* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Energy! - Epiphany Catholic School
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
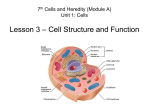
Introduction to Energy! 6th Grade Module H: Matter and Energy Unit 2: Energy Lesson 1 Energy is… There are two main types of energy • Kinetic energy - energy of an object that is due to motion. All moving objects have kinetic energy. • depends on its mass and speed. • increases as mass increases and as speed increases • Which has more kinetic energy? Why? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company • Potential energy - energy that an object has due to its position, condition, or chemical composition. • Gravitational potential energy –result of an object’s position • Increases as the object’s height or mass increases. • Which has greater GPE? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company • Condition of an object affects its potential energy. • Ex: Stretching a rubber band increases its potential energy. • Chemical potential energy - depends on chemical composition. • As bonds break and new bonds form between atoms during a chemical change, energy can be released. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Where is potential energy the greatest, when the archer has pulled back the bow or when it is in resting position? • An object can have both potential and kinetic energy at the same time. Read and do p. 102103 Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Forms of kinetic and potential energy • Energy is expressed in joules (J). 1. Mechanical energy is the sum of an object’s kinetic energy and potential energy. It is the energy of position and motion. "mechanical energy = kinetic energy + potential energy". 2. Sound energy is kinetic energy caused by the vibration of something. -vibrations in the air get transferred to the eardrum Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 3. Electromagnetic energy - transmitted through space in the form of electromagnetic waves. • caused by the vibration of electrically charged particles. • include visible light, X-rays, and microwaves • Kinetic or potential? What do you think? 4. Electrical energy is the energy that results from the flow (movement) of charged particles. (K or P?) 5. Chemical energy - form of potential energy that depends on the kinds of atoms and their arrangement. -examples: food, batteries, matches 6. Thermal energy - kinetic energy of an object’s particles. • faster the molecules move = more thermal energy • Heat: energy transferred from an object at a higher temperature to an object at a lower temperature 7. Nuclear energy - found in nucleus of an atom • When an atom’s nucleus breaks apart, or when the nuclei of two small atoms join together, energy is released. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 1 Introduction to Energy What forms can energy take? • What forms of energy can you identify in this pinball game? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 1 Introduction to Energy Transformers What is an energy transformation? • An energy transformation takes place when energy changes from one form into another form. • Any form of energy can change into any other form of energy. • Often, one form of energy changes into more than one form. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 1 Introduction to Energy What is an energy transformation? • In a flashlight, chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy. • The electrical energy is then transformed into light and thermal energy. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 1 Introduction to Energy Is energy conserved? • A closed system is a group of objects that transfer energy only to one another. Energy is conserved in all closed systems. • The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only change forms. • All of the different forms of energy in a closed system always add up to the same total amount of energy. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Energy Posters • Forms of Energy • Energy Transformation • State the form • Define • Kinetic or potential (or both)? • Examples with pictures • Use pages 104-106 • Check with Ms. R to make sure yours is not taken • State the type of energy it is transforming FROM and TO • Examples with pictures • Where is energy “lost” to the environment? • Use pages 108-109 & computer