* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Summer Work for Students Entering Physics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
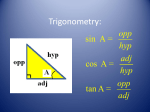
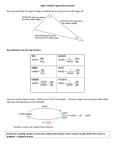
Summer Work for Students Entering Physics 2010-2011 All entering Physics students must be familiar with the following basic math skills, among others, before the start of the school year. Read the given examples carefully and do all the problems. You should show your work neatly for all problems throughout the packet. Write all of your final answers on the answer sheet at the end of the packet. You may consult textbooks and other sources. The packet will be collected on the first day of class and graded for accuracy. A. Rounding B. Multiplying fractions using the calculator C. Areas of rectangles and volumes of rectangular blocks D. Exponents E. Cross multiplication & division F. Simple Algebra problems G. Literal equations in Algebra H. Complex fractions I. Unit conversion J. Trigonometry and Geometry 1 A. Rounding If the next digit is 5 or higher, then round up; if the digit is less than 5, then round down. Round only once; do not round twice. e.g. If you want to round to whole number, then a) 24.45 = 24 b) 23.67 = 24 c) 1.443 = 1 e.g. If you want to round to 1 decimal place, then a) 24.45 = 24.5 b) 23.67 = 23.7 c) 1.443 = 1.4 Do Problems: 1. Round the following numbers to 3 decimal places: (i) 58.3382 (ii) 2.5546 (iii) 729.5005 (iv) 4.8898 B. Multiplying fractions using the calculator The parentheses are often used to indicate multiplication. e.g. (2.5)(4.6)(6.7) means 2.5 is multiplied by 4.6, which is then multiplied by 6.7 For a fraction, multiply the value above the fraction line and divide the value below the fraction line. 1.2 3.4 5.6 e.g. 2.3 4.5 6.7 = 0.33 (a) I suggest you solve the problem above by looking at one pair of parentheses at a time. So on your calculator, press: 1.2 2.3 x 3.4 4.5 x 5.6 6.7 It is also correct to (b) multiply all the numbers above the fraction line first, then divide by all the numbers below the fraction line; so on your calculator, press: 1.2 x 3.4 x 5.6 2.3 4.5 6.7 1.2 x 3.4 x 5.6 (2.3 x 4.5 x 6.7) or (c) press: (note: the parenthesis) (d) when multiplying and/or dividing with scientific notation, use parenthesis, or treat each part of the notation separately. (4.25) (6.20 x 1012) (3.42 x 106) = (4.25) (6.20) (1012) (3.42) (106) 2 2. Use method (a) above and your calculator to evaluate the following expressions. (i) 8.09 3.23 8.55 3.44 4.50 6.73 (ii) (iii) (2.96 x 105) (4.3 x 102) (8.58 x 103) (iv) 70.2 5.90 2.35 4.25 10.23 3.11 4.23 4.43 6.77 3.76 (6.67 x 10-11) (423) (570) (640 x 10-6)2 C. Areas of rectangles and volumes of rectangular blocks Area of rectangle = length x width Area of volume of a rectangular box = length x width x height Note that the units multiply and divide also. e.g. If then length = 5.02 cm, width = 2.34 cm, area = (5.02 cm)(2.34 cm) = 11.7 cm 2 e.g. If then length = 5.02 cm, width = 2.34 cm, height = 1.23 cm, volume = (5.02 cm)(2.34 cm)(1.23 cm) = 14.4 cm 3 3. If the length of a rectangle measures 35.6 cm and the width measures 2.30 cm, what is the area? (Don’t forget to write the unit.) Show work (setup) clearly. 4. A box measures 12.5 cm in length, 8.67 cm in width, and 3.30 cm in height. What is the volume? Show work (setup) clearly. 3 D. Exponents a) The value of any power expression with exponent zero is equal to 1, i.e., a 0 =1. e.g. 10 0 =1 110 =1 230 =1 etc. b) To multiply two powers having the same base, add the exponents, i.e. (a m )(a n ) a mn e.g. (32 )(35 ) 37 c) To divide one power by another having the same base, subtract the exponents, am 38 38 mn 6 i.e. e.g.1. e.g.2. a 3 310 n 2 2 a 3 3 d) To evaluate the power to another power, multiply the exponents, i.e. (a m ) n a mn e.g. (32 ) 5 = 310 5. Evaluate the following expressions: (i) (iii) (v) (53 )(510 ) (ii) 6 24 (iv) 63 10 23 (vi) 10 2 (5a 4 ) 3 10 23 10 11 513 5 4 5 22 5 6 e) Ten to a negative power gives a number less than 1. Therefore ten to a large negative power will give a small decimal number. 10-12 < 10-9 < 10-3 < 1 < 103 < 109 < 1012 i.e. 10 6 “<” sign means “less than” 1 = 0.000001 10 6 6. Which number is larger in each of the following? (i) 10-8 or 10-5 ? (ii) 10-4 or 0.1? 4 (iii) 10-3 or 0.01? E. Cross multiplication & division D e.g. M V If D = 3.42 g/mL and V = 12.2 mL, then upon substitution, 3.42 M M 3.42 = is the same as 1 12.2 12.2 thus: (1)M = (3.42) (12.2) = 41.7 g The idea is to put the unknown on one side and everything else on the other side of the equal sign. Cross multiply 3.42 and 12.2. This is the same as multiplying 12.2 on both sides and then canceling. M 3.42 = 12.2 (3.42) (12.2) = M M = 41.7 g e.g. If D = 3.42 g/mL and M = 45.6 g, then upon substitution, 3.42 = 45.6 V (3.42) V = 45.6 V = 45.6 V = 12.3g 3.42 7. If M n V and M = 2.1 and V = 3.8, calculate n. 8. If M n V and M = 2.1 and n = 5.5, calculate V. 5 F. Simple Algebra problems e.g. v = v0 + a t If v = 15 m/s, v0 = 10 m/s, t = 8 s, then write 15 m/s = 10 m/s + a(8 s) 9. GPE = m g h and GPE = 450 a = (15 -10) m/s 8s m = 24 a = 0.625 m/s2 g = 9.8 Solve for h. Don’t forget to check your units. 10. v = v0 + a t and v = 8 m/s v0 = 2 m/s a = 3.5 m/s2 Solve for t. Don’t forget to check your units. G. Literal equations in Algebra Express one variable in terms of other variables, without numbers. e.g. For the expression, (a) express F in terms of the other variables: (b) express m in terms of the other variables: (c) express v in terms of the other variables: 11. If M1V1 M 2 V2 , express (i) V2 in terms of the other variables. (ii) M1 in terms of the other variables. 6 Fd = (1/2) mv2 1 / 2mv 2 F d 2 Fd m= 2 v v= 2 Fd m 12. If M n , express V (i) n in terms of the other variables (ii) V in terms of the other variables H. Complex fractions The fraction line is a division line. Since A means A B, B C D E F = C E D F = C F x D E Do the same for units. 13. Evaluate the following expressions (i) 8.566 2.35 15.90 9.33 (ii) 7 3.56 2.00 4.44 9.33 I. Unit conversion Example 1: Change 26.2 miles to meters. 26.2 mi. x 1609 m 1 mi. = 42155.8 m Example 2: Change 4.75 liters to milliliters 4.75 liters x 1 milliliter = 4750 ml = 4.75 x 103 ml .001 liter Solve the following conversion problems using multiplication by conversion factors. Equivalent measurements and metric prefixes can be found on the next page. Please show all of your work in the space below or on a separate sheet of paper. 14. 45 cm = ? inches 15. 100 yards = ? meters 16. 1 mile = ? kilometers 17. 180 pounds = 18. 1,000,000 newtons = 19. 2 liters = 20. 10 gallons = 21. 400 m = ? km 22. 500 m = ? cm 23. 65 kg = ? grams ? ? newtons ? tons quarts ? liters 8 Equivalents and Conversion Factors Metric Prefixes Mega kilo deci centi milli micro nano pico femto Length Force Volume M k d c m n p f “million” “thousand” “tenth” “hundredth” “thousandth” “millionth” “billionth” “trillionth” “quadrillionth” 1 in = 2.54 cm 1 ft = 30.48 cm = .3048 m 1 yd = 91.44 cm = .9144 m 1 mi = 1609 m 1 pound = 4.45 newtons 1 ton = 8896 newtons 1 liter = 1000 ml = 1000 cm3 1 liter = 1.0576 quarts 1 gallon = 4 quarts 1 gallon = 3.79 liters 1 m3 = 1000 liters 9 1,000,000 1,000 .1 .01 .001 .000 001 .000 000 001 .000 000 000 001 .000 000 000 000 001 106 103 10-1 10-2 10-3 10-6 10-9 10-12 10-15 J. Trigonometry and Geometry Sine, cosine and tangent functions are essential in the study of physics in two dimensions. Read through the examples and complete all practice problems. What do Sine, Cosine and Tangent mean? Sin opposite hypotenuse SOH adjacent Cos hypotenuse Tan opposite Sin adjacent Cos hypotenuse (hyp) CAH opposite (opp) TOA adjacent (adj) Pythagorean Theorem: adj 2 opp 2 hyp 2 24. Using your calculator to evaluate the functions, complete the following table. Make sure your calculator is set in degree mode (not radian mode). θ = 30º θ = 60º θ = 45º Sin 30º = Sin 60º = Sin 45º = Cos 30º = Cos 60º = Cos 45º = Tan 30º = Tan 60º = Tan 45º = Using Sin, Cos and Tan to find the sides or angles of a triangle. Example 1: opp 20 opp 20 sin 30 sin 30 opp 20 * 0.5 10 20 adj cos 30 20 adj 20 cos 30 adj 20 * opp 30º 3 10 * 3 17.3 2 adj 10 Example 2: 12 18 12 sin 1 42 18 sin 18 12 12 adj 12 adj 13.4 tan 42 OR tan 42 adj adj 2 12 2 18 2 adj 18 2 12 2 13.4 Solve for the unknown side lengths (x, y, and/or z) and angles (θ) in the following triangles. Show your work. Write the answers on the line for that question on the answer sheet. 25. 26. 27. 6 z 9 y 5 y 60º 45º x 8 28. 4.5 29. 30. z z 6.5 35º 3.6 y 2.3 1.8 x 11 18º x Answer Sheet – Physics Summer Work 1. (i)_________ (ii)_________ (iii)_________ (iv)_________ 9. ____________ 10.____________ 11. (i)_________ 24. _____ ______ _____ _____ ______ _____ _____ ______ _____ (ii)_________ 2. (i)_________ (ii)_________ (iii)_________ (iv)_________ 3. ____________ 4. ____________ 5. (i)_________ (ii)_________ (iii)_________ (iv)_________ (v)_________ (vi)_________ 6. (i)_________ (ii)_________ (iii)_________ 7. ____________ 25. z =______ θ =______ 12. (i)_________ (ii)_________ 26. x =______ y =______ 27. y = _________ 13. (i)_________ (ii)_________ 28. z =______ θ =______ 29. x =______ z =______ 14. ____________ 15. ____________ 16. ____________ 17. ____________ 18. ____________ 19. ____________ 20. ____________ 21. ____________ 22. ____________ 23. ____________ 8. ___________ 12 30. x =______ y =______ 13