* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SPH 4C - mackenziekim
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
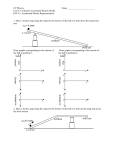
SPH 4C Energy Transformations Review 1. What is work? What is energy? What is the formula for calculating work? What are the units for work and energy? 2. Name 6 different types of energy and an example of a source of that energy. Ex. Sound (source = speaker) 3. An engineer uses a single car to test the roller coaster track, shown in Fig. B. In answering the following questions, assume that friction can be ignored and the speed at A is O. In each case, give a reason for your answer. (a) Where is the gravitational potential energy the greatest? (b) Where is the kinetic energy the greatest? (c) Where is the speed the greatest? (d) Give a written description of what happens to the speed of the car as it rolls from A to B and so on to E. Fig. B 4. A 30 kg box is held 5.0 m above the ground. How much gravitational potential energy does it possess? If it is lowered to 2.0 m above the ground, how much Eg was lost? (1470 J; 882 J) 5. A 0.025 kg bullet traveling at 245 m/s hits a tree. How much kinetic energy does the bullet impart on the tree? (750 J) 6. What does the law of Conservation of Energy have to say about a falling rock? 7. Why is energy never truly conserved in a mechanical system? 8. Dr. Boom sends his 3.5 kg monkey straight up with a velocity of 24.0 m/s. How high will the monkey go before it comes to a complete stop? (29.4 m) 9. A 40 g spring with a constant of 24 N/m is stretched by 30 cm. If it is let go, and no energy is lost, how high will the spring go? (2.76 m) 10. A ball of mass 2 kg has a starting velocity of 7.0 m/s at the bottom of a ramp. It only reaches a height of 2.0 m. a) Calculate the total energy of the ball at the bottom of the ramp. (49 J) b) Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the ball at the top of the ramp. (39.2 J) c) How much energy did the ball lose? (9.8 J) d) Where did lost the energy go? (friction = heat, sound) e) Calculate the efficiency of the ramp. (80%) \sph4C\energy\840982107 11. Write the energy transformation equation (diagram) for using a slingshot. 12. Explain why it is impossible to have a motor that is 100% efficient. 13. When thermal energy is transferred, when does it stop? 14. Why is the inside of an astronaut’s suit made from highly reflective material? From what form of heat transfer is this protecting the astronaut? 15. Describe each of the thermal energy transfer methods and give an example. 16. Give examples of thermal energy loss in the home, and the type of transfer they are (ie. conduction, convection, radiation). 17. How can we protect against heat loss (give 3 examples)? Which type of transfer does each insulation method prevent? 18. A thermos is a good device for maintaining a liquid’s temperature. What methods of insulation does it use? 19. Sketch an energy flow diagram illustrating the efficiency of a car engine if 100% is input from fuel, 5% is lost to air as sound, 4% is lost to the road as heat, and 70% is lost from the engine as heat. 20. Sketch an energy flow / path diagram for a propane barbecue. 21. If the average cost of electricity during mid-peak time of use is $0.089/kWh, how much does it cost to run a 60 W lightbulb for 3 hours a night for a week? ($0.112) 22. Which are the most efficient types of light bulb in the home today? Which are the least efficient? 23. a) Where is most of your electricity used in the home? b) How can you as an individual reduce how much energy you use / waste in your home? 24. In energy conservation, no energy is actually “lost”. Where, then, does the lost energy go? 25. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J/(kgC). The specific heat capacity of aluminum is 900 J/(kgC). If 2 kg of each substance had its temperature raised by 20 C, how much energy would be needed in total? (2.04 x 105 J) \sph4C\energy\840982107