* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pulse operation of film capacitors
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Ceramic capacitor wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor types wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor plague wikipedia , lookup
Electrolytic capacitor wikipedia , lookup
Aluminum electrolytic capacitor wikipedia , lookup
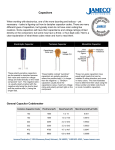
Pulse operation of film capacitors When capacitors are subjected to waveforms that contain fast rising (or falling) pulses care needs to be taken to prevent the capacitors from becoming damaged from these waveforms. The peak currents generated from these waveforms place a large amount of stress on the internal connections and contact areas of the capacitors which in turn generates localized heating in these areas. To prevent the capacitors from being damaged by the localized heating the peak current must be limited. The peak current for any given capacitors is determined by: 1. 2. 3. 4. The amplitude and shape of the pulse. The capacitance value. voltage rating of the capacitor. The shape of the capacitor. The pulse current rating of a capacitor is determined by the following formula: I=C*dv/dt Where I= the peak current rating for the capacitors. C= Capacitance value. dv/dt= maximum rate of change the capacitor can withstand. To determine the energy content of the waveform (Ko) the following formula is used: Ko=2 ∫ (dv/dt)2dt where dv=change in voltage over time interval. dt= Change in time of the slope section measured. For waveforms with straight edge transitions Ko=2Vpp2/t where Vpp = Peak to peak voltage of the waveform. t= Rise time of the voltage. For applications where short circuit type discharging is present Ko=VCH2/ (R*C) Where VCH = Charging voltage R= Resistance of circuit C= Capacitance 3757 W. Touhy Ave., Lincolnwood, Il 60712 ● (847)675-1760● Fax (847) 675-2850 ● www.illcap.com