* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Living things in their environment.
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
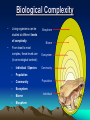
CHAPTER 1 / SECTION 1 •LIVING THINGS AND THE ENVIRONMENT! LIVING THINGS IN THEIR ENVIRONMENT • An organism or type of living thing needs to obtain food, water, shelter and other things it needs to live, grow, and reproduce from its environment. • An environment that provides the things an organism needs to live is called its habitat. Factors in an Environment Biotic – living parts of the environment. Ex. Producers and consumers. Abiotic – nonliving parts of the environment. Ex. water, sunlight, oxygen, temperature, and soil. Photosynthesis: The process of a plant making its own food. Biological Complexity • Living organisms can be Biosphere studied at different levels of complexity. • Biome From least to most complex, these levels are Ecosystem (in an ecological context): – Individual / Species – Population – Community – Ecosystem – Biome – Biosphere Community Population Individual Populations A species is a group of organisms that are physically similar and can reproduce with each other. Organisms do not generally live alone. A population is a group Migrating wildebeest population of organisms from the same species occupying in the same geographical area. This area may be difficult to define. Why? Tiger populations comprise widely separated individuals Communities and Ecosystems • A community is all the populations that live together in an area. • An ecosystem is the community of organisms that live in a particular area and along with their nonliving surroundings. **The community and the abiotic factors together form an ecosystem. Ecology • The study of how living things interact with each other and their environment.