* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key to pre/post test - TSDCurriculum
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
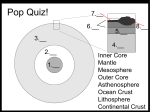
Pre/Post Test KEY Name _________________________ Per. ____ 1. On the drawing showing the layers inside of the earth, label the four layers. Learning Goal: The layers of the earth and their temperatures. 2. Beside each layer name, write a number to put the layers in order from hottest to coldest. LG: Same as above. 4. Crust 3. Mantle 2. Outer Core 1. Inner Core 3. Is the 2nd layer from the outside solid or liquid? The mantle is solid (but has plasticity) LG: Same. 4. We can’t dig down through even the thinnest outer layer of the earth. List 2 different ways humans find out about the structure and temperatures is inside of the earth. 1. Seismic waves. 2. Experiments on the properties of materials (such as density of iron at different temperatures and pressures) Learning Goals: We know what is inside of the earth by information from seismic waves and our knowledge of the properties of materials and explain how models help us illustrate relationships that we cannot measure directly. 5. Draw a diagram that shows the difference in the air particles inside a hot and a cold balloon. Hot Fewer dots widely spaced Cold More dots closer together Learning Goal: Temperature influences density for most materials. LG: Density differences cause 6. Choose one true statement: (Read each one carefully) some materials to fall and A) Large objects always sink and small objects always float others to rise. B) Cold always sinks and heat always rises C) Block A sinks in water but block B floats, therefore the mass of A is greater than the mass of B. D) More dense objects are always heavier than less dense objects E) More dense objects always sink below less dense objects 7. A blob of stuff has a mass of 20 grams and a volume of 4 cm3. What is its density? The 𝑚 formula for density is 𝐷 = 𝑉 . D = 20 g/4 cm3 = 5 g/cm3. LG: Calculate density given mass and volume. 8. A room was sprayed with a very fine dust that floated in the air and could be seen. The center of the room was heated by a hot bed of coals. After a while, the fine dust started rising over the coals. There was no blower, open window or door, or a fan of any kind in the room. Draw a model showing the flow pattern of the dust in the side view of the room below. LG: Determine convection current relationships. Convection is a process of heat transfer driven by density differences that occur with differential heating and cooling (stability and change). Communicate results. A B Hot coals 9. What is the name of the process that moves the dust around the room in question 5? Convection LG: Communicate results. 10. The air and dust are warmer at point A than at point B. Why do they rise at point A? The warmth causes the materials to become less dense than surrounding air, so they rise. LG: Convection is a process of heat transfer driven by density differences that occur with differential heating and cooling (stability and change). 11. If you used any science terms in your answer to question 10, explain what they mean here. Less dense – less mass in a given volume Convection – circular movement of a material driven by density/temp differences. LG: Communicate results. 12. Select ONE answer: What moves the earth’s massive tectonic plates? A) Seismic waves (earthquakes) LG: Convection currents in the mantle drive plate B) Mantle convection currents tectonics, according to current understandings C) Movement of the earth’s core (cause and effect). D) The earth’s rotation