, amino acids (mixed meals) • Action – inhibits gastric motility – stimulates insulin secretion Guanylin • Endocrine gland location – ileum and colon • Action – stimulates intestinal Cl- release – result: increased NaCl and water in feces Cephalic phase • First 30 minutes – Smell, sight, and taste of food stimulates vagus nuclei of brain (long reflex) • vagus nerve stimulates: – parietal and chief cells – Gastrin secretion by G cells • Also stimulates parietal and chief cells Gastric phase • Begins when food arrives in stomach • Stimulus – distension – chemical composition of chyme • short polypeptides and amino acids in stomach – Positive feedback, cells secrete gastrin – HCl and pepsinogen are released • Glucose – No effect • Lipids – Inhibition of gastrin secretion – pH<2.5 negative feedback inhibition of gastrin Intestinal phase • Begins when chyme enters small intestines • neural inhibition of gastric emptying and acid secretion due to: – increased osmolality – stretching • enterogastrone – stimulus: fat in chyme – inhibits gastric acid secretion • GIP = insulin secretion if glucose is present • CCK = inhibits gastric emptying when chyme in duodenum Intestinal reflexes • Gastroileal reflex – increased gastric activity = increased motility of ileum = increased chyme through sphincter • ileogastric reflex – ileal distension = decreased gastric motility • intestino-intestinal reflex – one segment overdistends = rest relax Regulation pancreatic juice & bile • Neural & hormonal • Pancreatic juice – secretin • pH <4.5 in duodenum • stimulates bicarbonate production by pancreas • cAMP as a second messenger – CCK • fat content in chyme • production of pancreatic enzymes • Ca++ as second messenger • Secretion of bile – continuous secretion – gallbladder contraction under influence of CCK and secretin Digestion and absorption of carbohydrates • Mouth – salivary amylase • Stomach – enzymes denatured • Small intestines – pancreatic amylase = maltose, maltriose – brush border enzymes = monosaccharides – secondary active transport with Na+ – Into capillaries in villus Mouth: Salivary amylase Digestion of Carbohydrates Stomach: Enzymes denatured Duodenum: Pancreatic amylase Brush border enzymes Absorption of carbohydrates Digestion and absorption of proteins • Mouth – nothing • Stomach – Pepsin = short chain polypeptides • Small Intestines – – – – – trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase carboxypeptidase aminopeptidase = from brushborder across into blood Whole proteins • babies • botulinum toxin Free amino acids Dipeptides tripeptides Digestion of proteins Stomach: Pepsin and HCl Small intestines: Trypsin, chymotrypsin Carboxypeptidase Brush border: aminopeptidases Protein absorption aa Na+ -Amino acids move into enterocytes by countertransport, in exchange for two Na+. -They are absorbed into a capillary bed on the basal side of the cell and taken to the liver via the hepatic portal system. Digestion and absorption of lipids • • • • Emulsification pancreatic lipase Mixed micelles to brushborder transport – across into epithelial cells – can be moved inside cell – chylomicron into lacteal Digestion of Fat Small intestines: Pancreatic lipase lacteal Lipid transport • From lymphatics to thoracic duct • Triglycerides removed by lipoprotein lipase on endothelial membranes • Free fatty acids and glycerol into tissues • Leftovers to liver – – – – Remnant particles contain cholesterol Combined with apoproteins to produce VLDL’s Deliver triglycerides to other organs Later converted to LDL’s when triglyceride has been removed Lipoproteins • What are they? – Lipid & protein complexes – Transport cholesterol & triglycerides in blood – Protein allows hydrophobic lipids to remain in suspension • Five classes: Based on density, molecular weight, size, chemical composition • Chylomicrons • VLDL • IDL • LDL – High levels associated with increased risk CVD • HDL – Low levels associated with increased risk of CVD – Best profile = high HDL, low LDL Treatment for morbid obesity Lapband Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass