* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 16 Heart A
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
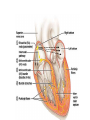
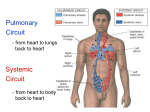
Myocardium 1 Inflamed outer layer of the heart. Pericarditis can be caused by damage to the blood vessels (from infection, wound, autoimmune disease, etc)--blood leaks into pericardial cavity Pericarditis can lead to pericardial friction rub, adhesions, additional excess fluid in the pericardial cavity, or improper heart beat (cardiac tamponade). It does NOT cause myocardial infarction. 2 CARDIAC TAMPONADE 3 Endocarditis 4 Pulmonary Semilunar Valves 5 Deoxy blood sup/inf vena cava R atrium tricuspid valve R ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary artery lungs pulmonary veins Left atrium mitral (bicuspid) valve Left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta rest of body. 6 The pulmonary circulation 7 The Semilunar valves 8 Vibrations that result from blood hitting the semilunar valves after they slam shut. 9 SYSTOLE -Ventricles contract -Atria relax DIASTOLE: -Ventricles relax -Atria contract 10 Start of Systole (ventricles start to contract): Closing of the large valves (tricuspid and mitral) End of Systole (ventricles are relaxing): Semilunar valves are closed (aortic and pulmonary) Note: Systole means that the ventricles are contracting. 11 Mitral valve prolapse 12 13 1. First the Sinoatrial (SA) node starts an action potential which causes the atria to depolarize. 2. This depolarization will then reach the AV node at the bottom portion of the right atrium and there is a delay here because these cells are so small in diameter. 3. Another delay in the transmission of the depolarization at the bundle of His (AV bundle) because these special heart cells travel through the atrioventricular septum which is non-conductive fibrous connective tissue. 4. Next, the depolarizing event travels through the left and right bundle branches, found in the interventricular septum, to finally arrive at the Purkinje fibers in the ventricular myocardium. 14 ARRHYTHMIA Treatment is medicines or a pacemaker. 15 Too fast: tachycardia Too slow: bradycardia VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 16 Angina 17 ISCHEMIA: Lack of blood/ oxygen Myocardial infarction No, death takes about 2 hours in 50% of the cases. 18 t-PA (dissolves blood clots) Beta-blockers (slows heart rate) Aspirin (prevents blood clots) Nitroglycerine (dilates coronary arteries) 19 Arteriosclerosis is hardening of the arteries, caused by a build-up of calcium deposits in the artery wall; artery cannot expand with blood surges. Tends to be hereditary. Atherosclerosis is caused by a build-up of fat in the arteries, from eating fatty foods -narrowing of artery -- Spasm shut or blood clot. Both cause High Blood Pressure 20 A thrombis is a blood clot. An embolism is a piece of blood or fat clot that has broken off and travels in the bloodstream. 21 If the embolism lodges in the coronary arteries - myocardial infarct (Heart attack). If the embolism lodges in an artery in the brain -- stroke If the embolism lodges in the lungs- pulmonary embolism 22 An ANGIOGRAM An ANGIOPLASTY 23 CORONARY BYPASS. saphenous vein 24 Aneurysm Stroke 25 Atherosclerosis- Fatty deposits Angina pectoris- chest pain Myocardial infarction- blocked coronary artery Silent ischemia- lack of blood flow that happens to not cause any pain or other symptoms; leads to unexpected heart attack. 26 Congestive Heart failure: Progressive weakening of the heart Blood backs up into lungs (may clog up blood) Cannot meet the body’s demands for oxygenated blood. 27 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a congenital condition where the walls of the left ventricle are so thick that the lumen is too small to hold much blood. 28 at the start of the fourth week 29 FOSSA OVALIS. 30