* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download motion
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
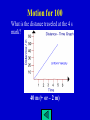
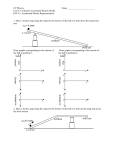
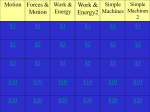
The Man’s Jeopardy Learning Objectives (Big Ideas) 1. Analyze an object’s motion and be able to determine distance, instant & average speed, or acceleration. 2. Describe how the various balanced and unbalanced forces can have an effect on an object’s motion. 3. Apply Newton’s Laws to real world examples. 4. Analyze the methods by which machines make work easier. 5. Examine situations where kinetic energy is changed into potential energy (and vice-versa). RULES 1. There will be round robin play and all questions will be all-play. 2. The teams who answers correctly win the point value of the question. 3. There are no daily doubles available. Let’s play Study Tools (Power Pts. Are on Mr. Nye’s website) 1. Physics Practice Test 2. Physics Final Review Games (Parts 1 & 2) 3. Past Tests & Quizzes (Motion, Forces, Work & Machines) 4. Class Power Points 5. Previous Review Games 6. Lab Notebook 7. Notes 8. Textbook *A on Final + Good Behavior = Special Reward* Motion Forces Work & Energy Machines 100 100 100 200 200 200 300 300 300 400 400 400 500 300 500 Final Jeopardy Motion for 100 What is the distance traveled at the 4 s mark? 40 m (+ or – 2 m) Motion for 200 Draw a distance-time graph for an object that is not moving at all. Straight horizontal line on a distance vs. time graph Motion for 300 Draw a speed-time graph for an object traveling at a constant speed. Graph should be a straight horizontal line indicating the same speed over a period of time for a speed-time graph. Motion for 400 Draw a distance-time graph for an object traveling at a constant speed. Graph should be a straight line slanted up and to the right or down and to the right (with distance on the y-axis and time on the x-axis) Motion for 500 Draw a speed-time graph showing an object slowing down. Graph should be a slanted line going down and to the right on a speed-time graph. Forces for 100 Which of the following would require the greatest force: a large truck accelerating at 5 m/s/s, a small stone accelerating at 6 m/s/s, or a person accelerating at 5.5 m/s/s. Explain your answer. The truck because its greater mass has a greater effect on the force it would exert than the slightly higher accelerations of the person and the stone. Forces for 200 Explain why a kicker can sometimes fly backward when kicking another person. Hint- Newton’s 3rd Law. The action force is the kick, while the equal and opposite reaction is the body of the person who’s being kicked pushing back on the kicker. Forces for 300 Why are larger people unable to move as quickly as lighter people? More force is required to accelerate a heavier mass. Forces for 400 Explain why your body moves backward when a car first takes off. Your body is at rest and attempts to remain at rest (due to your inertia). Forces for 500 Markie & Suzie conduct an experiment to determine how mass affects the force needed to move that object. They choose to push objects up a ramp. They both believe that heavier objects will require more force. How should they design the experiment? What is 1 constant? May give answer verbally. Design- Push objects of different masses up a ramp and measure the force exerted. Constants- Same ramp height/incline, same acceleration, same object, same position of release on the ramp Work & Machines for 100 Which class of lever is the input force opposite the direction of the output force? Is this the class that pliers belong to? How does the load weight (output force) compare the input force for 1st and 2nd class levers? 1st class Yes, b/c the fulcrum is in the middle. Load weight is greater than the input force. Work & Machines for 200 How can you increase the M.A. of a pulley system? Add more pulleys to create more sections of rope. Work & Machines for 300 Suppose the input force for a screwdriver is 15 N, then which of the following could be the output force: 0 N, 10 N, 15 N, or 30 N? Also, how does the M.A. compare to 1? 30 N (output is greater than input, M.A. > 1) Work & Machines for 400 Which of the following would be an example of a compound machine: scissors, ruler, wheelbarrow, or door stopper? CHOOSE ONE and list 2 types of simple machines that make up that compound machine. Wheelbarrow: wheel & axle and lever (2nd class) Scissors: Wedge & 1st class lever Work & Machines for 500 Explain how a screwdriver works (in terms of input and output force as well as input and output distance). The input force over the wheel (handle) travels a greater distance than the larger output force over the axle (metal rod). Energy for 300 If your throw a ball up in the air, how do the PE and KE change as the ball goes up and then comes back down? Explain your answer. PE increases as the ball goes up because it is higher off of the ground while the KE decreases until the ball starts to gain speed as it goes back toward the ground. As the ball goes down, the KE increases and the PE decreases (lower height). Forces Newton’s Cradle demonstrates how momentum (and energy) can be transferred between objects. However, after a period of time, the metal spheres do not bounce as high and eventually stop moving. Explain why this occurs. Friction between the spheres and strings as well as the air around the cradle cause the momentum and energy to be “lost”.