* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics - Helena High School
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
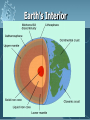
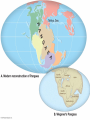
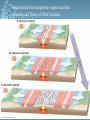
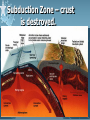
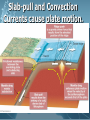
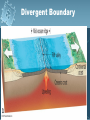
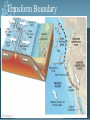
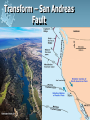
Plate Tectonics Earth’s Interior Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) - German astronomer/meteorologist - Died on expedition in 1930 - Proposed Continental Drift in 1912 Theory of Continental Drift - Continental Drift • Earth’s continents had once been joined as a single landmass - Pangaea “all lands” • Ancient landmass made up of all continents forming a supercontinent. • Began to break apart about 200 million years ago (mya) Pangaea Ultima? Evidence from Rock Formations - Same rocks are found in the Appalachians and also in Greenland and Europe. - Rock formations (ex. mountain ranges) fractured as the continents separated. Evidence from Fossils - Wegener found similar fossils of different land animals and plants on separated continents. Paleaoclimatology Evidence - Sedimentary Rock Coal • Coal forms from dead swamp plants. • Coal was found in Antarctica, therefore Antarctica must have been closer to the equator at one time. Continental Drift was rejected. - Scientists rejected the hypothesis because: • People believed continents and ocean basins were fixed features. • Wegener could not explain what forces could cause a continent to move. Paleaoclimatology Evidence - Glacial Deposits • 290 mya glacial deposits found in Africa, India, Australia, and South America. • These continents were once located on the South Pole. Theory of Plate Tectonics Evidence. - 1960s Technology: • Magnetometer –makes a map from detecting small changes in magnetic fields. • Geologists mapped volcanoes and earthquakes along plate boundaries. • Sonar – used to map out the seafloor (found mid-ocean ridge). Sea-Floor Spreading Check this out on Google EARTH. Theory of Plate Tectonics Evidence 1. Rock Age • • • Young Rocks –near ocean ridges. Older Rocks –near deep-sea trenches Seafloor Age – oldest part = 180 million years old. Oldest Continental crust = 3.8 billion years old. Theory of Plate Tectonics Evidence 2. Paleomagnetism is the past formation of rocks containing iron and show the direction of polarity of Earth’s magnetic field. Ex. Basaltic rocks. Magnetism & Paleomagnetism support sea-floor spreading and Theory of Plate Tectonics. Geomagnetic Time Scale Magnetic Reversal a change in Earth’s magnetic field. Normal Polarity a magnetic field that has the same orientation as Earth’s present field Reversed Polarity a magnetic field that is opposite to the present field Major plates of the world. Mid-ocean Ridge – crust is formed. Subduction Zone – crust is destroyed. Slab-pull and Convection Currents cause plate motion. Plate Boundaries Plate Boundaries Three Major Types 1. Convergent •plates come together. 2. Divergent •plates move away from one another. 3. Transform •plates move horizontally past one another - places where tectonic plates interact with one another. Divergent Boundary Divergent - Iceland Rift Convergent OceanicContinental Boundary Oceanic-Continental Cascade Range Convergent Oceanicoceanic Boundary Convergent ContinentContinent Boundary Continental-Continental Himalayas Transform Boundary Transform – San Andreas Fault Know this drawing!